The GSW UTS Server is
the software installed on your Windows computer. This software is responsible
for establishing connections and spawning agent processes that manage
each SSH2/Telnet session. The Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server
software enforces the number of allowed simultaneous sessions.
A SSH2/Telnet session is created each time a connection is established. A connection is established
when a user logs on to the Windows system using a SSH2/Telnet
Client. For each session that is created the GSW UTS software spawns an agent
process. The agent process is responsible for managing and communicating
with the user session. Screen optimizations are performed by the agent process
to facilitate faster data transfers. The capability of a configurable server-side
heartbeat timer exists for use by the agent process to help identify link
or remote PC failures. In addition, the configurable server-side inactivity
timer exists to help identify abandoned sessions so that they can be
properly terminated and made available to other users.
The Georgia SoftWorks
Windows SSH2/Telnet clients are proprietary software that run on remote PCs and
Pocket PC class devices and utilizes advanced features offered in the GSW UTS
server software. The advanced features are propriety extensions that enable a
wide range of functionality including mouse operation, enhanced printing methods,
automatic update of client software and much more! Well-designed optimizations
are included that enable the GSW Server software for Windows to be the fastest SSH2/Telnet
software available on the market.
The client software
contains a configurable heartbeat timer that notifies the agent process of its
presence. This mechanism helps to identify link or remote PC failures. It is
recommended that the Georgia SoftWorks Client software be used although it is not
required. The Georgia SoftWorks Windows Telnet Server is RFC 854 compliant which
allows any 3rd Party Telnet Client to be used. The GSW SSH Server allows connections
from any third party SSH compliant client.
The Georgia SoftWorks Windows
clients offer the Enhanced printing method as a component of True Client-Side
Printing (Page 226). This allows users to print to their local printer even
when connected across the Internet or RAS.
The Hostname or IP
address is displayed in the title bar of the Georgia SoftWorks Windows Clients
to provide an easy method of identifying to which host you are connected. Many
command line parameters are provided to enhance the convenience and power of
the client. Please see page 77 for detailed descriptions of these parameters.
The GSW Windows SSH2/Telnet
Clients automatically update to the appropriate version for the GSW UTS Server
when connected.
The GSW clients are
available on a wide variety of operating system platforms ranging from Windows
to Pocket PC 2003. See the table on page 25 for a detailed list of GSW Windows clients
available for each platform.
For Android customers,
GSW ConnectBot is a GSW Android SSH/Telnet Client product that can be purchased
separately. It has the strongest security of any commercially available SSH
client for Android. Learn more about it here (https://www.georgiasoftworks.com/connectbot-client-android)
The Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server is the core server software module that provides
the reliability, consistency, robustness and powerful features that has
distinguished GSW Server Products. The design of the GSW UTS facilitates integration
of protocol and application interfaces producing industrial quality server products.
The protocol and application
interfaces available for the GSW UTS are the GSW Telnet Interface and the GSW SSH
Interface. The GSW UTS is not sold as a standalone product. The standard
protocol interface provided is the GSW Telnet Interface.
Protocol Interfaces
other than the telnet interface require an application interface installer to
add the interface to the GSW UTS. The application interface installer for SSH
is the GSW SSH Shield. When the SSH application interface installer installs
the SSH Interface the Telnet Interface is disabled.
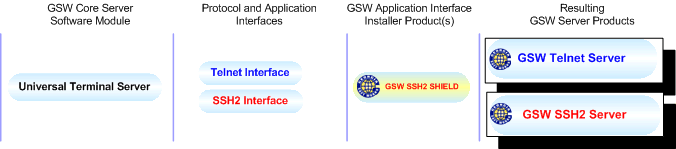
Figure 1: GSW UTS Components Overview
The
features, utilities and clients are provided by the GSW UTS. Unless noted all
features and utilities are available to all GSW Server Products.
The
GSW UTS supports a wide set of emulations that allows connections from most third-party
clients. Compliant 3rd party clients can exist on any operating system. Of
course, GSW Windows Clients are offered at no additional cost for Windows operating
systems, Pocket PC 2003 class devices and other Windows RF devices. A list
of these Windows Operating Systems is on page 25 .
GSW Also offers GSW
ConnectBot, a client for Android, which is available for purchase.
The standard protocol
interface included with the GSW Universal Terminal Server is the Telnet Interface.
No application or protocol interface installer is required.
The product purchased
is the GSW Telnet Server. The installation setup is quick and easy. You can be
up and running in the matter of minutes.

Figure 2:
GSW UTS - Telnet Server Components
The GSW SSH Server is
obtained by purchasing the GSW Telnet Server and the GSW SSH Shield. The GSW Telnet
Server provides the GSW UTS and the SSH Shield is the application and interface
installer for the GSW SSH interface.
First the GSW Telnet
Server is installed. Next the GSW SSH Shield is installed. Again, the installation
is quick and easy.
NOTE: When the SSH
Interface is installed the GSW Telnet Interface is un-installed. This is done
for security reasons as many view telnet as unsecured and thus should not be available
to malicious third parties.
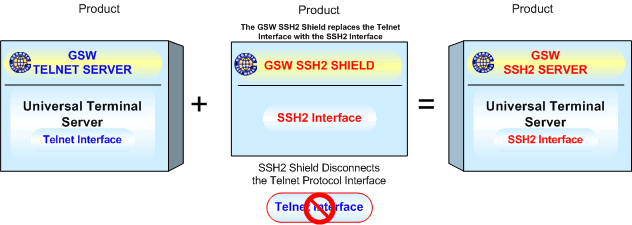
Figure 3: GSW UTS - SSH Server Components
Installation is simple
and quick. The same installation program installs the server software and the
client software. The installation software will prompt you for a full or
client only installation if on a Windows
system and automatically install client software if on a Windows 95/98 system.
As 64-bit computing rapidly
progresses towards mainstream computing, Georgia SoftWorks provides a 64-bit
edition of the GSW UTS Telnet Server named the Georgia SoftWorks UTS x64.
This edition is for 64-bit editions of Microsoft operating systems (Windows 7/8/10/VISTA/2008/R2/2012/R2/2016/2019
and Windows XP/2000/2003). The GSW UTS x64 provides all the performance benefits
and addressing capabilities expected when running on 64-bit platforms. Additionally,
extraordinary high session counts can be attained with the GSW UTS when running
on 64-bit platforms.
The GSW UTS 32-bit edition
runs on 64-bit platforms as well as on 32-bit platforms. When running a GSW UTS
32-bit version on a 64-bit platform significant performance benefits are also
realized.
If the application that
you are accessing via the UTS is a 64-bit application then use the UTS x64.
When using the GSW
Directed Terminal Input Output (DTIO) Engine, it is recommended to use the same
platform edition of the GSW DTIO and GSW UTS. For example, use the GSW DTIO x64
with the UTS x64.
Both the GSW UTS and
GSW UTS x64 editions are included on the CD when purchased. Simply navigate to
the corresponding folder to run the setup program. If the software is a downloaded
rather than using a CD then be sure to download the desired edition.
The GSW UTS 32-bit
edition installs trouble free on either platform. The GSW UTS x64 will install
only on a 64-bit platform. If you accidentally try to install the GSW UTS x64
on a 32-bit platform you will be alerted and setup will exit.
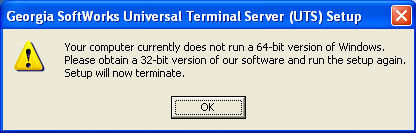
Figure 4: 32-bit platform alert.
The GSW Desktop client
provided with all editions is a 32-bit client and will install on both 32-bit
and 64-bit platforms.
Server Installation
From Windows
perform the following:
Run the gsw_x64.exe
program. (recommended)
The Welcome screen of
the setup program I displayed. Remember that you must have administrative
privileges to install this program. Click Next.
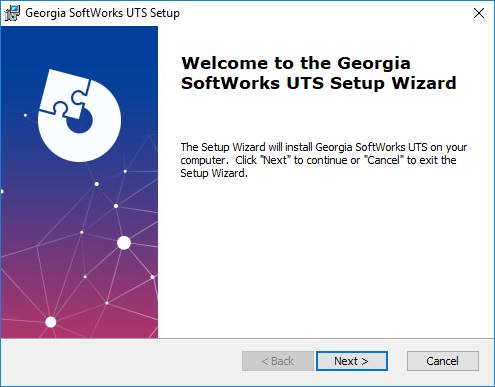
Figure 5: GSW UTS x64 Initial
Setup Dialog - Welcome
Power Users: .msi
is also provided for administrators using mass deployment tools, for example GPO.
Additionally .msi files are suitable for creating customized deployment
configurations using Microsoft Orca and MSI transforms.
Note: You cannot install
the same UTS version with both the .exe and .msi setup package programs. If you
start with one, stick with it.
2. A screen is
displayed indicating the directory that the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server
will be installed. The default is C:\gs_uts. You may change the installation directory
at this time. Note: If you install on a drive other than the system drive
and have NTFS (on the installation drive) then you must make sure that the
system has full permissions to get to the installation directory and subdirectories.
Click Next.
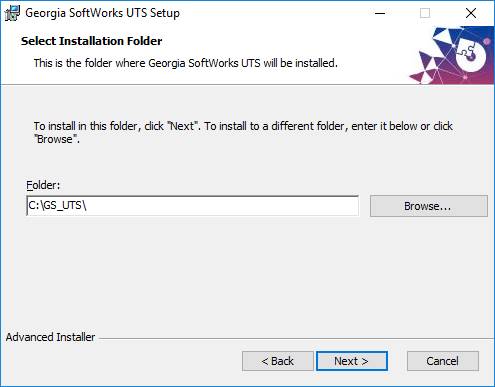
Figure 6: GSW UTS Installation
Path
4. The Ready to Install
dialog is displayed.
Click Install.
Figure 7: GSW UTS Installation
Progress Meter
A progress meter window
is displayed indicating the installation progress
Figure 8: UTS Installation
Progress meter
5. The Setup Succeeded
screen is displayed. Click Finish. The service has been installed and
is automatically started.
Figure 9: GSW UTS Installation
Setup Succeeded
Please view the readme.txt
file as it may contain late breaking information about the telnet server that has
not yet made it into the user guide. Release notes are also contained in the
ReadMe file. NOTE: TCP/IP must be installed and operational. TCP/IP comes as
part of Windows.
6. A "Georgia SoftWorks
UTS Program Group" is created.
Figure 10: UTS Program Group
The
items in the shortcuts in the Program Group are:
·
Certificate Mapping Tool for GSW SSH Shield – Certificate to User
account mapping for SSH customers.
·
GS SSH Client – This is the Desktop GSW SSH Client. Use if the
GSW SSH Server is installed.
·
GS Telnet Client – This is the Desktop GSW Telnet Client. Use if
the GSW Telnet Server is installed.
·
Installation Status – This displays the GSW UTS version, the
service status and if the GSW SSH Server is installed. The version and service
status are also displayed for the GSW SSH Server.
·
ReadMe SSH/ReadMe UTS – ASCII text file containing current release
notes and other late breaking important information for both the GSW UTS and SSH
Servers.
·
Registration – Registration utility used to permanently activate
the GSW UTS software.
·
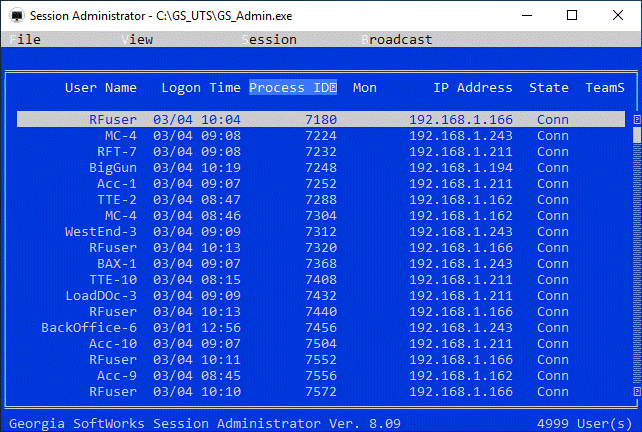
Session Administrator – Powerful tool for monitoring/shadowing sessions,
broadcasting and more.
·
SSH Users Guide
·
UTS Configuration Tool
·
UTS Users Guide – The complete User Guide in MS Word format for
the UTS and SSH.
You can view the GSW Software Installation Status
by double clicking on Installation Status.
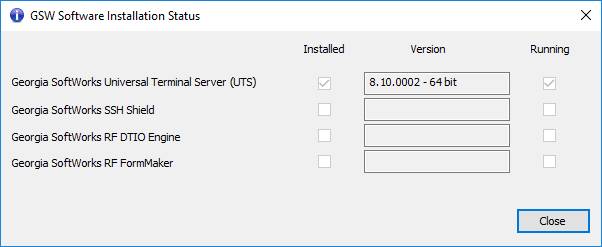
Figure 11: GSW Software Installation Status
This
information indicates that the GSW UTS is installed and running. The version is
also displayed and will indicate if the 64-bit edition is installed. The GSW SSH
Server (SSH Shield) is also installed.
The
installation status also indicates that the Georgia SoftWorks RF Directed
Terminal Input/output (DTIO) Engine is not installed. This item will only be checked
as installed and running if it was purchased and installed. GSW RF DTIO boosts
performance and can increase the number of sessions that an application can
handle in many environments. Please visit GSW website for more information on
the RF DTIO Engine.
Note: If you are
performing a fresh install of the 30-day trial copy, you do not need to register
the software. Skip the registration steps.
Note: For UTS
versions 7.51 and older, do not use Remote Desktop or Windows Terminal Server
to perform software registration.
Two options exist for
registering the license for the GSW UTS Server software. The first option is a
software method that is sent to GSW using the GSTicket system. Instructions for
the software registration are below. The second option is a Floating License
(hardware key) that can be installed on a USB or Parallel port on the server.
The registration instructions for the Floating license are on page 21.
To run the Georgia SoftWorks
UTS Server for Windows you must first register the software. This registration
is NOT required if you purchased the Floating License (Page 16). This entails just a few steps that involve obtaining the Product ID and providing
this Identification to Georgia SoftWorks so a Serial Number can be generated.
- NOTE: Read System Signature chapter at the end of User’s Guide.
To run the registration
software either -
1.
Click on the Registration Shortcut in the GSW UTS program group OR
2.
Select the Start button on the task bar, select Programs,
then Georgia SoftWorks UTS and then Registration.
The registration screen
is displayed. The Registration software automatically fills in the Product
Information fields as show in Figure 12.
Figure 12: Registration - Initial Screen
Please complete the Customer
Information, the Purchased From and the Sessions Requested
fields in the Registration Screen. Enter the name of the software that will be your
primary application to use with Telnet/SSH in the Application software field.
Examples could be HighJump, SAP, QAD, Catalyst, System Administration, etc.
Figure 13: Registration:
Customer Information Entry
Save the file using the
“Save to file” button.
The registration
information must be provided to Georgia SoftWorks to obtain the Serial Number.
Several methods are available for your convenience.
a.
Go to: https://www.georgiasoftworks.net/support_gsw/open.php
to submit a ticket for Registration. Complete necessary fields and attach the
file you saved in the previous step. - Preferred method – Fastest response
time.
OR
b.
Email the file to registration@georgiasoftworks.com
c.
Print the information and Fax it to Georgia SoftWorks- 706.265.1020
Once Georgia SoftWorks
receives the information, we can generate a Serial Number on demand and will
send it to you. You may close the registration program at this time.
3.
When the Serial Number is provided, Run the Registration Program again
(by right clicking and Run as Administrator)
and enter the Serial Number. The easiest method to get the serial number is to
highlight the returned Serial Number and copy (ctrl-c).
Then position the mouse in the Serial Number field in the Registration Information box and paste (ctrl-v).
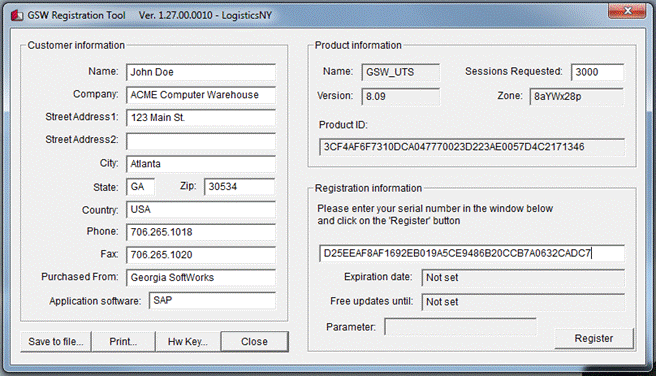
Figure 14: Registration - Serial
Number Entered
4.
Click Register.
Figure 15: Registration Successful
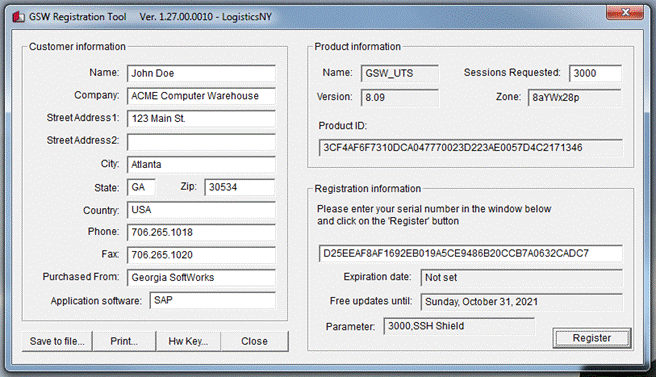
Figure 16: Registration:
Complete
Now the software is registered.
You may now run the Georgia SoftWorks Windows
Telnet Server. Note that you will be able to obtain Free Updates until the date
specified.
IMPORTANT: READ
SYSTEM SIGNATURE CHAPTER AT END OF USER’S GUIDE (PAGE 420).
Georgia SoftWorks
offers an optional Floating License for customers that require the
flexibility to rapidly move the telnet server from one machine to another. If
you did not purchase the Floating License - skip this section and go to the machine
specific license on page 16.
With the Floating
License No registration is required for the telnet server to operate.
Common scenarios where
the Floating License is useful include:
·
Laboratory usage in a development or test environment
where the telnet server is required for short periods of time on any particular
machine and then moved to a new machine.
·
Backup Servers in a production environment. Typically,
additional telnet servers are purchased for backup systems. However, with a Floating
License the Hardware Key can be quickly moved from the primary machine to the
backup without any other registration requirements.
·
Environments where a failed server must be replaced or rebuilt
and immediately restored to operation with full telnet capability.
The Georgia SoftWorks
floating license is a hardware key that can be ordered for a USB Port or a
Parallel port.
|
Parallel Port Floating License
|
USB Floating License
|
|

Figure 17:
Floating License – Parallel Port
The Parallel Port Floating License is a Pass Through allowing
normal function of the port.
|

Figure 18:
Floating License - USB Port
Not attached to a
Server
|
|
The Parallel Port Floating License connects to a female parallel
port on the server and does not impact functionality of the port for other
uses. It acts pass though allowing normal connections to the other side of
the key.
|

USB LED Lights when Installed
|
Table 1 - Floating Licenses - Parallel and USB Ports
The SSH2/Telnet server will recognize the presence of the key and activate the software for the correct
number of sessions and the proper date for which free version upgrades can be
obtained. It does not matter which parallel or USB port on the server the
Hardware Key is installed, as all ports will be scanned for the installation of
the key.
The Floating License
currently is installed using the manufacturer SafeNet, previously Aladdin of the
hardware key setup program. It is described below. The name of the hardware key
is HASP4 and you will see it displayed in the setup screens. The best drivers
for the HASP4 are the HASP HL drivers.
Note:
If you are using a USB Floating License on a Windows NT system - run the
file aksnt4usb.exe prior to the following steps.
1.
Copy the files from the Floating License folder (hardkey) to the hard drive
on your server.
2.
Run the HASPUserSetup.exe program and follow the installation instructions.
After installation of the hardware key install the GSW Telnet Server as
described on page 9 (if it is not already installed). See the GSW SSH Server
User’s Guide for installation instructions of the GSW SSH Server.
3. If
you have User Account Control enabled you may get a prompt that says “Do you
want to allow the following program to make changes to this computer?” Click Yes
Figure 19: Hasp Preparing to Install
4. You will first see the gemalto (formerly
SafeNet) initial Welcome Screen.
Figure 20: Sentinel welcome screen
Click
Next
5. The next screen displayed is the gemalto
License Agreement screen.
Figure
21: SafeNet License Agreement
Read
the license agreement and select “I accept the license agreement”
Click
Next
6. Ready to Install Sentinel Runtime
Setup
Click Next.
Figure 22: gemalto
Sentinel Runtime Setup
7. Install Drivers - Progress bar,
updating system.
Figure 23: gemaltor Sentinel Runtime Setup Progress bar
8. Gemalto Sentinel Successfully
Installed.
Figure
24: SafeNet Validating Install
Click Finish.
9. Plug the hardware key onto the
parallel or USB port on the server.
NOTE: On some systems you may have
to reboot the server after installation. If the Floating License is not
recognized (by the UTS) after installing the driver, please reboot the server.
In the event that you
need to uninstall the Floating License (SafeNet HaspHL) please use the Windows
Control Panel Add/Remove Programs administrative utilities.
NOTE: Removing or
uninstalling the Floating License will disable the GSW UTS Server.
In
addition to the GSW UTS clients the Georgia SoftWorks UTS Server is compatible
with all Telnet or SSH compliant third-party clients.
All
the powerful and popular GSW Client options and features described in the GSW UTS
are available both for the GSW Telnet Server and GSW SSH Server except where
specifically noted. Georgia SoftWorks offers Telnet/SSH Clients for the following
platforms:
Operating System |
GSW Telnet Client |
GSW SSH Client |
Client Type |
Window 98/ME |
Yes |
Yes |
GSW DESK TOP CLIENT |
Windows NT 4.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows 2000 |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows XP |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows 2003 |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows Vista |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows 2008/2012/2016/2019 |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows 7/8/10 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
GSW Mobile Pocket PC Device Clients |
Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+ |
Yes |
Yes |
GSW Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+ Client |
Pocket PC 2003 |
Yes |
Yes |
GSW PPC2003 Client |
Windows Mobile 2003 |
Yes |
Yes |
GSW PPC2003 Client |
Windows Mobile WM5, WM6+ |
|
|
GSW WM56 client or PPC2003 client |
LXE MX3X Teklogix 7535 devices Teklogix 8525 Symbol MC9060G Intermec CK30, CV60 (All of these devices when Running Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+) |
Yes |
Yes |
GSW Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+, WM6+ Clients |
|
|
|
GSW Java Clients |
Java Client |
Yes |
No |
|
Java Applet |
Yes |
No |
|
Table 2 - GSW SSH Client Platforms
Both the Windows SSH
and the Telnet clients are included with the Georgia SoftWorks UTS. Please note
that only the clients appropriate for the server purchased will be able to
connect. In other words, if you have a Telnet Server, only GSW Telnet and
compliant third-party clients will connect. If you have the GSW SSH Server only
GSW SSH and compliant third-party clients will be able to connect.
NOTE: SSH clients
can NOT connect to the Telnet Server and Telnet clients cannot connect to the SSH
Server.
For Android customers,
GSW ConnectBot is a GSW Android SSH/Telnet Client product that can be purchased
separately. It has the strongest security of any commercially available SSH
client for Android. Learn more about it here (https://www.georgiasoftworks.com/connectbot-client-android)
The following diagram
may be helpful in visualizing the GSW Client to use with various Windows
Operating Systems.
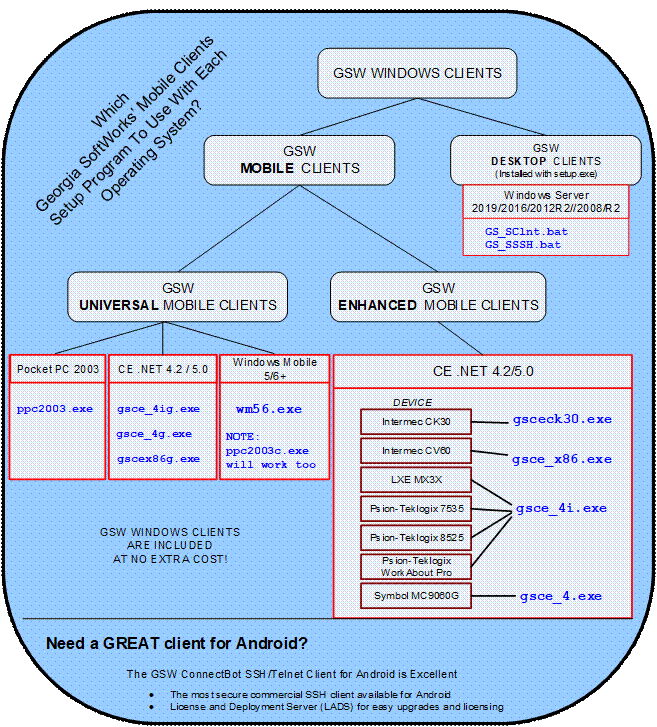
Figure 25: GSW Client and Operating System Diagram
.
Georgia SoftWorks has collaborated
with Vangard Voice Systems, Inc. to develop and implement the required software
to enable the UTS Mobile and Desktop clients to operate with AccuSpeech®
Mobile, their enterprise voice solution. Vangard Voice System’s solution creates
a custom voice-user interface for controlling existing mobile, devices,
application and business processes. Configuration is simple.
The robust, full
featured GSW UTS installed at thousands of mission critical location around the
world, coupled with Vangard’s AccuSpeech® Mobile provides a reliable and
innovative solution that is nothing less than a quantum leap in mobile
workforce productivity.
The GSW Windows Clients
are now voice enabled for operation with AccuSpeech Mobile so workforces can
voice-collect, access and transact information, while performing and focusing
on the task at hand.
GSW UTS Windows Mobile
and Desktop clients support Vangard Voice
Systems, Inc. AccuSpeech® Mobile on Windows and are
enabled by GSW Client configuration.
UTS and GSW Windows clients
version 8.04 or higher is required for Vangard Voice AccuSpeech support.
Configuration of the
GSW UTS clients to enable operation with Vangard Voice AccuSpeech Mobile is
described on page 307.
The GSW Desktop (Telnet
and SSH) clients are automatically installed on the computer that the UTS is
installed.
To install the GSW Desktop
clients on other Windows computers the following:
Run the gsw_uts_clients.exe (recommended) or gsw_uts_clients.msi
program. They are located in the GS_UTS Desktop folder.
The Welcome screen of the
setup program is displayed. Remember that you must have administrative
privileges to install this program. Click Next.
Figure 26: GSW UTS client
Initial Setup Dialog - Welcome
Power Users: .msi
is also provided for administrators using mass deployment tools, for example GPO.
Additionally .msi files are suitable for creating customized deployment
configurations using Microsoft Orca and MSI transforms.
Note: You cannot
install the same UTS Clients version with both the .exe and .msi setup package programs.
If you start with one, stick with it.
2. A screen is displayed
indicating the directory that the Georgia SoftWorks desktop clients will be installed.
The default is C:\gs_uts. You may change the installation directory at this
time. Note: If you install on a drive other than the system drive and have
NTFS (on the installation drive) then you must make sure that the system has
full permissions to get to the installation directory and subdirectories.
Click Continue.
Figure 27: GSW UTS Desktop Client
Installation Path
4. The Ready to Install
dialog is displayed.
Click Install.
Figure 28: GSW UTS Clients “Ready
to Install” dialog
Click Install.
You will get a User Account Control prompt asking if you
want to allow Georgia SoftWorks UTS to make changes to this device. (your computer).
Click Yes
.
Figure 29: GSW UTS Clients Install
is complete.
Click Finish.
You can now use the GSW
Telnet / SSH Clients.
A program group will be
created.
Figure 30: GSW UTS Desktop
programs group.
To uninstall the Georgia
SoftWorks Windows Software, use the Windows Apps & Features Uninstall.
GSW Mobile Clients
Georgia SoftWorks provides
mobile clients for PPC 2003, Windows Mobile and Windows CE .NET 4.2/5.0+ class
devices. As with the GSW desktop clients, the GSW Windows Mobile Clients are no
extra cost, which can amount to a substantial savings. For Android customers,
GSW ConnectBot is an Android client product which can be purchased separately. GSW
Windows Mobile Clients are categorized into Universal Mobile Clients and
Enhanced Mobile Clients. An overview of each follows.
GSW Universal Mobile
Clients eliminate the need for operation verification for specific devices by
GSW. The Universal Mobile Client can simply be installed by the customer. This
opens a broad range of compatible devices while maintaining the rich feature
set provided by GSW Mobile Clients.
Universal
Mobile Clients for Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+
The
GSW Universal Mobile Clients for Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+ are designed to be
compatible with all Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+ systems running on ARMv4+, ARMv4i+
and x86 based devices. Each device type requires a particular Universal Mobile
Client. The Mobile Client and the location of its setup program are identified
in the table on page 34.
GSW
Universal Mobile Clients for Windows Pocket PC, Windows Mobile 2003/WM5/WM6+
The
GSW Universal Mobile Client for Pocket PC 2003 is designed to be compatible
with all Pocket PC and Windows Mobile systems running on ARMv4+ based devices.
The Windows Pocket PC and Windows Mobile devices that are based on the ARMv4+
architecture each require a particular Mobile Client. The Mobile Client and the
location of its setup program are identified in the table on page 33.
In some cases, for
particular devices there may be features available that may not be obvious.
When appropriate we have provided special instructions on how to take advantage
of those features. Additionally, there may be devices that have been verified
for correct operation. Please review page 36 to see if your particular device
has special instructions, tips or has been officially qualified.
In many mission
critical environments operation verification by GSW may be a requirement. If
your company would like operation verification please contact us at sales@georgiasoftworks.com or call
706.265.1018 for more information.
In addition to the
Universal GSW Mobile Clients, specialized or Enhanced Clients are
available for many devices that take advantage of device specific
features. Device specific features range from special key and light operation
to application locking features. Each Enhanced Mobile Client has a Tips
section that should be reviewed. To determine if your device has Enhanced Mobile
Client please see the table on page 35.
GSW Enhanced Mobile
Clients with verified operation on Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+ devices include the
Intermec CK30, CK31, CV60, LXE MX3X, Symbol MC 9060G MC9090G, Psion-Teklogix
7535, Psion-Teklogix 8525, Psion-Teklogix WORKABOUT Pro. Other CE .NET
V4.2/5.0+ based devices may be compatible but have not been certified as of
this writing.
If you have a device that
has unique capabilities and would like custom client features please contact us
at sales@georgiasoftworks.com
or call 706.265.1018 for more information.
·
If your device is
running Android, then look at the GSW ConnectBot for
Android. It has the strongest SSH security of any commercial SSH client for
Android available. It operates as a 3rd party client meaning it will
connect with any telnet/ssh server that is protocol compliant.
·
If your device is a Windows Mobile 5,
6+ then use the GSW mobile client setup program WM56c.exe. However,
the ppc2003c.exe will also run fine.
·
If your device is a PPC 2003/Windows Mobile
then use the GSW mobile client setup program ppc2003c.exe
·
If your device is running Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+, look at the
table on page 35 to determine if an Enhanced GSW Mobile Client is available. If
so, then use the GSW Enhanced Mobile Client Setup Program Identified in the
table and be sure to look to see if any Tips are available for that client.
·
If your device is running Windows CE .NET 4.2+ and an Enhanced
GSW Mobile Client is not available then you can use a Universal GSW Mobile
Client.
o If your device
type is ARMv4i+ then use gsce_4ig.exe
o If your device
type is ARMv4+ then use gsce_4g.exe
o If your device
type is X86 then use gscex86g.exe
o If you do not
know the device type then
§ First - Try the gsce_4ig.exe client, if that does not work
- then
§ Next – Use the gsce_4g.exe client, if that does not work
- then
§ Last – Use the gscex86g.exe client
|
|
GSW Mobile Client
Installation Programs
|
|
|
GSW
mobile clients are located in a subfolder on the CD or where the download was
unzipped with one of the following names
|
|
|
GSW Universal Mobile Clients
|
|
|
Operating
System
|
Device Type
|
GSW
Client Setup Program location / name
|
|
|
Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+
|
ARMv4+
|
/clients/gsce_4g.exe
|
|
|
|
ARMv4i
|
/clients/gsce_4ig.exe
|
|
|
|
X86
|
/clients/gscex86g.exe
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PPC 2003
|
ARMv4+
|
/clients/ppc2003c.exe
|
|
|
Windows Mobile 5,6+
|
|
/clients/wm56c.exe or
|
|
|
|
|
/clients/ppc2003c.exe
|
Table 3 - GSW Mobile Client Setup
Program Locations
Note: ARMv4+ includes ARMv4, ARMv5, and ARMv7 etc.
|
|
GSW Enhanced Mobile Clients
for Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6 Devices
|
|
|
Operating
System
|
Device Type
|
GSW
Client Setup Program location / name
|
|
|
Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6+
|
ARMv4+
|
/clients/gsce_4.exe
|
|
|
|
ARMv4i
|
/clients/gsce_4i.exe
|
|
|
|
ARMv4i
|
/clients/gsceck30.exe
|
|
|
|
X86
|
/clients/gsce_x86.exe
|
|
|
NOTE: See the table (page 35) for
Enhanced Mobile Clients to determine if your devices can use one of the above
clients.
|
|
|
Table 4 - GSW Mobile Client
Setup Program Locations - continued
Installation steps
- Install
current version of the Georgia SoftWorks UTS Server (Version 6.50 or
higher).
- Determine
the location and name of the GSW Mobile Client Setup program for your
device. See page 33.
- Copy
the appropriate setup executable to the computer which established
partnership with your device.
- Turn
on your device.
- Start
the Mobile Device Center or Active Sync on the device and connect.
- Run
the self-extracting executable on the computer selected in Step 3.
- Confirm
the prompts asking to continue with the installation.
- You
should see the setup program launched on your device.
- Press
the OK button on the device to complete the installation.
Please review any Tips for your device in the Enhanced
(page 35) and Universal clients
section (page 36 ).
GSW
has Enhanced Mobile Clients for the following devices that take advantage of
unique features on the listed devices. Be sure to review the Tips section for each device.
Table 5
- Enhanced GSW Mobile Clients
Universal GSW Windows Mobile Clients Special Tips or Qualifications List
The GSW Universal
Mobile Clients operate on ARMV4, ARMV4I and X86 devices. In some cases, special
instructions or tips may exist to take advantage of unique features or provide
ease of use pointers for that particular device. If there are special tips
or a particular device has been verified for correct operation then it
will be listed in the table below.
|
Devices
Qualified with Universal GSW Mobile Client for CE
.NET V4.2 +
|
|
|
Device
Model
|
Device Type
|
GSW
Client
|
|

|
PSC Falcon
4410
Tips for PSC Falcon 4410 on page 65
|
ARMv4i
|
gsce_4ig.exe
|
|

|
Datalogic
Elf CE 6.0
|
ARMv5
|
gsce_4g.exe
|
|

|
Datalogic
Falcon X3 CE 6.0
|
ARMv5
|
gsce_4g.exe
|
|

|
Honeywell
Dolphin 6500 CE 5.0
|
ARMv5
|
gsce_4g.exe
|
|

|
Honeywell
LXE Thor CE 6.0
|
X86
|
gsce_x86.exe
|
Table 6 – Devices qualified with
Universal GSW mobile clients for Win CE
|
Devices Qualified with Universal GSW Mobile
Client for CE .NET V4.2+
|
|
Device Type
|
GSW
Client
|
|
|
|

|
Janam XG100
CE 6.0
|
ARMv5
|
gsce_4g.exe
|
|

|
Motorola
MC9190 CE 6.0
|
ARMv5
|
gsce_4g.exe
|
|

|
Motorola
Psion Teklogix Omni XT10 CE 6.0
|
ARMv7
|
gsce_4ig.exe
|
Table 7 - Devices qualified with
Universal GSW mobile clients for Win CE
|
Devices Qualified with Universal GSW Mobile Client for Windows
Mobile
|
|
|
Device
Model
|
Device Type
|
GSW
Client
|
|

|
Bluebird Pidion
BIP-6000 Windows Mobile 6.1 Pro
|
ARMv5
|
ppc2003c.exe
|
|

|
Intermec CK71
Windows Mobile embedded 6.1 Classic
|
ARMv7
|
ppc2003c.exe
|
|

|
Intermec CN3
Windows Mobile 5.0
|
ARMv5
|
ppc2003c.exe
|
|

|
Honeywell
Dolphin 9950 Windows Mobile 6.1 Classic
|
ARMv5
|
ppc2003c.exe
|
|

|
Nautiz X4
|
ARM
Cortex-A53
|
Windows Mobile 6.5
|
Table 8 - Devices qualified with
Universal GSW mobile clients for Win Mobile
|
Devices Qualified with for Correct Operation with GSW UTS
|
|
|
Device
Model
|
Device Type
|
Operating
System/Client
|
|

|
Bluebird Pidion
BIP-6000 Android 2.3.7
|
ARMv5
|
Android
2.3.7
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
MobileDemand
xTablet T7000 Windows 7
|
X86
|
Windows
7
|
|

|
Nautiz X2
|
Texas Instruments
AM3715
|
Android
6.0
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Algiz 10X
|
X86
|
Windows
10
|
|

|
Widefly WF 68
Mobile Computer
|
Intel
|
Android
6.0
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
Table 9 - Other devices that
operate with the GSW UTS
|
Devices Qualified with GSW UTS
|
|
Device Type
|
Device
Model
|
Device Type
|
Operating System
|
|

|
Janam XG100
CE 6.0
|
ARMv5
|
Windows
gsce_4g.exe
|
|

|
Janam XG200
|
Qualcomm Snapdragon
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Janam XM75
|
Qualcomm Snapdragon
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Janam
XT2
|
Qualcomm Snapdragon
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|
|
Janam XT100
|
Qualcomm Snapdragon
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Janam XG3
|
Arm
Cortex A53
|
CE 5.2
ppc2003c.exe
|
Table 10: Janam devices
qualified with GSW UTS
|
Devices
Qualified with GSW UTS
|
|
Device Type
|
Device
Model
|
Device Type
|
Operating System
|
|

|
Cipher Labs
9700 Series
|
Arm
Cortex A53
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|
|
Cipher Labs
RS30
|
Arm
Cortex A53
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Cipher Labs
RS50
|
Arm
Cortex A53
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Cipher
Labs RS31
|
CPU Cortex A53 Quad-core
1.3GHz
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Cipher
Labs RS51
|
Octa-core 1.8GHz
|
Android
8.0 with GMS
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Cipher
Labs RK 25
|
Quad-core 1.4 GHz Cortex
A53
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
Table 11 -Cipher Labs qualified
devices
|
Devices Qualified
with UTS
|
|
Device Type
|
Device Model
|
Device Type
|
Operating System
|
|

|
Juniper
Archer 3
|
1.2GHz quad-core ARM Cortex A9
i.MX6
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Juniper Mesa
3
|
Qualcomm® Snapdragon™
Octa-core Kryo™ 260
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Nautiz
X6
|
Qualcomm® Snapdragon 626 MSM8953 Pro,
8 cores 2.2 GHz
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
|

|
Keyence
BT-AT700
|
Qualcomm Octa-core
|
Android
gsw-connectbot.apk
|
Table 12 – Nautiz X6 and Keyence
BTAT700 qualified devices
If your device is not in
the list above and it is an Android device the GSW ConnectBot will most likely
be your best choice. If your device is not in the list above and it is an ARMv4+,
ARMv4i+ or X86 devices, it is likely that a Universal GSW Mobile Client will
operate. Please use the steps in section above (page 33) to determine the
correct mobile client.
In
order to facilitate the varied commercial requirements GSW has provided extended
features for the GSW Mobile Clients for Windows CE .NET 4.2/5/6. These
additional features offer useful flexibility and efficiency for both the device
user and the System Administrator. The table below provides a brief description
of the features. The details on configuration and enabling the options follow.
|
|
Mobile Feature
Name
|
Brief
Description
|
|
1
|
Stay Connected
|
Automatically
attempts to reconnect when a session becomes disconnected
|
|
2
|
Allow Suspend
|
Power Saving
Feature
|
|
3
|
Beep Sound
|
Correct
Operation of Beep Sound
|
|
4
|
Menu Accelerators / Shortcuts
|
Function keys
provide quick access to common menu commands
|
|
5
|
Free Function Keys
|
Function Keys,
F1-F12 are freed (released) from operating system control and are available
for the application
|
|
6
|
Raster Font Selection
|
Additional Raster
fonts available - 9x16,10x12,10x13,12x16
|
|
7
|
Simplified Chinese font
|
GSW Mobile
Clients support Simplified Chinese Font GB (True Type)
|
|
8
|
Select Configuration
|
Several configurations
are allowed. This provides a quick way to select the desired configuration.
|
|
9
|
Portable Session Configuration
|
File format for
Session Configuration allows easy cloning of sessions
|
|
10
|
Last Active Session Memory
|
After a restart
the client returns to the last active session
|
|
11
|
No Scrollbars option
|
Save Space on Screen.
Especially useful on devices with small screens.
Also supported
on Pocket PC 2003 devices.
|
|
12
|
Automatic Logon
|
Automatically
logon without Host, Domain, Username, Password prompting
|
|
13
|
Keyboard Marcos
|
Remap Function and
Special Keys to send a sequence of characters.
|
|
14
|
Configuration and Application
Persistence
|
Save Mobile
Client Configuration Across Reboots
- Allows for ease
of configuration deployment to multiple devices
|
|
15
|
Toggle Status
& Task Bar display
|
Use View menu
item to enable or disable the display of the status bar and/or the task bar.
|
Table 13 - GSW Mobile CE .NET
4.2/5.0 Client Extended Features
Automatically attempts to reconnect as soon as a
session is disconnected. Operates as if the connect button was pressed.
Stay Connected is enabled by selecting the option Stay Connected.
Session|Settings|Session|Stay connected
To break out of the automatic
connection loop press
ctrl-shift-b
To facilitate the fastest possible operation, the
default GSW Mobile Client operation disables mechanisms that allow the device
to suspend. There may be scenarios that require the device to Suspend. You can
configure the GSW Mobile Client Software to allow the device to Suspend by setting
the option Allow Suspend
Session|Settings|Session|Allow suspend
Beep sound –
Correct Operation
No configuration
is required.
In order to provide a more convenient
method of configuration for the administration the following accelerator keys
are available.
Note: The following Accelerators
are available for all CE .Net 4.2 devices.
F2 – Save Session Settings
F5 – File|Session Configurations …
F6 – Session|Connect
F7 – Session|Settings
F8 – File|Exit
The GSW SSH/Telnet mobile clients support Simplified
Chinese fonts. Follow the steps below to setup the GSW mobile client:
- GSW
Universal Terminal Server and GSW Mobile Clients must be V7.51 or higher.
- Install
the Simplified Chinese font GB (True Type) on the mobile device.
- Open
the GSW SSH/Telnet client on the mobile device and navigate to:
Sessions -> Settings
Select
the Font tab and select the GB font.
The Simplified Chinese font does not have to be
installed on the Universal Terminal Server. Note: The GB font will not
display in the GSW Desktop SSH/Telnet client or Session Administrator. GSW
engineering has verified correct operation with the GB (True Type) font.
You can create and save a number of Session
Configurations settings that you can use as needed. The Select Configuration
option displays the saved Session Configurations that reside in the same folder
as the GSW Mobile client software. This folder may vary from device to device
so please see the tips section (in this user’s guide) for your specific device
to determine its location. Put another way, Session Configurations are not displayed
if they do not reside in the same folder that the GSW Mobile Client software
resides.
You select the desired Session Configuration by using
the associated function key (F5).
Display the Select Session Configuration by using the menu bar.
File | Select Configuration …
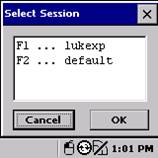
Figure 31: Mobile Client Select Session
The file format of the Session Configuration is such
that it can be used to clone or duplicate the session configuration on other devices.
Session device settings are kept completely in files with no external references.
This provides a portable configuration file that can be used when setting up
other devices. This can be a significant time saver when 40, 100 or more devices
are being set up.
The configuration files have the gswtc extension. The
file has an “ini” format with Username, Host, etc.
See also the section on application persistence
capabilities to view the usefulness of the GSW automatically created CAB files
when deploying GSW Mobile Clients (page 53).
After a restart the
client returns to the last active session. This works if default. gswtc is not
present (otherwise default. gswtc is loaded).
No Scrollbars
Option
Set this option to
eliminate the use of scroll bars to save screen space. The application should
display itself in the top-left corner of the screen. For example,
this is the position that SAPConsole assumes. Of course, this assumes that the application
does not require scroll bars.
Normally
Scrollbars are enabled.
The No Scrollbars option is enabled by selecting the
option No scrollbars.
Session|Settings|Session|No scrollbars
Check
the “No
scrollbars”
box to eliminate scrollbars as shown below.

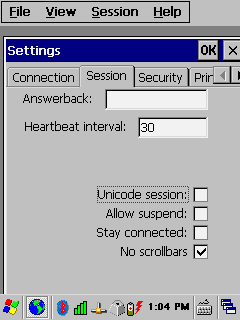
Figure 32: Mobile Client - No Scrollbars Option
Use the view menu item to toggle the display of either
the status bar and/or the task bar. Set this option just see the information
you need to see.
|

Figure 33: Windows CE - Choose
to view status and/or task bars. Neither enabled.
|

Figure 34: Just status bar is
enabled
|
|
|
|
|

Figure 35: Just taskbar enabled
|
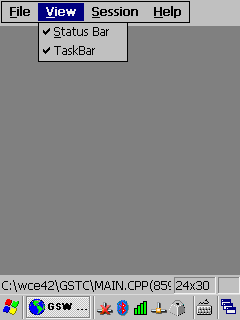
Table 14: Both status and task
bar are enabled
|
Set this option to eliminate the use of scroll
bars to save screen space. The application should display itself in the
top-left corner of the screen. For example, this is the position that SAPConsole
assumes. Of course, this assumes the application does not require scroll bars.
Normally Scrollbars are enabled.
The No Scrollbars option is
enabled by selecting the option No scrollbars.
Session|Settings|Session|No scrollbars
Check
the “No
scrollbars”
box to eliminate scrollbars as shown below.


Figure 36: Mobile Client - No Scrollbars Option
Automatic
Logon for Mobile Clients
Set this option to enable the GSW Mobile client for
Automatic Logon. The GSW Server Side Automatic Logon configuration must also be
completed (See page 111 ).
Critical Note 1: Make sure that Automatic
Logon entries for GSW Mobile clients are made in the gs_auto.txt configuration file.
Critical Note 2: IP addresses configured for
Automatic Logon for GSW Clients must NOT overlap with IP Addresses configured
for Automatic Logon for 3rd party clients.
The Automatic Logon option is enabled by
selecting the option Automatic logon.
Session|SettDjsexton1
ings|Session|Automatic logon
Check the “Automatic logon” box to enable the client
for Automatic Logon as shown below.

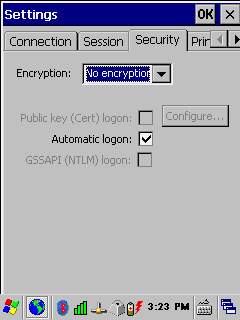
Figure 37: Mobile Client – Automatic Logon Option
Keyboard Macros
Keyboard macros are a powerful and time saving feature
that lets the administrator define custom keys on the device when the session
is active. Macros are used for remapping
Function keys (F1 – F12) to keystroke sequences.
Macros definitions have the form:
Function
Key=Keystroke Sequence
Where
Function Key is F1 through F12
and
Keystroke Sequence follows the same format as the GSW Termination
strings (page
158).
The keys that can be remapped are
Function Keys: F1,F2,F3,F4,F5,F6,F7,F8,F9,F10,F11,F12
Configuration
The keyboard macros are defined in the session
configuration files. These have gswtc extensions. The configuration files have
the “Windows ini” format. A new section [Macros] needs to be manually added
to the configuration file.
For example, to remap all Functions Keys to send
capital F, followed by function key index and the enter key you
would add the following section to the configuration file on the device (usually default.gswtc).
[Macros]
F1=shift-f,1,ENTER
F2=shift-f,2,ENTER
F3=shift-f,3,ENTER
F4=shift-f,4,ENTER
F5=shift-f,5,ENTER
F6=shift-f,6,ENTER
F7=shift-f,7,ENTER
F8=shift-f,8,ENTER
F9=shift-f,9,ENTER
F10=shift-f,1,0,ENTER
F11=shift-f,1,1,ENTER
F12=shift-f,1,2,ENTER
Disconnects the session. There may be times when you
want to disconnect the session. To disconnect the client from the server, enter
the Break-Out sequence.
After the session is disconnected, further behavior on
the session observes the rules configured on the server such as Graceful
Termination, Session Saver, etc. The Break-Out is accomplished by entering the
sequence
ctrl-shift-d
Note: Do not confuse this sequence which disconnects
the session with the Ctrl-Shift-b sequence (see page 43 )
|
|
Mobile Feature
Name
|
Brief
Description
|
|
1
|
Keyboard Macros
|
Remap Function
and Special Keys to send a sequence of characters.
|
|
2
|
Free Function Keys
|
Function Key’s
(F1-F12) are freed (released) from Operating System control and are available
for the application.
|
|
3
|
Application Launch Bypass
|
Interoperation
with application launch utilities such as Intermec’s iLaunch.
|
|
4
|
Simplified Chinese font
|
GSW Mobile
Clients support Simplified Chinese Font GB (True Type).
|
Table 15 - GSW Mobile PPC 2003
and Windows Mobile 2003/WM5+ Client Extended Features
Keyboard Macros
GSW has provided Keyboard Macros for the GSW Mobile Clients for Windows Pocket PC 2003
and WM5/WM6+. They operate the same as described for the Windows CE .NET
4.2/5.0+ mobile clients.
Allows Function keys F1-F12 to be used by the
application. Windows Pocket PC, Mobile and CE .NET operating systems may take
control of one or more of the function keys making them unavailable to the
application software.
All GSW Mobile Clients free the function keys from the
operating system so they can be used by the application. To restore operating
system control of the function keys, reboot the device.
GSW Telnet/SSH client for PPC2003 and Windows Mobile
5/6+ may be configured so it will easily interoperate with application launch utilities
like Intermec’s iLaunch, such that the client will terminate immediately when
the session ends. Additionally, if the feature is enabled the client will turn
off all menu options except ‘Disconnect’.
The configuration is performed by setting the value
of a new parameter ‘Bypass’ that resides in the “cppc2003.ini” file in the section called ‘Settings’
Possible Values are:
0 – disabled
(default)
1
– enabled
If
the Bypass parameter is not present in the file, then the default value used
is: 0 (disabled).
Simplified Chinese fonts are supported when using the
GSW Mobile Clients for Windows Pocket PC 2003/WM5/WM6+ (Windows Mobile). The
setup is the same as described
for the Windows CE .NET 4.2/5.0+ mobile clients.
Configuration and Application Persistence
It can
be frustrating and time consuming if your configuration information is lost
over a reboot which is common with Windows CE and Pocket PC operating systems.
GSW has provided a reliable mechanism to ensure that the GSW Mobile Client application
and configuration can be persistent across all types of reboots. Instructions vary
depending of the type of GSW mobile client being used. Please review the appropriate
section for your client.
- GSW
Enhanced Mobile Clients:
Follow the Tips section for your device. Do not follow
the Configuration Persistence configuration below for the GSW Universal Mobile
Clients. See page 35 for Enhanced Client Tips.
- GSW
Pocket PC 2003 Universal Mobile Clients:
Follow the instructions on page 56.
- GSW
Universal Mobile Clients for Windows CE .NET 4.2+
Follow the instructions below.
.
In brief, the steps are simply to configure the
device, save the configuration and move our .CAB files to a persistent folder.
Mobile Client Configuration
Persistence
The GSW Mobile Client configuration is saved as a .cab
file, which is a compressed archive package definition format.
For each created Session Configuration there will be a
corresponding CAB file. For example, if a session was saved with the name ‘lukexp.gswtc’ then a corresponding cab
file with the name ‘lukexp.cab’ is automatically created.
Non session specific configuration data is stored in
the CAB file c735x.cab. When these files are placed
in the persistent CAB folder on your device the GSW mobile client configuration
is restored upon reboot. The persistent CAB folder location is device manufacturer
and model specific.
Mobile Client Application Persistence
The GSW Mobile Client application is available as a
.cab file, which is a compressed archive package definition format. The .cab
file location and name of the application is
|
Location (on your PC)
|
CAB File Name
|
|
C:\Program Files\Georgia
SoftWorks Universal Telnet and SSH Client for Windows CE ARM4\WCEG_4.ARMV4_G.CAB
|
|
C:\Program Files\Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Telnet and SSH Client for Windows CE ARM4I\WCEG_4I.ARMV4I_G.CAB
|
|
C:\Program Files\Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Telnet and SSH Client for Windows CE X86\WCEG_X86.INTEL_X86_G.CAB
|
Table 16
- GSW Mobile Client Application CAB File Location
When this file is placed in the persistent CAB folder
on your device the GSW mobile client application is restored upon reboot. The
persistent CAB folder location is device manufacturer and model specific.
Mobile Client Persistence
Instructions
Once you have the GSW Mobile Client configuration set
for your implementation you should save the configuration.
Step 1: Install and run the GSW Mobile
Client
Step 2: Configure the GSW Mobile Client
as required for your environment
Step 3: When
satisfied with the configuration from within the GSW Mobile Client perform the
menu item
File|Save
And save the settings in
location below.
\Program Files\GSW_Clnt\default.gswtc
The file below will
automatically be generated upon the Save command
\Program Files\GSW_Clnt\default.cab
Step 4: From within the
GSW Mobile Client, switch to ‘User Mode’ using the menu item
File|Security
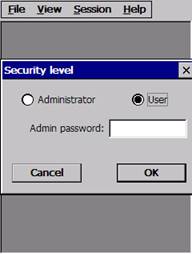
Figure 38: Switch from Administrator to User Mode
Step 5: On the device
launch the File Manager and copy the configuration and application .cab files
\Program Files\GSW_Clnt\default.cab
\Program Files\GSW_Clnt\c753x.cab
to the Persistent CAB folder.
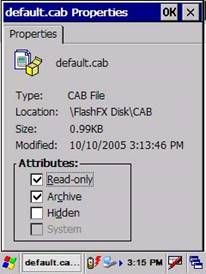
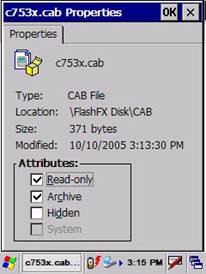
Figure 39: Note that the files are already marked as
Read Only.
Mark the files as Read
Only.
In this case the persistent CAB folder location is \FlashFX
Disk\CAB,
however the persistent folder is device manufacturer and model specific.
Step 6: Copy the
application cab file defined in the Application Persistence section (page 53) to the Persistence folder on
the device. Mark it as Read Only
Step 7: Now you should be
able to cold boot the device and the client should automatically launch with
the correct configuration.
PPC 2003 Configuration Persistence
The GSW Mobile Client configuration is saved as a .cab
file, which is a compressed archive package definition format.
For each created session configuration there will be a
corresponding CAB file. For example, if a session was saved with the name ‘lukexp.gswtc’ then a corresponding cab
file with the name ‘lukexp.cab’ is automatically created.
Non session specific configuration data is stored in
the CAB file cppc2003.cab. When these files are placed
in the persistent CAB folder on your device the GSW mobile client configuration
is restored upon reboot. The persistent CAB folder location is device manufacturer
and model specific.
PPC 2003 Application Persistence
The GSW Mobile Client application is available as a .cab
file, which is a compressed archive package definition format. The .cab file
location and name of the application is
|
Location (on your PC)
|
CAB File Name
|
|
C:\Program Files\Georgia
SoftWorks Universal Telnet and SSH Client for PPC2003\CPPC2003.PPC2003_ARM.CAB
|
Table 17
- GSW PPC 2003 Mobile Client Application CAB File Location
When this file is placed in the persistent CAB folder
on your device the GSW mobile client application is restored upon reboot. The
persistent CAB folder location is device manufacturer and model specific.
PPC 2003 Persistence
Instructions
Once you have the GSW Mobile Client configuration set
for your implementation you should save the configuration.
Step 1: Install and run the GSW Mobile Client
Step 2: Configure the GSW Mobile Client as
required for your environment
Step 3: When satisfied
with the configuration from within the GSW Mobile Client perform the menu item
File|Save
And save the settings in location
below
\My Documents\default.gswtc
The file below will automatically
be generated upon the Save command.
\My Documents\default.cab
Step 4: On the device
launch the File Manager and copy the configuration and application .cab files
\My Documents\default.cab
\Program Files\Georgia SoftWorks\CPPC2003\cppc2003.cab
to the Persistent CAB folder
Mark the files as Read
Only
The persistent folder is
device manufacturer and model specific
Step 5: Copy the
application cab file defined in the Application Persistence section (page 56) to the Persistence folder
on the device. Mark it as Read Only
Step 6: Now you should
be able to cold boot the device and the client should automatically launch with
the correct configuration
Tips for
Intermec CK30 / CK31
Following are a few Tips
when installing the GSW SSH/Telnet Windows Client for the above device running
Windows CE .NET Version 4.2+
1.
Menu Accelerators / Shortcuts
As of
this writing the Intermec CK30/CK31 does not provide mouse/stylus capability
via a touch screen. In order to provide a more convenient method of configuration
the following accelerator keys are available. They are available for all Mobile
Clients for Windows CE .NET 4.2+ but are especially useful for the Intermec
CK30/CK31.
F2 – Save Session Settings
F5 – File|Session Configurations …
F6 – Session|Connect
F7 – Session|Settings
F8 – File|Exit
2.
Persistence over a ‘Cold Reset’
After
initial installation, please complete these steps as well as anytime the
configuration changes.
Once
the connection settings are configured and tested you can ensure that these
settings will still exist after a ‘Cold Reset’ of the Intermec CK30/CK31. This
is done by saving the file system and registry to flash memory. This is
accomplished by performing the following steps.
System Main Menu|Configuration Utility|File Backup|Backup
the File System
and
System Main
Menu|Configuration Utility|Save to Flash
3.
Startup – Default Connection Settings
·
The file “\CK_FFS\Georgia
SoftWorks C753X\default.gswtc” is loaded on startup if found.
·
If the security level is ‘user’
then the GSW SSH/Telnet Client will attempt to connect.
4.
Application Protection
Use
the File|Security dialog as
described in the Application Protection
(page 70 ) section.
5.
Warm boot the device after you install the client. The GSW Mobile
Client will automatically launch.
6.
The GSW Mobile Client is also accessible via
System Main Menu|GSW Client
7.
How to disable the automatic launch of the TE2000 client
a.
Either delete or rename the file \Windows\StartUp\TE2000.lnk
b.
Run
System Main Menu|Configuration Utility|File
Backup
8.
BEEP Sound – Complete beep operation. Extended features available
for SAP - See below.
9.
LED Color / Blink and beep Association – For use with SAP,
SAPConsole
Using the ABAP Code Generate Bell you can
associate different light-blink-colors based on the notify_bell_signal value.
You can control the number of beeps, the color of the led (green/orange) and the
number of blinks.
Example: notify_bell_signal = XYZ
Where
X = Number of beeps
Y = Color of LED
1 = green (left most light),
2 = orange (right most light)
Z = Number of blinks
Each blink is
turned on for the same time as the beep
10.
Scrolling and Mouse Support
The
Intermec CK30 / CK31 does provide screen scrolling and mouse support via
keyboard control. The Alt-Down combination
puts the CK30 / CK31 into a “Screen Scrolling and Mouse Mode” and brings up a
pointer that can be manipulated by numeric keys. Please see the Intermec manual
for further details. To dismiss the pointer, enter the Alt-Down again.
Note:
Keyboard data entry functionality is not fully available when in the “Screen
Scrolling and Mouse Mode”. Simply put, dismiss the pointer prior to entering
text.
Following are a few Tips
when installing the GSW SSH/Telnet Client for the above device running Windows
CE .NET Version 4.2+
1.
Persistence over a ‘Cold Reset’
After
initial installation, please run START | Shutdown on the device.
Shutdown
saves the device registry to persistent storage.
2.
Uses Standard
Accelerators and Shortcuts for all CE .NET 4.2 devices (page 44).
3.
Startup – Default Connection Settings
·
The file “\Application Data\Georgia SoftWorks
C753X\default.gswtc” is
loaded on startup if found.
·
If the security level is ‘user’
then the GSW SSH/Telnet Client will attempt to connect.
4.
Application Protection
Use the
File|Security dialog as described
in the Application Protection (page 70
) section.
5.
Warm boot or cold boot the device after you install the client.
The GSW Mobile Client will automatically launch.
6.
The GSW Mobile Client is also accessible through
'Program Files' and a Desktop shortcut
7.
How to disable the automatic launch of the TE2000 client
a.
Either delete or rename the file \Windows\StartUp\TE2000.lnk
8.
BEEP Sound – Complete beep operation.
Tips for PSION-TEKLOGIX WORKABOUT Pro, 7535 and 8525 devices
Following are a few Tips
when installing the GSW SSH/Telnet Client for the above devices running Windows
CE .NET Version 4.2+
1.
Persistence over a ‘Cold Reset’
By default,
the GSW Telnet Client is installed to a persistent directory. The directory is
\Flash Disk\Georgia SoftWorks C753X
·
User Fonts – Your fonts need to reside in two locations.
\Windows\Fonts
And ALSO
\Flash Disk\Georgia SoftWorks C753X
2.
Use Standard
Accelerators and Shortcuts for all CE .NET 4.2+ devices (page 44).
3.
Startup – Default Connection Settings
·
The file “\Flash
Disk\Georgia SoftWorks C753X\default.gswtc” is loaded on startup if found.
·
If the security level is ‘user’
then the GSW SSH/Telnet Client will attempt to connect.
4.
Additional Files
The setup program will install the file “\Flash Disk\StartUp\reinst.bat”.
Please
do not delete or modify this file as it is required for persistence and automatic
startup of the client.
5. Application
Protection
GSW
Telnet supports the security settings available on the Psion-Teklogix devices.
The settings are available via Start|Security
Following are a few Tips when installing the GSW SSH/Telnet
Client for the above devices running Windows CE .NET Version 4.2+
1. Persistence
over a ‘Cold Reset’
By default, the GSW Telnet
Client is installed to a persistent directory. The directory is
\Application\Georgia
SoftWorks C753X
·
User Fonts – Your fonts need to reside in two locations.
\Windows\Fonts
And ALSO
\Application\Georgia
SoftWorks C753X
2. Uses
Standard Accelerators and
Shortcuts for all CE .NET 4.2+ devices (page 44).
3. Startup
– Default Connection Settings
·
The file “\Application\Georgia
SoftWorks C753X\default.gswtc” is loaded on startup if found.
·
If the security level is ‘user’
then the GSW SSH/Telnet Client will attempt to connect.
4. Additional
Files
The setup
program will install the file “\Application\StartUp\reinst.bat”.
Please do not delete or modify this
file as it is required for persistence and automatic startup of the client.
5.
Application Protection
Use the File|Security dialog as described in the Application Protection (page 65)
section.
Following are a few Tips
when installing the GSW SSH/Telnet Client for the LXE MX3X running Windows CE
.NET Version 4.2+
Note: Please verify that you are running version MX3XGC4201C or later of the LXE
firmware. You can view the version on your device by
Start|Settings|Control Panel|About|Versions
1. Persistence
over a ‘Cold Reset’
By default,
the GSW Telnet Client is installed to a persistent directory. The directory is
\System\Georgia SoftWorks C753X
·
User Fonts – Your fonts need to reside in two locations.
\Windows\Fonts
And ALSO
\System\Georgia SoftWorks C753X
2.
Uses Standard
Accelerators and Shortcuts for all CE .NET 4.2+ devices (page 44).
3.
Startup – Default Connection Settings
·
The file “\System\Georgia
SoftWorks C753X\default.gswtc” is loaded on startup if found.
·
If the security level is ‘user’
then the GSW SSH/Telnet Client will attempt to connect.
4.
Additional Files
The setup program will install the file “\System\autoexec.bat”.
Please
do not delete or modify this file as it is required for persistence and
automatic startup of the client.
5. Application
Protection
The
LXE MX3X provides Applock application security software. The GSW SSH/Telnet
Mobile clients are compatible with Applock and may be launched from Applock.
In the
Applock configuration you must specify which application is to be launched and
you must specify a full path to the application. Please specify the following
path in the dialog.
\Windows\GSW_lnch.exe
Before
configuring the system for Applock, pre-configure all the settings (in particular
the default.gswtc file) and then
go to File|Security and
configure the security to the user level and press OK.
Following are a few Tips
when installing the GSW SSH/Telnet Client for the above device running Windows
CE .NET Version 4.2+
The PSC Falcon 4410 has
the capability for full application lockout. The steps for implementation of
this feature follows.
1. Application
Protection
Step 1: Run
gsce_4ig.exe
on your PC and install the GSW Universal Mobile Client for ARMV4I.
Step 2: Configure the GSW Mobile Client as
required for your environment
Step 3: When satisfied with the configuration from within
the GSW Mobile Client perform the menu item
File|Save
and save the settings in
\Program Files\GSW_Clnt\default.gswtc.
And this will automatically
generate the file
\Program
Files\GSW_Clnt\default.cab
Step 4: From
within the GSW Mobile Client, switch to ‘User Mode’ using the menu item
File|Security

Figure 40: Switch from Administrator to User Mode
Step 5: On the device launch the
File Manager and create the Folder
 \FlashFX Disk\CAB
\FlashFX Disk\CAB
And copy the device files
\Program
Files\GSW_Clnt\default.cab
\Program
Files\GSW_Clnt\c753x.cab
 to the folder created
above.
to the folder created
above.
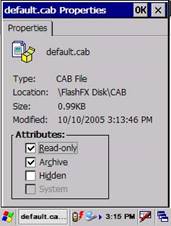
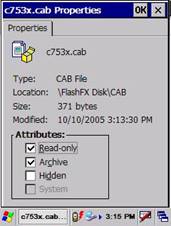
Figure 41:
Note that the files are already marked as Read Only.
Step 6: Copy the file
C:\Program
Files\Georgia SoftWorks Universal Telnet and SSH Client for Windows CE ARM4I\WCEG_4I.ARMV4I_G.CAB
From your PC (the
PC used in Step 1) to
\FlashFX Disk\CAB on
your Falcon 4410 device, and mark it Read Only
|
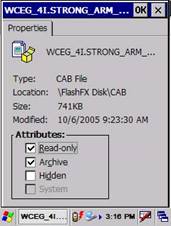
Figure 42: File copy from PC to Device
|
 Now, three (3) file exist in this folder. Now, three (3) file exist in this folder.
 Mark file as Read Only Mark file as Read Only
|
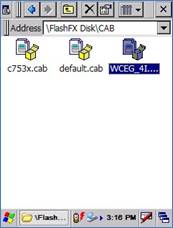
|
Step 7: On the device go to:
Start|Programs|Falcon Management|FDU Admin Tool
And set the configuration options as shown using the
different Tabs below.
|
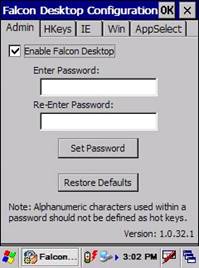
Figure 43: Falcon 4410 Application Title
|
A. Make sure that the Enable Falcon Desktop
checkbox is checked.
|
|
   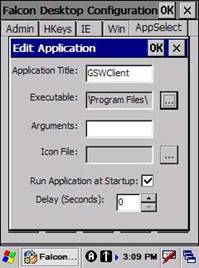
Figure 44: Falcon 4410 Application Title
|
B.
Enter the Application Title
 C. Next Click on the ‘…’ button. When you click
the button, it opens up the File Selection dialog below. C. Next Click on the ‘…’ button. When you click
the button, it opens up the File Selection dialog below.
|
|
D. Navigate to the
GSW_Lnch.exe in the folder \Program Files\GSW_Clnt Select the GSW_Lnch.exe
Click OK and the filename of the Executable is filled in.
|
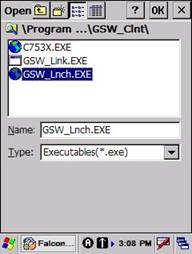
Figure 45: File Selection Dialog
|
Next Select
the Win tab and make sure that the Show
Taskbar checkbox is clear.
|
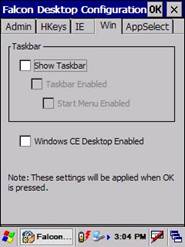
Figure 46: Falcon Clear Win Tab Checkboxes
|
E. Select the Win Tab and
make sure that the Show Taskbar checkbox is clear.
F. Also make sure that the
Windows CE Desktop Enabled checkbox is clear.
|
Make sure the two checkboxes are clear.
Step 8: Cold boot the device.
The GSW Mobile Client
will automatically launch and connect after the boot.
Many times, System Administrators
request the capability to protect certain configuration values associated with
the application from being inadvertently or accidentally modified by users.
Georgia SoftWorks Mobile Clients either provide this functionality or
integrates and cooperates with devices that contain this feature.
The GSW Mobile Clients accomplish
this protection by recognizing a user and a password protected administrator
security level. If the device provides a user and administrative
level, the GSW Mobile client integrates and cooperates with the device feature.
Otherwise the GSW Mobile Client provides a user and administrative
security level.
The administrator
security level is allowed unrestricted access to the application. The user
security level is not allowed to modify the configuration values or exit the GSW
Mobile Client application.
The System Administrator
can protect access to operations and values associated with the following menu
items.
o
File|New, File|Open, File|Exit
o
Session|Settings
Upon selecting the menu
item File you will notice that
while at the user security level the menu items New, Open
and Exit are disabled. The same
is true for the Session|Settings
menu item.
Figure 47: GSW Mobile Client
Security Levels
Only the administrator
security level has access to these items.
When using the GSW Mobile
Client Application Protection you can enable the administrator security
level by selecting the menu item File|Security
as shown above. The File|Security
menu item is enabled on Intermec, LXE and Symbol devices. The File|Security menu item is disabled on
Psion-Teklogix devices because the GSW Mobile Client uses Psion-Teklogix
security levels and is settable under Start|Security.
Upon selecting the
Security menu item, the Security level dialog is presented.
Figure 48: GSW Mobile Client Security
Level Selection
To switch from User to
Administrator Security level you select Administrator
and enter the Admin Password. The Admin Password is 7062651018. Click OK. This will enable all configuration
and operations for the Administrator.
To switch from Administrator
to User Security level, select User
and click OK. A user password is not required.
Please see the tips
section for these mobile device clients for any special tips for Application Protection.
·
Intermec CK30 / CK31
·
Intermec CV60
·
LXE M3X3
·
Psion-Teklogix 7535, Psion-Teklogix
8525
·
Symbol MC 9060G / MC9090G
·
PSC Falcon 4410
At certain times you may
encounter a scenario where your system needs to be rebuilt and you want to transfer
the GSW and its settings. This entails two steps.
1. Back
up the GSW UTS installation directory and all of its subdirectories.
2. Back
up the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters
If you are using the SSH Server
then you need to also back up the following registry key.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\GeorgiaSoftWorks\GSW_SSHD\Parameters
On 64-bit operating systems the key will be:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\GeorgiaSoftWorks\GSW_SSHD\Parameters
On the rebuilt system you will need to:
1. Restore
the GSW UTS Installation directory as on the original system.
2. Re-run
the GSW UTS setup program.
3. If
using the GSW SSH Server, re-run the GSW SSH SHIELD setup.
4. Restore
the registry keys that were backed up in step 2 above.
5. Re-register
the software using the standard registration procedure or install the Floating
license.
Note: The example below
is for the GSW Telnet Server however the same procedures apply to the GSW SSH Client
unless noted.
Follow these instructions to open the Georgia SoftWorks
Client window.
1. Click
the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Click
Programs
3. Move
the mouse cursor to "Georgia SoftWorks UTS" entry.
4. Click
to the right where you see "GS Telnet Client"
At this point, the Client window is open and you will get
the host prompt (Figure 49 ).
At this prompt, you should
enter the hostname that you wish to connect. The hostname is the name your Windows
computer is referenced by via TCP/IP. This can be a text string or an actual IP
address. This name will appear in the client windows title bar.
Example:
Host: Soloman
OR
(if you know the IP address you can enter the address)
Host: 100.100.100.101
Or
Host: <ENTER>
This will connect to the local
host. You must be at the server for this to work (Useful for testing).

Figure 49: Host Prompt
After the Host is found
you will see the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server connection banner.
The connection banner contains the version of the telnet server as well as the
number of sessions available and connected. You are then presented with the Windows
logon prompt.
At this prompt you should enter a valid Windows
login id.
Example:
Login: JohnSmith
Figure 50: Logon Prompt
Below is a screen shot of the GSW SSH Connection Banner.
Figure 51: SSH Connection Banner
This is the password
associated with the Login ID. It will not be displayed when typed.
Figure 52: Password Prompt
This is an optional
field. If you do not wish to connect to a specific domain then you may simply
press "<enter>". Otherwise type in the domain you want
to connect. You may eliminate the domain prompt either by using command line
options or by setting a default domain on the Windows
Server. To set the default domain for all users follow the instructions on page
282. The Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client Command line options are described
next.
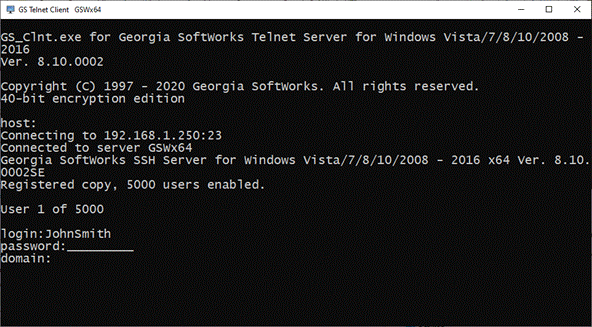
Figure 53: Domain Prompt
In addition to superior
Perfect PC terminal emulation the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet and SSH Clients have
powerful command line options facilitating faster, easier and more flexible
connections. Many of these options such as the Host, Username, Password and
Domain can be used to eliminate prompting by the client or server when connecting
to the UTS Server. The following optional command line parameters may be used.
Parameter |
Description |
-4 or -6 |
Restricts protocol to IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses.
Otherwise both are supported.
|
-a |
This specifies that this Georgia SoftWorks Client can AutoLogon
(page 110)
|
-b |
Answerback Text passed to the Server and stored in the Environment
variable gwtn_answerback. See page 82 for more
details and PPC configuration.
|
-c |
TELNET client only: Specifies that the client uses Encryption. This option works only in conjunction with corresponding settings on the server. See page 93 on setting up encryption. |
-cCertificateName |
SSH client only. Specifies the Certificate name for certificate-based authentication. This feature is integrated with Microsoft Certificate Stores. |
-dDomain |
Specifies the domain of the user. Use '.' if you want to use default domain or no domain |
-f[index] or –F[index] |
This allows additional form feed control capabilities. With some applications unexpected form feeds will be generated at the end of the document causing misalign output and paper waste. If this behavior is noticed then the -f option may help in suppressing the extra form feeds. Optional index is the virtual printer index. This option uses the copy command to print. |
-hHostname |
This specifies host name to connect to. |
-Hheartbeat Time |
Specifies our client-side heartbeat. You need that parameter for the session cleanup! See page 156. |
-i |
Enable SSH client to use FIPS 140-2 when connecting to SSH server. Note: SSH Server must be installed and FIPS must be Enabled. Only valid with SSH client. |
-I |
SSH client only. Activates public key authentication by specifying the path to the private key file. -Ipath_to_private_key_file |
-k |
Disables the mouse in the telnet or SSH session |
-m |
SSH client only. Specifies Single Sign-On through Kerberos over GSSAPI |
-n |
SSH client only. Specifies Single Sign-On through NTLM over GSSAPI |
-pPassword |
SSH and Telnet client: Specifies password for the user. Use '.' if user has no password. Notice that this is a lowercase "p". SSH Client only: If public key authentication is activated then this is the password for a password protected private key file. |
-PportNumber |
Specifies the port number to use for telnet or SSH. This port must also be set on the Server in the services file. Notice this is an uppercase “P” |
-r1=printername -r2=printername … -r9=printername |
This specifies Printer1, Printer 2, and Printer 3 … Printer 9 for Enhanced Mode client-side printing. No spaces are allowed in the printer name. Please see page 226 for more information. |
|
Continued on Next Page |
-scmddelay |
This specifies the Command Output Display Delay time (Milliseconds) for the results data displayed in the gs_clnt.exe/gs_ssh.exe window as a result of executing a Client Side Command (page 261 ) from within a telnet or SSH session. A primary function of the Client software is to display and refresh the Telnet or SSH Session Window based on Server Output. So, when a Client-Side Command displays results in the Session Window, a time is specified for the display of the Client-Side Command Output in the gs_clnt.exe/gs_ssh.exe window before the display of server-side data is resumed. The default is 2000[ms] (two seconds). |
-uUserName |
Specifies the name of the User
|
-U |
Enable Unicode character processing for input and output. See page 252. |
-vPathXMLFile |
Enable Vangard Voice, specifies path to Vangard XML file See page 314. |
-xClient Caption String |
The User has additional control over the caption text displayed in the Title bar of the client window when using the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet or SSH Client. This helps identify specific sessions especially when multiple sessions are opened simultaneously. No spaces are allowed in the Client Caption string. See example on next page for further details |
-XClient Title Bar String |
SSH and Telnet can change the Title Bar content. Note: This clears the Title Bar and displays the Title Bar String. It overrides the “-x” Client Caption String. |
-z |
Disable the Automatic Update of the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet or SSH Client. |
Long Options |
The “+” plus sign designates “Long Option” parameters |
|
The list of algorithms that can be used are in the GSW SSH User’s Manual. |
+Ciphers= |
SSH client only - The list of Ciphers provided to the server for Cipher negotiation |
+KexAlgorithms= |
SSH client only – The list of Key Exchange algorithms provided to the server for Key Exchange Algorithm negotiation |
+HostKeyAlgorithms= |
SSH client only – The list of Host Key Algorithms provided to the server for Host Key Algorithm negotiation |
+Macs= |
SSH client only – The list of Message Authentication Codes (MACs) provided to the server for Message Authentication Code negotiation |
Table 18 - GSW Telnet and SSH
Client Command Line Options
Example
- Georgia SoftWorks Client Caption String
-xClient Caption String
The User has additional control over the caption text
displayed in the title Bar of the client window when using the Georgia
SoftWorks clients. This helps identify specific sessions especially when multiple
sessions are opened simultaneously.
The command-line option
-xText
specifies a text string that is displayed in the caption
section of the title bar on the client window. The text is appended to the caption
after space as x:Text. For instance, if the option -xDavid was entered the
title bar in the client window would be displayed as show below (soloman is the
hostname).
Figure 54: Client Title Bar
Caption
GSW Telnet
and SSH Client command line options - Usage
Following is an example
for specifying client command line parameters. The GS SSH2/Telnet Client shortcut invokes the batch file GS_SClnt.bat (for Telnet) or GS_SSSH.bat (for SSH) which in
turn launches the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client. The GS_SClnt.bat and GS_SSH.bat files reside in the GS_UTS installation
directory. The contents of the batch files look as follows.
@echo off
:start
@if exist once1.bat do call once1.bat
@if exist once1.bat do del once1.bat

 @gs_clnt.exe
@gs_clnt.exe
@if errorlevel 2 goto copy
@exit
:copy
@copy gs_clnt.new gs_clnt.exe > gsnull.txt
@if exist once2.bat do call once2.bat
@if exist once2.bat do del once2.bat
@goto start
The
line @gs_clnt.exe
is the line
that launches the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client. For SSH the client
name is gs_ssh.exe.
Command Line Parameters will be added to this line in the batch
file.
In most cases the GS_SClnt.bat/GS_SSH.bat files will be
modified to provide the parameters in a transparent manner to the user.
Example - Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client Command Line Options
Host: soloman
Heartbeat: 150
UserName: johndoe
Password: fastest
Domain: Use
the default domain.
Encryption: Yes
Client
Caption: System1
The Command Line Parameters used are:
-H150
-hsoloman -ujohndoe -c -pfastest -d. -xSystem1
Note: The last dot is for the
default domain
And thus the GS_SClnt.bat
file will be modified as shown below adding the command line parameters.
@echo
off
:start
@if
exist once1.bat do call once1.bat
@if
exist once1.bat do del once1.bat
@gs_clnt.exe -H150 -hsoloman -ujohndoe -c -pfastest
-d. -xSystem1
@if
errorlevel 2 goto copy
@exit
:copy
@copy
gs_clnt.new gs_clnt.exe > gsnull.txt
@if
exist once2.bat do call once2.bat
@if
exist once2.bat do del once2.bat
@goto start
Always use the
matching version of the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client with the Georgia SoftWorks UTS Server.
When a Georgia
SoftWorks Client connects to the GSW Universal Terminal Server, the GSW UTS is
able to determine the version of the GSW Windows Client that is connecting. If
the version of the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client is different than the GSW UTS
version, the GSW UTS updates the remote (client) computer with the appropriate
GSW Client for that version of the GSW UTS Server.
As new versions of the
software are released, occasionally matching versions of the GSW Windows Client
and UTS is required to take advantage of certain features. Sometimes this
required the System Administrator to either visit the remote site or via
telephone walk remote users through instructions to install or update the GSW
Client software.
Additionally, System
Administrators may be administering many GSW Universal Terminal Servers distributed
throughout a large region. Different versions of the GSW UTS may be installed
at different sites. Regardless of the version installed the Administrator will
be able to automatically use the appropriate version of the GSW Windows Client.
Important Note to Customers of Versions Prior to
6.26
Previous versions of the GSW Telnet Client invoked the
client executable directly from the shortcut.
Starting with Version 6.26 the short cut invokes the
batch file GS_SClnt.bat which launches the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client.
The batch file must be invoked for the Automatic Client Update to occur.
|
|
Note: This feature requires the minimum GSW Telnet Server and
Client version 6.26.
If you want to disable the Automatic Update of the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client then use
the –z command line
option.
When the Remote User connects to the GSW UTS Server
computer and the versions do not match the User will see the following screen.
The Text Upgrade initiated is displayed. While the appropriate client is being
transferred a series of periods is displayed indicating the progress of the transfer.
Figure 55: Automatic GSW Client Upgrade
Initiated
Once the transfer of
the client is complete you will see a screen similar to the one below displayed
requesting a key to be pressed to continue.
Figure 56: Automatic Client
Upgrade – Session Restart
After the session is restarted you will be prompted again
for the Host. Proceed and log on as usual with the proper GSW Client version
for the GSW UTS Server for which you are connected.
Figure 57: Automatic Client
Upgrade - Host Prompt
Developer
Tip: If a client-side application must launch the Georgia SoftWorks Client then
the application should check the return code from the call to gs_clnt.exe/gs_ssh.exe.
If the rerun code is two (2) then the client and server versions are different
and newer client was copied to the file gs_clnt.new. It should be renamed and
copied to gs_clnt.exe/gs_ssh.exe and then launched.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – See Client Control page 408
Or
use legacy style below
|
You may want the Application Title to display in the title
bar of the Georgia SoftWorks Client Windows Title. This capability is disabled
by default. To enable you should set the gwtn_show_console_title
environment variable in your logon script (Learn more about logon scripts on page
408).
The environment variable for displaying the Application
Title in the Georgia SoftWorks Client Window title bar is:
gwtn_show_console_title
Possible values are Y
(or 'N', or 'y' or 'n')
Y – Enable the
display of the application title in the Georgia SoftWorks Client Window Title
N – Disable
the display of the application title in the Georgia SoftWorks Client Window Title
(default)
For example, to enable the display of the Application
Title in the Georgia SoftWorks Client you would enter:
set gwtn_show_console_title=Y
in the Logon Script for a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting
environment variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_show_console_title=Y is correct
set
gwtn_show_console_title = Y is
not correct.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – See Client
Control page 408
Or
use legacy style below
|
You may not want the ‘x’
(close button) to display in the top-right title bar of the Georgia SoftWorks
Desktop Client. If the ‘x’ is pressed in the top-right corner then the
connection between the client and server is abnormally closed. The session may
get suspended if the system is configured to do so. The administrator may require
a specific method for the user to exit the application and thus may want to
eliminate the ‘x’ (close button) as an option for the user.
The ‘x’ is displayed (enabled)
by default. To disable you should set the gwtn_clnt_no_x
environment variable in your logon script (Learn more about logon scripts on page
218).
The environment variable
for disabling the display of the ‘x’ in the Georgia SoftWorks Desktop Client window
title bar is:
gwtn_clnt_no_x
Possible values are 'Y' or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Disable the display of the ‘x’ in the title bar in
the Georgia SoftWorks Desktop Client window Title
N – Enable the display of the ‘x’ in the title bar in
the Georgia SoftWorks Desktop Client window Title (default)
For example, to disable
the display of the ‘x’ in the Georgia SoftWorks Desktop Client you would enter:
set gwtn_clnt_no_x=Y
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_clnt_no_x=Y is correct
set
gwtn_clnt_no_x = Y is not
correct.
The User can pass a text string (up to 20 characters) from
the client to the server when connecting. The received text string is stored the
environment gwtn_answerback. The
command-line option
-bText
specifies a text string that is passed to the server. For Example,
the command line parameter
-bdelta187
would be available on the server in the environment
variable gwtn_answerback. The example
below shows both the client MAC address and the Answerback text.
Figure 58: Answerback and MAC
Address environment variable
GSW Mobile Device
(Windows Mobile and Windows CE .NET V4.2/5.0+) client’s configuration.
Below is a screen shot
of the GSW Mobile Device configuration for the Answerback text.
Figure 59: GSW PPC Client Answerback
text configuration
Desktop Keyboard Macros
Keyboard
macros are a powerful and time saving feature that lets the administrator
define custom keys on the device when the session is active. Macros are used for remapping
Function keys (F1 – F12) to keystroke sequences.
Macros definitions have the form:
Function Key=Keystroke
Sequence
or
Function
Key=(shift:ctrl:alt) Keystroke Sequence
Where
Function Key is F1 through F12
and
(shift:ctrl:alt)
This is optional extended syntax that provides the
capability to specify the Shift, Ctrl and Alt key states. You may want to
have a Shift F1 or a Ctrl F1, Shift Alt F2, etc. and the syntax of (Shift:Ctrl:Alt ) is a fast way to specify if
the key is pressed. To indicate a key is pressed is by using the value 1 and so specify that it is
not pressed is to use the value 0.
For example
(1:0:0) specifies that the SHIFT key
is pressed but not the CTRL or ALT.
(0:1:0) specifies that the CTRL key
is pressed but not the SHIFT or ALT.
(0:0:1) specifies that the ALT key
is pressed but not the SHIFT or CTRL.
Or combinations can be
specified:
(1:1:0) specifies that the SHIFT key
and CTRL keys are pressed but not the ALT.
Whitespace is optional.
See
the example in the configuration section below for detailed examples.
and
Keystroke Sequence follows the same format as the GSW Termination
strings (page
158).
The keys that can be remapped are
Function Keys: F1,F2,F3,F4,F5,F6,F7,F8,F9,F10,F11,F12
Configuration
The keyboard macros are defined in the session
configuration files. The session configuration file for the desktop client is GSWClnt.ini.
For mobile clients the file name is up to the
administrator as long as the extension is .gswtc.
The configuration files have the “Windows
ini”
format.
A new section [Macros] needs to be manually added
to the configuration file.
For example, to remap all Functions Keys to send capital
F, followed by function key index and the enter key you
would add the following section to the configuration file GSWClnt.ini.
[Macros]
F1=shift-f,1,ENTER
F2=shift-f,2,ENTER
F3=shift-f,3,ENTER
F4=shift-f,4,ENTER
F5=shift-f,5,ENTER
F6=shift-f,6,ENTER
F7=shift-f,7,ENTER
F8=shift-f,8,ENTER
F9=shift-f,9,ENTER
F10=shift-f,1,0,ENTER
F11=shift-f,1,1,ENTER
F12=shift-f,1,2,ENTER
F1=(1:0:0)SHIFT-S, SHIFT-F, 1
F2=shift-f,2,ENTER
F3=shift-f,3,ENTER
F4=shift-f,4,ENTER
F5=shift-f,5,ENTER
F6=shift-f,6,ENTER
F7=shift-f,7,ENTER
F8=shift-f,8,ENTER
F9=shift-f,9,ENTER
F10=shift-f,1,0,ENTER
F11=shift-f,1,1,ENTER
F12=shift-f,1,2,ENTER
Terminating a session
Type exit at the
client window prompt (command prompt) followed by the ENTER key and the session
will terminate and the window will clear and then close. If you are unable to
get to the command prompt then you should use the client self-termination (see
below).
The client user can terminate
their session by entering Ctrl-X
followed by F9.
In situations where the
client user believes that the application has hung or is not responding, the user
can self-terminate the session without getting the system administrator involved.
Please note that the
Team Services Hotkey (see page 143 ) must be enabled. It is enabled by default.
If it is disabled then the ability for a client to self-terminate is also
disabled.
Please see the section
on Emulations for descriptions in connecting to
the Georgia SoftWorks UTS for Windows using 3rd party clients (page 166).
The Georgia SoftWorks
Windows Universal Terminal Server is packed with features. The
aggregation of the features is geared toward industrial and commercial
application. The features logically group into units called packs. All feature
packs are included with the Georgia SoftWorks UTS at no extra cost!
Security Pack – (see
page 92 )
The Security Pack
provides the system administrator with confidence that the Windows
System and the data transferred remains secure. Encryption, access and usage
restrictions are among security features implemented.
Performance Pack – (see
page 109)
Advanced proprietary
algorithms, optimizations and compressions provide for the fastest SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows on the market.
GSW Team Services – (see page 117)
Allow mobile users to
quickly share resources to improve productivity while keeping cost down without
requiring system administrator / IT intervention.
Failure Detection/Recovery Pack – (see page 149Error! Bookmark not defined.)
Industrial and
commercial applications demand sophisticated failure detection and recovery methods.
Georgia SoftWorks recognized the requirement and has unequaled capabilities in
this area.
Legacy Pack – (see
page 163)
Proper operation with
Legacy applications is the foundation of a quality SSH2/Telnet
server. The Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Universal Terminal Server for Windows
will meet or exceed all expectations with respect to running character oriented
and legacy applications.
Emulation Pack – (see
page 166)
The Emulation Pack provides
all the popular emulations required by most 3rd party clients. Not
only are the emulations provided but they are implemented correctly.
Power Features Pack
– (see page 187)
The Georgia SoftWorks
UTS provides the most powerful, needed and useful features on the market.
Compatibility Pack –
(see page 244)
RFC 854 compliance
provides access from other platforms allowing the Telnet Server to be utilized
by a variety of users.
RF Terminal Features
- (See page 244)
Utility Pack – (see
page 259)
Several utilities are provided
for the telnet user to simplify and ease the use of SSH2/Telnet.
Security Pack
Georgia SoftWorks
provides unmatched security when using our Telnet Server for Windows. It
is the only Telnet Server that offers complete Data Stream Encryption.
The Georgia SoftWorks Telnet server has been submitted to the United States
Department of Commerce and has obtained the proper license exceptions so it can
be legally exported around the world.
Data Stream encryption can be enabled on a global or a per
user basis with undetectable performance loss. This is useful if users are
running accounting, banking, medical or other applications that contain
sensitive data.
Logon only encryption may also be employed. This
protects User Ids, Passwords and other logon data.
The Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server is
integrated with Windows Security. All Windows
security concepts apply. The Georgia SoftWorks UTS allows the system administrator
to optionally restrict telnet access based on User ID or IP address. These are
additional security measures above the normal Windows
security. The system administrator can specify the users that are allowed to
logon via telnet
|
Security Pack
|
Configurable
|
GSW Windows
Clients
|
3rd Party Client
|
|
Encrypted Data Stream - Telnet Server Specific
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Encrypted Data Stream –
Strong 128 Bit*
- Telnet
Server Specific
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Encryption - Enable or
Disable based on IP Address – Telnet Specific
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
|
SSH Strong Encryption -
AES-256
(End to End – Authentication and Data Stream)
- GSW
SSH Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Encrypted Logon Session - Telnet Server Specific
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
FIPS 140-2 Compliant Option – SSH Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
AES-256 Encrypted Logon
Session – SSH Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Connection Restrictions
|
|
|
|
|
-
User Id
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
-
IP Address
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
-
3rd Party Clients
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
-
Connection count
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
-
Connection count by User ID
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
-
Connection count by IP Address
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Encrypted Sessions Only – Telnet
Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Encrypted Sessions Only – SSH
Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Specific
application
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Expired Password Handling
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Integrated with Windows
Security
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 19 - Security Pack
Encryption of the Data Stream for Telnet on Windows
is another feature pioneered by Georgia SoftWorks. Complete Data Stream
encryption is available on a global or per user basis when using the Georgia
SoftWorks Telnet Client. For encryption to work both the sending and receiving
ends of the data must know to encrypt and decrypt the data. Since third party
clients would not be aware of encryption or decryption, data stream encryption
is only available with the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client.
The Setup for Data Stream Encryption requires:
1. The
encryption parameter must be passed when invoking the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
Client
2. The
setting of an environment variable on the server in either a Global or User
login script
3. The
registry variable EnableEncryption is set to 1.
4. The
proper Microsoft Windows operating system DLLs and API’s are installed on both
the client and server systems.
The parameter -c
should be passed when invoking the Georgia SoftWorks Windows
Telnet Client. This can be passed from the command line via the following
command:
gs_clnt.exe
-c
The shortcut may be modified to pass Data Stream Encryption
parameter.
An environment variable must be set on either a Global or
Per User basis to activate Data Stream Encryption.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global 370
or Per User 408
Or
use legacy style below
|
The environment variable for the complete data stream
encryption is:
gwtn_encrypt_session
in the Logon Script for
a particular user (or the Global Logon Script for all users.).
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting environment
variables.
For example: To Activate Data Stream Encryption the
following line should be present in the logon script.
set
gwtn_encrypt_session=1 is correct
set
gwtn_encrypt_session = 1 is
not correct
For example: To De-activate Data Stream Encryption the following
line should be present in the logon script.
set gwtn_encrypt_session=0 is
correct
The variable EnableEncryption
is a registry key value. This Registry key enables or disables the ability to
activate Encryption. If it is disabled then all encryption environment
variables are ignored. Also, the client command line parameter must not be
used when the registry value is disabled. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableEncryption
The default value is 0(That is disabled.) The value 1
enables the ability to use Encryption. The value 0 disables the ability to use
encryption.
This is how to change the registry key for Encryption.
Note: You must be on the Windows
system that the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server is installed. However, you may
connect to the Windows Registry from a remote location.
1. Click
the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Click
RUN
3. Type
REGEDIT
4. Click
OK
5. Select
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableEncryption
6. Select
the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7. Enter
the new value for the EnableEncryption and click OK
The new EnableEncryption
value will take effect for all new connections.
Encryption requires specific operating system Dll’s (that
are present on most systems) to exist to run the telnet client and server.
These files come with Windows NT 4.0/XP/VISTA/2000/2003/2008/W7/W10
and are included in Microsoft Internet Explorer Version 3.0 and above. If you
do not have these system files encryption will not operate.
If you have Windows 95 then you
must have Windows 95 OSR2 (OEM Service Release 2) or later (or Windows 95 with
IE 3.02 or later). Windows 98 and newer versions have all the
required files.
Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
Server SE: 128-bit Strong Complete Data Stream Encryption.
Some
applications require extremely strong Complete Data Stream Encryption. For
these customers, Georgia SoftWorks offers their Telnet Server in a Strong Encryption
(SE) version. This utilizes a full 128-bit data stream RSA encryption
algorithm.
NOTE:
128-Bit Complete Data Stream is the default version when shipped on a CD.
The
Georgia SoftWorks configuration needed to run the 128-bit encryption is the
same as for the 40-bit encryption. The system requirements needed to run the
encryption are slightly different. In order to run the 128-bit encryption the system
requires either:
Server or Client Requirements
·
Windows NT 4.0 with domestic version of SP 3 or domestic version of SP4
or
·
Windows 7/8/10/VISTA/2008/R2/2012/2016/2019, XP/2000/2003
Additional Client Options
·
Windows 95 with domestic version of Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0. or
·
Windows 98 with domestic version of Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0.
·
Windows ME with domestic version of Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0
If
you have further questions about of ensuring that your computer systems can
accommodate 128-bit encryption please see the Microsoft Web site.
Both
the client and server must meet the system requirements for the SE version. Also,
both the Client and server must be of the SE version.
You may choose to only
encrypt the logon sequence when using the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client. This
entails the same steps as described with Complete Data Stream encryption except
there are no environment variables to set in the logon scripts.
In certain situations,
it may be desirable to have encryption enabled or disabled based on the IP
Address of the connecting telnet session. Complete Encryption (both Logon and
Data Stream) can be enabled/disabled based on the IP address using the configuration
text file gs_ipenc.txt. The Data Stream Encryption Client-side
parameter must also be used when configuring encryption based on IP addresses
as described on page 93.
When configured the
settings in the gs_ipenc.txt file
overrides the normal encryption registry and environment settings.
The order of the fields
in the gs_ipenc.txt
file is as follows:
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
IP Address
|
The IP address/IP Address
Range of the client
|
|
Enable or Disable Encryption
Value
|
0=Disable, 1=Enable
|
Table 20
– Encryption based on IP Address - gs_ipenc.txt
when using GSW Clients
For example, the
following entry in the file:
168.92.55.4 0
disables logon and
session encryption for GSW Telnet Clients connecting from 168.92.55.4
Another Example:
205.20.63.* 1
enables logon and
session encryption for GSW Telnet Clients connecting from 205.20.63.*
NOTE1: The IP
address must start in the first column. IP Address Ranges and wildcards are allowed.
Please see the file gs_ipenc.txt for further details.
NOTE2: For
security reasons it is prudent to set the file gs_ipenc.txt to allow only SYSTEM – Read Access. NO other
accounts should be allowed to access this file.
NOTE3: This feature
is for power users that have a thorough understanding of the network and system
security issues and topics.
The GSW SSH Server
offers very strong end-to-end encryption for all data. This includes the
authentication and data stream. Please see the GSW SSH User’s Guide for more
information on the SSH Server encryption.
A Federal Information Processing
Standards Publication (FIPS) 140-2 compliant option is available and may be
purchased for the GSW SSH Server. This standard specifies the security requirements
that will be satisfied by a cryptographic module utilized within a security
system protecting sensitive or valuable data. This option is available to
Federal agencies, including the US Military. It may also be purchased by other
organizations such as state governments, educational and research institutions,
commercial businesses and other entities with the need or desire to comply with
this security requirement for cryptographic modules standard. Please see the GSW
SSH User’s Guide for more information on the SSH Server FIPS option.
When the FIPS 140-2
option is enabled on the GSW SSH server, FIPS 140-2 compliant connections can
be identified by using the Session Administrator.
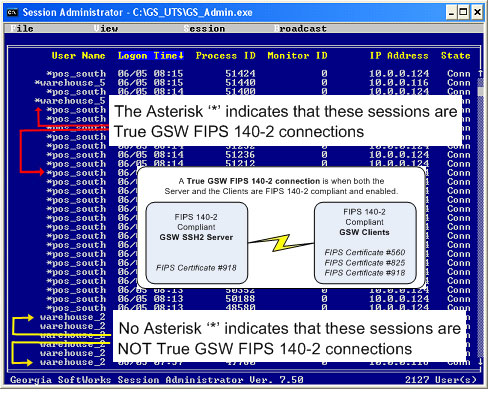
Figure 60: Session Administrator
view FIPS 140-2 sessions
A True GSW FIPS 140-2
connection is identified by an asterisk “*”
prepended to the username in the session administrator. This means that
a GSW FIPS 140-2 compliant client is connected to a FIPS 140-2 compliant
server. Both ends are compliant and thus you can have confidence that this is a
GSW True FIPS 140-2 compliant connection. Usernames without an asterisk “*”cannot be confirmed as FIPS 140-2
compliant.
The system administrator
may restrict access to the SSH2/Telnet
Server based on a variety of criteria advancing the level of security.
The system
administrator may optionally restrict connections via SSH2/Telnet
based upon the user id. This is useful when you have a defined set of users
that you would allow access to the Windows
Server via SSH2/Telnet . If the system administrator decides to limit the users
allowed to logon via SSH2/Telnet then the local group Gwtn Users
must be created. If this group exists then only members of this group will be
allowed to logon via SSH2/Telnet . If this group does not exist then all users
that can logon locally can log on via SSH2/Telnet.
Once the group Gwtn Users is created, each user allowed to logon via SSH2/Telnet must be added to this group. Windows
does not instantaneously update the group membership after the user manager is
closed. You will have to restart the Windows
server after creating the group and adding users.
The system
administrator may optionally restrict connections via telnet based upon the
Host IP address. Remote access may be limited only to specific IP addresses.
The system administrator may also restrict specific IP addresses from
connecting via SSH2/Telnet.
Restrictions based on
IP address are enforced when the file thosts
exists. The IP addresses of interest are listed in the thosts file. In short, only IP addresses listed in the thosts file are allowed to connect via
telnet/SSH. The provision also exists to exclude specific IP addresses from
connecting via SSH2/Telnet. A keyword [Exclude] is used that indicates all IP
Addresses listed in the file should be excluded from logon via SSH2/Telnet.
How to set up Host IP Address Restriction.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Edit thosts file 371
Or
use legacy style below
|
You must create the file:
thosts
The file must reside in the Georgia SoftWorks Universal
Terminal Server installation directory. The directive [EXCLUDE] indicates if
the IP Addresses should be excluded from connection.
NOTE: The System account must have
permission to read the thosts
file.
The rules are simple for setting up the thosts file.
1. It
is a text file
2. The
# character is the comment character
3.
[EXCLUDE] directive placed in the 1st line will force the interpretation
as the exclusion file, otherwise only IP addresses listed are allowed.
4.
Data after the IP address is ignored and therefore can be used for
additional comment data.
Following are example thosts
files.
Example - IP Restriction: restrict
certain Hosts from connecting.
Bill and Tom have
machines that are in a public location and are not secure. The system
administrator does not want to allow SSH2/Telnet
access from those machines. However, Bill and Tom have other machines that need
SSH2/Telnet access to the server. This is how to set up the thosts file to
exclude those particular machines.
Information needed:
IP
address of Bill's machine: 198.68.20.21
IP
address of Tom's machines: 198.68.22.25
Edit the file thosts and add the following lines.
[EXCLUDE]
# Here is the list of hosts that are not allowed
to log in via SSH2/Telnet
198.68.20.21 Bob's machine
198.68.22.25 Tom's machine
Now let’s look at the
contents of the file.
The [EXCLUDE] directive
specifies that all IP addresses listed in the thosts file are not allowed to
connect via telnet.
The next line is a
comment reminding the System Administrator that the following Host IP addresses
will not be allowed to connect via SSH2/Telnet
.
Next is the list of Host
IP addresses to exclude. The list can be as long as you desire.
Example
- Restriction: allow only specific Hosts to
connect
ACME Accounting has 3
remote locations. For the machines at each location there may be dozens of
different users that may be connecting at different times of the day. The
system administrator only wants to allow SSH2/Telnet
connections from the 3 remote locations.
However, the ACME remote
Location 3 office is temporally closed and is under remodeling. Therefore, the
system administrator wants to easily comment remove them from the "allowed"
list and quickly add them back as soon as the office reopens.
Information needed:
IP address of ACME accounting location
1 machine: 198.68.35.21
IP address of ACME accounting
location 2 machines: 198.68.35.25
IP address of ACME accounting location
3 machines: 198.68.35.26
Edit the file thosts
and add the following lines.
# Here is the list
of hosts that are allowed to log in via SSH2/Telnet
#
198.68.35.21 ACME
accounting location 1 machine
198.68.35.25
ACME accounting location
2 machine
#Let’s not allow
location 3 until the office reopens.
#198.68.35.26 ACME accounting location 3
machine
#
Restrict users access to a specific application
The system
administrator may optionally limit a user to run a specific application. This
is accomplished using the c_start.bat
file logon scripting technique. A detailed example and description is on page 219.
This feature allows
connections only from the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client. This is another level of security that the system administrator can configure.
Many times, the system administrator will not want users using any generic
client to connect to his or her system.
The variable EnableRFC854Clients is a registry key
value. This Registry key enables or disables the ability to restrict connection
from 3rd party clients. If it is disabled then only users using the
Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet client are allowed to connect. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
The default value is
1(That is enabled.) The value 1 enables the ability for connection from all
telnet/SSH clients. The value 0 restricts connection to the Georgia SoftWorks
Telnet/SSH client.
This is how to change
the registry key for 3rd Party Client Restriction.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks Windows UTS is installed.
However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the EnableRFC854Clients
and click OK
The new value will take
effect for all new connections.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Set Max Sessions 372
Or
use legacy style below
|
This feature specifies
the total number of connections allowed. This is another level of security that
the system administrator can configure. Many times, the system administrator may
want to limit the total number of connections to be a smaller value than the
number of connections purchased.
The variable MaxSessions is a registry key value.
This Registry key enables or disables the ability to restrict connection to the
number of sessions specified. If it is disabled (0xffffffff) then all of the
sessions purchased are available, otherwise then the MaxSessions Registry value is compared to the number of
sessions purchased. The smaller of the two numbers is used as the number of
sessions to allow. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\MaxSessions
The default value is 0xffffffff (That is disabled). Other
values limit the number of connections allowed to the value chosen.
This is how to change
the registry key to limit the number of connections.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server is
installed. However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\MaxSessions
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7. Enter
the new value for the MaxSessions
and click OK
The new value will take
effect for all new connections.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Set Max Sessions 372
Or
use legacy style below
|
The system
administrator may want to limit the number of simultaneous logons for specific
User Ids. This is especially useful for ASP environments where an entire company,
department or group is assigned a single User Id that everyone shares. The system
administrator may want to limit the number of simultaneous connections for that
company for a variety of reasons that range from server resource allocation to
purchased access.
Restrictions based on the number of User Id sessions are
enforced when the file gs_l_usr.txt
exists. The User Id’s with connection restrictions counts are listed in the gs_l_usr.txt file. For each entry in
the gs_l_usr.txt file two fields
are specified: The User ID and the Count.
How to set up User ID Count Restriction
Notice the file in the GSW UTS installation directory:
gs_l_usr.txt
The file must reside in the Georgia SoftWorks Universal
Terminal Server installation directory.
NOTE: The System account must have
permission to read the gs_l_usr.txt file.
This file is used for configuration of the User ID Count
Restrictions.
The rules are simple for setting up the gs_l_usr.txt file.
-
It is a text file
-
The # character is the comment character
-
Each entry must start in the first column.
-
Each entry consists of the User ID and the Count
-
The User ID and the Count are separated by a single space
Following is an example for using the gs_l_usr.txt file.
Example – USER ID Count Restriction
ACME ASP is an Application
Service Provider (ASP) where they have a Specialized Database Lookup Application
(SDLA) located on a server at their headquarters. They sell access to the SDLA
to companies where pricing is based on the number simultaneous connections.
Each company accesses the SDLA via the Internet from undetermined or varying
locations. Each company that purchases access to the SDLA is provided a User ID
on the ACME server, that everyone from their company shares.
Currently AMCE has sold
access to the SDLA to six companies. Four companies purchased three connections
each; the remaining two companies purchased twelve connections each.
ACME wants to restrict
each company to the number of sessions that they have purchased.
The ACME System Administrator
can configure the gs_l_usr.txt
file that specifies the number of sessions allowed for each User ID.
The Information for
each company is:
|
Company Name
|
User Id Assigned to Company
|
Number of Concurrent Sessions
|
|
BigBrain Intelligence
|
bbrain
|
12
|
|
Vigorous Investments
|
viginv
|
3
|
|
Sweet Apple Suppliers
|
sweeta
|
3
|
|
Warehouse Storage
|
warstore
|
3
|
|
Sure Shipping Co
|
surship
|
3
|
|
Wireless Security
|
Wiresec
|
12
|
Figure 61: Security: Restriction
based on User ID Count.
This is how to set up the
gs_l_usr.txt file to limit the number of connections for each company.
Edit the file gs_l_usr.txt and add the following
lines. (Be sure to start in column one)
bbrain 12
viginv 3
sweeta 3
warstore 3
surship 3
Wiresec 12
Each time a logon
request occurs the GSW Universal Terminal Server determines the number of active
sessions associated with that User ID. If the count of active sessions exceeds
the configured count in the gs_l_usr.txt
file then the logon is denied.
A sample gs_l_usr.txt file with examples is installed
with the software. It can be easily modified and used for your purposes.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Set Max Sessions 372
Or
use legacy style below
|
The system
administrator may want to limit the number of simultaneous logons from specific
IP Addresses. This is especially useful for ASP environments where many users
access the GSW UTS from locations that can be identified by a specific IP
Address. The system administrator may want to limit the number of simultaneous
connections for a variety of reasons that range from server resource allocation
to purchased access.
Restrictions based on the number of sessions originated
from specific IP Addresses are enforced when the file gs_l_ip.txt exists. IP Addresses with connection restrictions
counts are listed in the gs_l_ip
file. For each entry in the gs_l_ip
file two fields are specified: The IP Address and the Count.
How to set up IP Address Count Restriction.
Notice the file in the GSW UTS installation directory:
gs_l_ip.txt
The file must reside in the Georgia SoftWorks Windows
Universal Terminal Server installation directory.
NOTE: The System account must have permission
to read the gs_l_ip.txt file.
The file gs_l_ip.txt
is used for configuration of the IP Address Count Restrictions.
The rules are simple for setting up the gs_l_ip.txt file.
-
It is a text file.
-
The # character is the comment character.
-
Each entry must start in the first column.
-
Each entry consists of the IP Address (or IP Address Range) and
the Count.
-
The IP Address and the Count are separated by a single space.
Following is an example for using the gs_l_ip.txt file.
Example – IP ADDRESS Count Restriction
ACME ASP is an Application
Service Provider where they have a Medical Database Lookup Application (MDLA)
located on a server at their headquarters. They sell access to the MDLA to
companies where pricing is based on the number simultaneous connections. Due to
the sensitive nature of Medical information access is only granted from
specific locations that can be associated with known IP Addresses. In addition,
each User has access to private medical information based on their User ID. The
typical ACME customer may have 300 users that need access to the MDLA but no
more than 20 will be using the system at any given time.
Currently AMCE has sold
access to the MDLA to four companies. Two companies purchased twenty
connections each; the remaining two companies purchased twenty-five connections
each.
ACME only wants to
restrict each company to the number of sessions that they have purchased.
The ACME System Administrator can configure the gs_l_ip.txt file that specifies the
number of sessions allowed for each User ID. The Information for each company
is:
|
Company Name
|
IP Address or Range
|
Number of Concurrent
Sessions
|
Heath Matters Inc. |
192.71.34.107 |
20 |
Live Long Insurance |
170.40.255.231 |
25 |
Grow Tall Pharmaceutical (They want access from any the following IP Addresses to work.) |
164.10.15.210 164.10.15.211 164.10.15.212 164.10.15.213 164.10.15.214 164.10.15.215 164.10.15.216 164.10.15.217 164.10.15.218 164.10.15.219 |
164.10.15.220 164.10.15.221 164.10.15.222 164.10.15.223 164.10.15.224 164.10.15.225 164.10.15.226 164.10.15.227 164.10.15.228 164.10.15.229 164.10.15.230 |
20 |
Sharp Doctors for You (Sharp Doctors for You has a large range of IP Addresses that are valid.) |
205.20.63.0 Through 205.20.63.255 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
Figure 62: Security: Restriction
based on Count. from IP Address
This is how to set up
the gs_l_ip.txt file to limit
the number of connections for each company.
Edit the file gs_l_ip.txt
and add the following lines.
192.71.34.107 20
170.40.255.231 25
164.10.15.210-164.10.15.230 20
205.20.63.* 25
Each time a logon
request occurs the GSW Universal Terminal Server determines the number of
active sessions associated with that the originating IP Address. If the count
of active sessions exceeds the configured count in the gs_l_ip.txt file then the Logon is denied.
Note 1: An Address range is specified in
line 3
164.10.15.210-164.10.15.230
20
This translates to include all
IP Addresses between:
164.10.15.210
and 164.10.15.230
Note 2: An Address Wilde Chard is specified
in line 4
205.20.63.* 25
This translates to include all IP Addresses
no matter what the values for the last field. The list below helps visualize
the IP addresses included.
164.10.63.0
164.10.63.1
164.10.63.2
…
164.10.63.253
164.10.63.254
164.10.63.255
A sample gs_l_ip.txt file with examples is
installed with the software. It can be easily modified and used for your
purposes.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Telnet Encryption see page 370
Or
use legacy style below
|
This feature allows
connections only from the encrypted Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client. This is
another level of security that the system administrator can configure. Many times,
the system administrator wants to ensure that ALL connections to the GSW UTS
are encrypted.
Note: This feature is
only relevant for Telnet. By the nature of SSH all connections are encrypted.
The variable RequireEncryptedSession is a registry
key value. This Registry key enables or disables the ability to restrict encrypted
only sessions. If it is disabled then only users using the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
client are allowed to connect. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\RequireEnctyptedSession
The default value is 0(Disabled.)
The value 1 only allows encrypted session to connect. The value 0 allows both
encrypted and un-encrypted sessions to connect to the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
client. This value must be left set to 0 (the default) if running the GSW SSH Server.
Use of this feature overrides user settings in
the logon script and force clients to use encrypted session data stream.
Please make sure the registry parameter:
EnableEncryption
is set to 1 and that
the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client uses the /c
command line option.
After you complete your
settings you will notice the following:
a. 3rd
party clients will report disconnected session before the user even tries to
type his logon name.
b. GS
clients which do not have /c option
will fail to connect.
This is how to change
the registry key for connection by only Encrypted Sessions.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks Windows UTS is installed. However,
you may connect to the Windows Registry from a remote location.
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\RequireEncryptedSession
6. Select
the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7. Enter
the new value for the RequireEncryptedSession
and click OK
The Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Terminal Server has pioneered and introduced another expected
but missing feature in the Windows world. Typically, when a user password is
expired connections are simply refused by Windows SSH2/Telnet
servers. This is not the case with the Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal
Server. The user is prompted for the new password just as if they were logged
on locally to the Windows Server.
The Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Terminal Server for Windows is integrated with Windows security, adhering to the native security already existing on Windows.
Performance Pack
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server is the fastest SSH2/Telnet
Server available for Windows . The Georgia SoftWorks UTS is designed to work in
the most demanding industrial and commercial applications. This means that it
must have reliable and consistent operation all of the time. It does not matter
if there is one connection or 100 connections. It is dependable, reliable,
consistent and robust.
|
Performance Pack
|
Configurable
|
Georgia
SoftWorks Client
|
3rd
Party Client
|
|
Fast,
Fast, Fast!
|
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Compression
for slow speeds
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Slow
Link, Internet Support
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Proprietary
performance algorithms
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Proprietary
code optimizations
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
DOSBOSS
- MS
DOS application performance booster!
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Automatic
Logon
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
(page 183)
|
|
GSW
UTS x64 native 64-Bit Software
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
|
RF
DTIO Interface
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 21
- Performance Pack
The Georgia SoftWorks
UTS provides incredibly fast screen updates, in fact the fastest on the market.
Several optimizations have been implemented with respect to screen updates. For
example, when data is sent from the server to the client only the screen data that
has changed is sent.
Keyboard response is
also incredibly fast. When you type a character, it is displayed immediately. A
fast typist will have to work hard to outrun the keyboard response of the
Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server.
The Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Terminal Server for Windows compresses data to increase the overall
throughput of data. Incredible performance optimizations are utilized
when using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Clients.
Many access the host
system via slow dialup links or by the Internet. Significant performance
optimizations are realized when using any SSH2/Telnet
client.
To accomplish the
desired performance, the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server designers used object oriented C++ for the foundation of the software,
providing a modular, easily extensible and maintainable design. In addition to sophisticated
performance algorithms, all time critical sections of the software are written in
highly optimized C code.
The Georgia SoftWorks
DOSBoss dramatically improves system performance in situations when MSDOS
applications are running under Microsoft Windows NT. In fact, some say it is
incredible!
NOTE: DOSBoss will
only run on 32-bit platforms.
Many MSDOS applications
run under Windows but do not perform well, especially when multiple instances of
them are being used at the same time (This is without SSH2/Telnet
in the picture). This is because MSDOS applications do not know about Windows
and assume they are the only application(s) running on the computer. As a result,
the MSDOS applications are not always Windows
friendly.
For example, start 3
instances of the Microsoft Edit program in 3 separate command prompt windows. Next
start the Performance monitor. You will notice the CPU usage is very high even
though you are not actively using the editors. Your computer does not perform
well when the CPU usage is high. This problem occurs with many MSDOS
applications.
To enable the Georgia SoftWorks DOSBoss put the following
line at the beginning of your logon script:
<telnet_dir>\dosboss
where <telnet_dir> stands for the Georgia
SoftWorks Telnet Server Directory, for example:
c:\gs_uts\dosboss
The above activates the DOSBoss with default parameters
that satisfies most users requirements.
Note for power users
You can specify additional command line parameters
for the DOSBoss. Valid command lines are:
/cnn
- specifies the count of time slices to release. Default is /c3.
In the case where DOSBoss is already loaded the installed
instance will change its parameter(s) to the new value(s).
/h
- to display the help message
/r
- uninstall the resident part of the program (Do not use with /c option)
/s - show
statistics of the resident portion (DOSBoss must be loaded first)
Examples:
DOSBoss /c5 /s ' Set time
slices to release to 5, dump statistics
DOSBoss /r /s ' uninstall the DOSBoss,
dump statistics.
DOSBoss /h ' display the
help message
This feature allows you
to pre-configure a list of IP addresses that will be able to connect and log on
without any User ID, Password or Domain prompting when using the Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Clients or 3rd Party Telnet Clients.
Autologon is useful in
many situations; however, the real power of this feature is realized when
coupled with the Session Saver (page 149) for fast and easy connection
establishment. For example, when a connection is broken due to a link failure you
can reconnect without the time consuming UserID, Password and Domain prompts
and resume work exactly where you left off before the link failure.
The configuration
procedure for Automatic Logon is different for GSW Windows Clients and Third-Party
Clients. A list of IP address can be associated with either GSW Windows Clients
or 3rd Party Clients but NOT both.
Automatic Logon for GSW Clients is
configured using the gs_auto.txt file. Automatic Logon for Third
Party Clients is configured using the gs_logon.txt
file.
Automatic Logon for GSW Telnet and
SSH Clients is configured using the gs_auto.txt file.
Automatic Logon for Third Party
Telnet Clients is configured using the gs_logon.txt file.
Automatic Logon for Third Party SSH
Clients requires the use of Public/Private key authentication. For more
information please contact Georgia SoftWorks support
The format of the files is exactly
the same but it is important to remember which files are used for each
client type.
Note: An IP address cannot be associated
with both a GSW Client
and a Third-Party Telnet Client. No overlap
between IP Address ranges defined in the gs_auto.txt and gs_logon.txt is allowed. Unpredictable
results will occur.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Automatic Logon see page 368
Or
use legacy style below
|
For correct operation
of the AutoLogon feature when using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client two steps must occur.
First, the Georgia
SoftWorks Telnet/SSH Client must be enabled for automatic logon.
·
GSW Desktop Clients – Automatic Logon is enabled using the
command line parameter –
when initiating the client (See page 77).
·
GSW Windows Mobile Clients – Automatic Logon is enabled by
checking the Autologon checkbox on the Session|Settings|Session
menu options. (see page 49)
Second,
a server-side configuration text file is used for specifying the IP address
that will AutoLogon. The name of the file for the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client is gs_auto.txt
and is installed in the GSW UTS Root Directory. All Clients connecting with IP
addresses specified in the gs_auto.txt
file must be GSW Clients AND the IP Addresses CAN NOT also be used in the 3rd
Party Automatic Logon configuration text file. No overlap between IP Address
ranges defined in the gs_logon.txt and gs_auto.txt is allowed.
The order of the fields
in the gs_auto.txt
file is as follows:
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
IP Address
|
The IP address of the client
|
|
Domain
|
Specify the dot ‘.’ character
if no domain is used.
|
|
User Name
|
The User ID for the
connection
|
|
Password
|
The Password
|
Table 22 – Automatic Logon Specifications gs_auto.txt when using GSW Clients
An IP address can be associated
to AutoLogon with a Georgia SoftWorks OR a 3rd Party
Telnet Client but NOT both. No overlap between IP Address ranges defined
in the gs_auto.txt and gs_logon.txt
is allowed.
For example, the following entry in the file:
63.80.112.70 .
rayr sharpbook
Instructs the system
that when a user connects from the IP Address 63.80.112.70
that the connection should be authenticated as ‘./rayr’
with the password set to ‘sharpbook’.
The ‘#’ character in
the first column designates a comment line.
NOTE1: The IP
address must start in the first column. IP Address Ranges and wildcards are
allowed.
NOTE2: For security
reasons it is prudent to set the file gs_auto.txt to allow only SYSTEM – Read Access. NO other
accounts should be allowed to access this file.
NOTE3: The
format of this file is the same as gs_logon.txt,
the automatic logon configuration file used with 3rd party clients.
Only the name of the file is different.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Automatic Logon see page 368
Or
use legacy style below
|
This feature allows you
to pre-configure a list of IP addresses that will be able to connect and log on
without any User ID, Password or Domain prompting when using 3rd
Party Telnet Clients.
Autologon is useful in
many situations; however the real power of this feature is realized when coupled
with the Session Saver (page 149) and/or used with RF Data collection devices
for fast and easy connection establishment. For example, when a connection is
broken due to a link failure you can reconnect without the time consuming UserID,
Password and Domain prompts and resume work exactly where you left off before
the link failure.
A server-side text file
is used for specifying the IP addresses that will AutoLogon. The name of the
file is gs_logon.txt
and is installed in the UTS Root Directory. No client configuration is required
for 3rd party telnet clients.
The order of the fields
in the gs_logon.txt
file is as follows:
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
IP Address
|
The IP address of the telnet
client
|
|
Domain
|
Specify the dot ‘.’
character if no domain is used.
|
|
User Name
|
The User ID for the
connection
|
|
Password
|
The Password
|
Table 23
- Automatic Logon Specifications gs_logon.txt
when using 3rd Party Clients
An IP address can be
associated to AutoLogon with a Georgia SoftWorks OR a 3rd
Party Telnet Client but NOT both. No overlap between IP Address ranges
defined in the gs_logon.txt and gs_auto.txt
is allowed.
For example, the
following entry in the file:
63.80.112.70 . rayr sharpbook
Instructs the system
that when a user connects from the IP Address 63.80.112.70 that the connection
should be authenticated as ‘./rayr’
with the password set to ‘sharpbook’.
The ‘#’ character in
the first column designates a comment line.
NOTE1: The IP
address must start in the first column. IP Address Ranges and Wildcards are
allowed.
NOTE2: For
security reasons it is prudent to set the file gs_logon.txt to allow only SYSTEM
– Read Access. NO other accounts should be allowed to access this file.
NOTE3: The
format of this file is the same as gs_auto.txt, the automatic logon configuration file used
with the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet/SSH clients. Only the name of the file is different.
Automatic
Logon requires Server-Side Configuration and Client-Side Configuration for GSW Clients.
|
Server-Side
Configuration
|
|
|
Automatic Logon
Configuration File on Server
|
|
|
GSW Windows Client
|
Third Party Client
|
|
|
|
|
|
Edit
specific Server File that contains Automatic Logon Information
|
gs_auto.txt
|
gs_logon.txt
|
|
|
|
|
Table 24 - Automatic Logon Configuration
Files
Client-Side Configuration
for Automatic Logon
|
Client-Side
Configuration
|
|
|
GSW Desktop Client
|
GSW Mobile Client
|
Third Party
Telnet Client
|
|
|
None Required
|
|
|
Add the command line parameter
-a when
initiating the client (page 77). This tells the client not to send logon
information to the server.
|
 Check
the Box in the configuration options screen (page 49). Check
the Box in the configuration options screen (page 49).
|
|
|
Example in the GS_SClnt.bat
file
@echo off
:start
@if exist once1.bat
do call once1.bat
@if exist
once1.bat do del once1.bat
@gs_clnt.exe –a
if errorlevel 2
goto copy
@exit
:copy
@copy gs_clnt.new
gs_clnt.exe > gsnull.txt
@if exist
once2.bat do call once2.bat
@if exist once2.bat
do del once2.bat
@goto start
|
 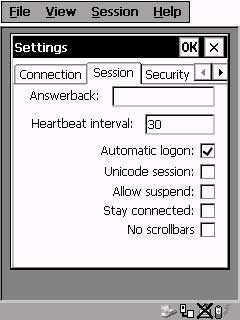
|
|
Table 25
- Automatic Logon Client-Side Configuration
GSW
UTS x64 Native 64-Bit
Georgia SoftWorks
created a native build optimized for 64-bit platforms. Indeed many 32-bit
applications will run on a 64-bit platform including the standard GSW UTS, but
our philosophy of continuous improvement demands that we put forth the effort
to make the software native on the powerful 64-bit platform. This eliminates
potential compatibility issues of non-native code running while taking full advantage
of the performance and addressing opportunities afforded by the 64-bit
platform.
Figure 63: Extraordinary High
Session Count (Actual Screen Shot)
The above is a screen
shot of gs_admin when GSW Engineering performed burst connection testing with
the GSW UTS x64. This is where hundreds of connections are initiated rapidly
over and over taxing the system until several thousand connections are
maintained. Even though this test goes beyond what is considered real world it
provides information as to the benefits of a 64-bit system as well as the glimpse
of the extensive testing performed to ensure the GSW UTS meets and exceeds the
demands of commercial environments. At this point in testing GSW UTS x64 the screen
shot was taken from GS_Admin with over 4999 connections.
This
particular test was performed on a modest 2 GHz dual processor Xeon with 6 GB
RAM running Windows 2008 Server. We have observed over 2400 sessions on a
modest 2 GHz dual processor Xeon with 2 GB RAM running Windows XP!
The GSW UTS
has a built-in interface to work with the GSW RF Directed Terminal Input/output
Engine. The GSW Directed Terminal I/O Engine is an add-on component that
intercepts a specific set of terminal input/output operating system calls initiated
by your application
and directs terminal I/O through
a specialized high-performance interface within the GSW Universal Terminal
Server (UTS).
A new
performance standard is realized when using the GSW Directed Terminal I/O
Engine with the GSW UTS for Windows. Large systems will experience a
dramatic performance improvement as well as a substantial increase in the
number of sessions on a server.
The GSW DTIO
Engine is specialized software, focused on a narrow set of goals. The objectives
are to provide significant performance improvements and a higher number of
sessions on a server than previously possible due to processing bottlenecks and
CPU Limitations
Please visit the GSW website for more
information on the GSW RF DTIO Engine.
Team Services is
about collaboration and efficiency
GSW Team Services
provides your mobile device users a breakthrough in telnet/SSH technology that shatters
all prior usability and efficiency standards by allowing for unprecedented user
collaboration and cutting the costs of hardware. The implications are enormous.
GSW Team Services has the potential to radically transform the client/server applications
universe from isolated and fragile sessions to the world of persistence and
creative collaboration of empowered users.
Team Services furnishes your mobile device users with innovative
session management tools that are initiated from the client. Team Services is
fast and easy to use.
GSW Team Services empowers
the mobile device users to share resources, transfer, swap, share and recover mobile
device sessions from the mobile device! This provides your mobile device
users the capability to quickly solve common mobile device session and device
problems without having to perform administrative operations on the server or needing
to involve Information Technology (IT) personnel.
- Empowers
Mobile Device User – session management operations initiated from the mobile
device. This is a breakthrough feature!
- No
system administrator intervention required.
- Works
with GSW and 3rd party clients.
- Incredible
Features – Sharing, Swapping, Transfer and Recovery of sessions.
- Fast
and Easy - No technical degree required and the fastest way to resume work.
Team members helping team members. Instead of purchasing
multiple types of devices per user; or all high-end devices for the occasional
need for high end features, team members can maximize device utilization by quickly
sharing or swapping devices without even having to log off or involving the
system administrator.
Often user(s) needs to
use a different or an additional device, while preserving their session. GSW Team
Services Transfer, Swap and Share operations addresses this need.
·
Transfer – Transfer (move) your session
to another team member’s device. Terminates the existing session on the second device
when the transfer is complete.
·
Swap – (Swap devices but keep
your session) Transfer your session to another team member’s device and at the
same time Transfer their session to your device.
·
Share – Two devices share the
same session. Either device may be used within a single session. This is
similar to the GSW Session Administrator Shadowing feature, except Share is initiated
from the client. The Share Team Service can be used when a forklift operator
has a vehicle mount device and also needs a wireless mobile device, both using
the same session. It can also be used for training and assistance. The range of
possibilities for Team Service Share is so powerful it is limited only by your
imagination.
Recover dropped sessions. It doesn't matter if
the session is dropped due to battery failure, device destruction, network
problems or simply because the user went out of range. With GSW, the session
is maintained on the server and with Teams Services the session can be recovered
from the same or another team member's device. Of course, you
will resume work at the exact point where you were when the session dropped.
GSW Team Services increases
productivity by allowing your team members to minimize down time when ordinary
work flow interruptions occur and resume work with unmatched speed and ease.
Strict Teams. Often workflows are specific to
distinct groups (or teams) and the administrator wants to allow only members
within that group to have the capability initiate Team Services operations SHARE,
SWAP, TRANSFER and RECOVER.
With Strict Teams, system administrators can create multiple Teams such that only members within each team can
participate in Team Services operations with other members of their team. This
is particularly useful in Application Server Environments and in situations
when the pool of SSH/Telnet users span multiple departments, locations or
companies.
Individuals may be assigned
to more than one team, allowing flexibility such
as supervisors overseeing multiple teams or specifying floating individuals for
overflow situations.
- Only
users defined as part of a team can participate in Team Services operations
with other members in the team.
- Organize
groups, departments, locations into Teams such that they can help each
other, but not impact other Teams.
Configuration
instructions and examples are contained in the tsgroups.txt
file. This file resides in the GS_UTS installation root folder.
Team Services
operations are straightforward to understand and use. Below is an overview for using
GSW Team Services. In this document GSW Team Services is often abbreviated
"TS".
The Team Services
Transfer, Swap and Share operations requires the team member who originates the
operation first communicate with the 2nd team member
in order to request that the 2nd team member put their device
(session) in the proper Team Service Accept mode for the operation. The 2nd
team member must affirm that they are willing to accept a Transfer, Swap or
Share. This way the 2nd team member's session is not unknowingly
altered without expressly consenting to the operation.
The 2nd team
member initiates Team Services and enters the “Accept Mode” for the specific
Team Service to consent to the operation. This is done by pressing the corresponding
function key for the Team Service operation. Session Identification information
is displayed and can be quickly communicated to the originating team member.
The originating team
member then enters Team Services, selects the Team Service operation, identifies
the 2nd team member's session and completes the operation.
The entire process can
take less than 60 seconds.
In summary, the Transfer,
Swap and Share Team Service operations each have an Accept Mode
and a Team Services Operation.
The Recover Team
Service does not have an Accept Mode. You could consider a suspended session as
consenting by default.
The Transfer, Swap and
Share Team Service general procedural flow is:
1.
One
team member (originator) requests a 2nd team member to participate
in a Team Service operation.
2.
The 2nd
team member puts their session in Accept Mode for the Team Service operation.
3.
Team member
(originator) starts Team Service operation.
4.
Team member
(originator) identifies 2nd team member's session, selects and
completes operation.
The Recover Team
Service operation general procedural flow is:
1.
Team
member initiates the Team Service Recover option.
2.
Team
member identifies the suspended session, selects and completes operation.
Team Services state and
status information is displayed in the Session Administrator. This allows the
administrator to know which devices are sharing, waiting for Team Service Transfers,
Swaps, Shares and etc. Please view page 145 for more information on the Session
Administrator and Team Services.
Enter Team Services Tasks by typing Ctrl-x (see page
121 for more details) or the configured hot key. The Team Services Tasks menu
is show below.
Figure 64: Team Services Tasks Menu
Each of the Team
Service tasks is initiated by using a function key on the device. Team Service tasks
that require an Accept mode use a pair of function keys, one for the Accept
and the other for the Team Service tasks. When Accept Mode for a Team Service
is performed, the client device display is similar to Figure
65.
|
Accept Mode Display
|
|
Session Selection Display
|
|
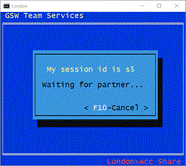
Figure 65:
Accept Mode Display
|
On the left we see the display after a user has entered
Accept Mode for Team Service Share. Note that the Session Id is s5.
On the right we see the display after the Team Service operation
Swap is entered. A list of all sessions available for a Swap is displayed.
Note: Only sessions in Accept Swap mode are displayed. So, there will be no confusion swapping with
someone that did not consent to a swap.
|
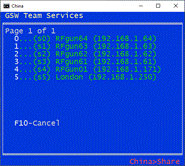
Figure 66:
Session Selection Display
|
The associated Team
Service operation displays a list of sessions available for that operation
similar to Figure 66. The session is selected for the operation by entering
the displayed line number for that session. For example, to swap with session s5 the user would enter a 2 since that is the line number for session
s5.
The Transfer operation
uses the F1 key for Transfer Accept Mode and the F2 key to perform the Transfer
operation. The Swap operation uses the F3 key for the Swap Accept Mode and the
F4 key for the Swap operation. The Share operation uses the F5 key for Accept
Share Mode and the F6 key for the Share operation.
|
|
|
2nd Team Member
|
Originating Team Member
|
|
Team Services Operation
|
Description
|
Accept
Mode
|
Operation
|
|
Transfer
|
Transfers
your session to another device
|
F1
|
F2
|
|
Swap
|
Transfers
your session to another device
Transfers the
other session to your device
|
F3
|
F4
|
|
|
|
Share
|
One session
is shared by two devices
|
F5
|
F6
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recover
|
Recovers a
suspended session to your device
|
n/a
|
F7
|
|
My TS Info
|
Display
Session ID, User Name, IP Address
|
n/a
|
F8
|
|
Reserved
|
|
n/a
|
F9
|
|
Cancel
|
Cancel Team
Services Operation, Exit Menu
|
n/a
|
F10
|
|
Enter Team
Services
|
Open Team Services
Menu
|
Configurable hot key
|
Table 26 - Teams Services
Function Keys
A
configurable hot key is used to enter GSW Team Services. The default hot key is
Ctrl-x. When initiated, Team Services presents the user with a menu that
is used to transfer a session, recover a session, swap sessions, share a session
etc. Learn more about the configurable hot key on page 143.
Devices come with a variety
of screen sizes offering large display areas on stationary or truck mount
devices and smaller display areas on smaller hand held mobile devices. With GSW
Team Services the text is automatically adjusted based on the number of columns
and rows defined with the "Mode Con" command (page 298)
in your logon script. If there are not enough columns to display the complete
Team Service text then intelligent abbreviations are used so you can view the
essential information in the normal font for your application.
This works well with
the small hand held mobile device displays as well as the larger truck mount displays.
No magnifying glass is required to read the text, nor do you have to be a detective
to decipher the meaning of the abbreviations.
The three most used
Team Services screens are:
·
Team Services Main Menu
·
Team Services "Accept Mode" Display
·
Team Services "Select Session" Menu
Below is an example of
the full text of the Team Services tasks menu on the left and the abbreviated
text on the right. In order to maximize the readability alternate abbreviations
are used based on the number of columns and rows defined.
|
Team Services Main
Menu
|
|
Abbreviated Team
Services Tasks
|
|

|
Set the number of columns and rows for your application and
GSW Team Services will display all the text or abbreviate it based on your
configuration.
|

|
Table 27 - Team Services Tasks Menu
Abbreviations
Note that
"Accept" is abbreviated "Acc", and "transfer"
uses the common abbreviation "xfer" while the words "session",
"mode" and "suspended" are completely omitted.
Below is an example of
the Team Services Accept Transfer mode display. The Accept modes for the other
operations are similar. The unabbreviated version is on the left and the
abbreviated version is on the right.
|
Accept Transfer Mode
Display
|
|
Abbreviated Accept Transfer
Mode Display
|
|

|
An unabbreviated "Waiting for transfer" dialog
is shown on the left.
On the right is simply the session id (s5) and
"Waiting..."
|

|
Table 28 - Team Services Accept
Mode Abbreviations
Note that the text "My session id is" and
"for transfer" is omitted yet the essential session id (s5) is
presented as well as the "Waiting..." text providing a reminder to
the user.
The TS Select Session display is shown below.
There are a few items
to note.
o If more than
one page is required to display all the available sessions then the function
key F2 is used to display the
next page. F1 navigates to the previous page. This is true for both the abbreviated
and unabbreviated lists.
o Each page has a
Page x of y count display, where x is the page you are viewing and y is the total number of pages.
o On each page
the line numbers corresponding to the session id are zero based. Below on page 1,
line 0 corresponds to session id (s0).
On page 2, line 0 corresponds to session id (s5).
|
Accept Transfer Mode
Display
|
Abbreviated Select
Session Display
|
|
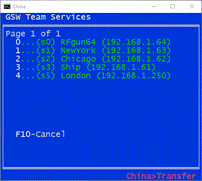
Figure 67: Unabbreviated Select Session
|
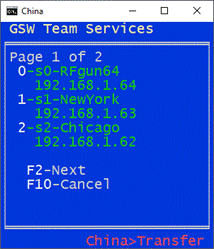
Figure 68: Abbreviated Select Session Page 1 of 2
|
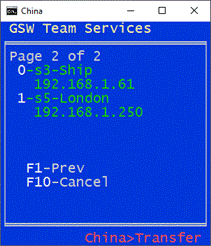
Figure 69: Abbreviated Select Session Page 2 of 2
|
Table 29- Team Services - Select
Session Display
The Team Services Transfer
operation takes a session on one device and moves it to a 2nd device. It
terminates the existing session on the 2nd device. The session will resume exactly
where it was when the transfer occurred.
In the diagram below we
have two people, Barry and Sam. Each has a session and a device. Sam is going
to lunch and Barry wants to use Sam’s wireless mobile device to scan some items
his truck mount device cannot reach. With TS Transfer, Barry can transfer his session
to Sam’s device without even logging off.
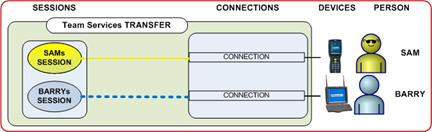
Figure 70: Before Team Service - TRANSFER
|
SAM
|
BARRY
|
|
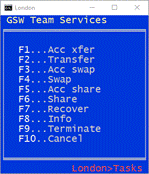
Figure 71:
Enters Team Services (Ctrl-x)
|
Figure 72:
Accept Transfer Mode (F1).
Note session id is s5
|
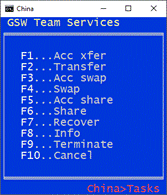
Figure 73:
Enters Team Services (Ctrl-x)
& presses F2
|
Figure 74:
Session s5 is not listed on
page 1 so Barry presses F2.
|
|
Barry asks Sam if he
can Transfer to his device. Sam consents and enters Team Services (Figure 71) and presses F1 to enter Accept
Transfer mode. Sam’s display shows he is session id “s5” (Figure
72).
Barry enters Team
Services on his truck mount device (Figure 73) and presses F2 to initiate the Transfer
operation. Figure 74 shows a list of sessions in Accept Transfer mode. Barry
does not see session s5 so he presses F2 to go to the next page. Now he sees
session s5 is listed by line number
0(Figure
75). He presses 1 to complete
the transfer to session s5.
Sam’s session is terminated and Barry's session is on Sam's mobile device and
Barry can resume exactly where he left off.
|
Figure 75:
Presses 1 to select session s5
|
|
|
|
|
The TS Transfer example is described below.
Notice that Barry is now
on the mobile device and is still using his original session. He did not have
to log off or get administrative assistance.
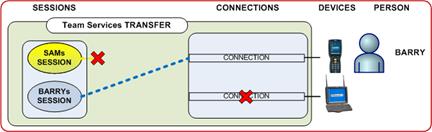
Figure 76: After Team Service - TRANSFER
The session Sam was
using is terminated during the process, freeing Sam to take his lunch break.
The Team Services Swap
operation takes two sessions on two devices and moves the session on the 1st
device to the 2nd device and moves the session on the 2nd
device to the 1st device. Each session is preserved and will resume
exactly where it was when the swap occurred.
In the diagram below we
have two people, Doug and Andy. Each has a session and a device. Doug wants to
use Andy’s wireless mobile device to scan some items his truck mount device cannot
reach. Andy still needs to work but can finish his work with the truck mount.
With TS Swap, Doug can transfer his session to Andy’s device, while simultaneously
transferring Andy’s session to Doug’s truck mount device. Both can continue their
work in the application and not even have to log off.
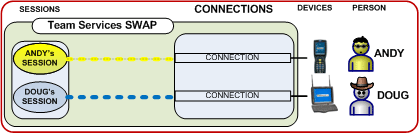
Figure 77: Before Team Service -SWAP
Doug asks Andy if they
can Swap devices. Andy consents and enters Team Services and presses F3 to
enter Accept Swap mode. Andy’s display shows he is session id “s5”.
|
ANDY
|
|
DOUG
|
|
Figure 78: Enter Team Services (Ctrl-x)
|

Figure 79: Accept Swap Mode (F3) Note the session id is s5
|
Figure 80:
Enter Team Services (Ctrl-x)
& press F4
|
Figure 81:
Selects 2 to Swap with s5
|
|
|
|
|
|
Doug enters Team
Services on his truck mount device and presses F4 to initiate the Swap operation.
Figure 81 shows a list of sessions in Accept Swap mode. Doug sees s5 is listed by the number 2. He
presses 2 to complete the swap with session s5.
Andy’s session is moved to the truck mount device and Doug's session is on the
mobile device and both can resume exactly where he left off.
Notice in the following
diagram that Doug is now using the mobile device yet he is still using his
original session. Likewise, Andy is now using the truck mount device and is still
using his original session as well.
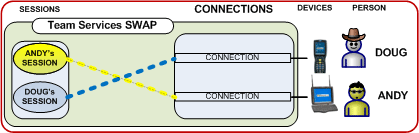
Figure 82: After Team Service - SWAP
If in Andy and Doug
want their original devices back, they can just perform a TS Swap again!
The Team Services Share
operation allows two devices to share a single session. Input from either
device is sent to the session. Output from the session is displayed on both
devices. This is similar to the Session Administrator "Shadow"
feature (page 195) but developed for Team Members.
This feature has
several applications. One is to allow a single user to work with two devices in
the same session. Another application is when one team member needs to help
another team member. Share can also be used for quality control purposes. You
may have ideas for your own environment.
In the diagram below we
have two devices and one person - Tom. Tom's device is a truck mount device.
He is the only one working in the warehouse today and also wants
to have a wireless mobile device to scan items his truck mount device cannot
reach. Tom needs all his work be in a single session and he does not want to
log on and off each time he uses each device. Tom can use the TS Share feature
and have two devices connected to a single session. With each scan he can use
the most convenient device.
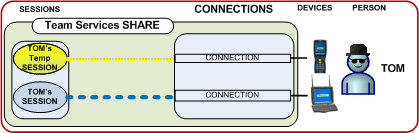
Figure 83: Before Team Service -SHARE
Tom obtains the
wireless mobile device. He is already connected with his truck mount device.
Tom wants to allow his truck mount device session to be shared. From
the truck mount device, he enters Team Services (Figure
84) and then initiates the task Accept
Share by pressing F5. The
truck mount device display shows his session id is “s5” and waiting for a partner (Figure
85).
|
Tom's Truck Mount Device
|
|
Wireless Mobile Device
|
|
Figure 84:
Enters Team Services (Ctrl-x)
|
Figure 85:
Accept Share Mode (F5) Note session id is s5
|

Figure 86:
Enters Team Services (Ctrl-x)
& presses F6
|
Figure 87:
Selects 2 to Share session id s5
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tom takes the wireless
mobile device and connects creating a temporary session. Tom enters Team
Services on his wireless mobile device and presses F6 to initiate the Share task (Figure
86). The list of sessions in Accept Share mode is shown (Figure
87). Tom sees s5 is listed by the
number 2. He presses 2 to
join session s5. Tom's mobile
device is now connected to the same session as the truck mount device. The
result is shown in Figure 88.
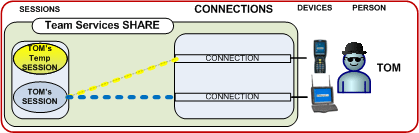
Figure 88:
After Team Service - SHARE
Undo Share
Tom's original
temporary session is maintained and he can return to it by undoing the
share by pressing control-x from the wireless mobile device.
The truck mount device continues in its session. This is shown in Figure
89.

Figure 89:
Undoing the Share
This can be useful when
a Team Member is working and needs to temporally join another team member's
session (for assistance, support, quality assurance, etc.) and then needs to
resume his work.
Note: If you exit
the session (from either device) the truck mount session is closed and the
mobile device is returned to its original session as shown below.
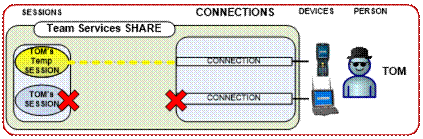
Figure 90: Exit
typed in Share
The Team Services Recover
operation allows a suspended session to be recovered to another device. This differs
from the Session Saver Auto-Reconnect which allows the same device to recover a
suspended session.
In the diagram below we
have two devices and two team members. Amos is working, but laid his device
down to look behind a crate. Barry, just learning to drive the fork lift, ran
over Amos's device. Amos was in the middle of some critical work and cannot
afford to lose his session. Team Services can Recover Amos's session to a
different device.
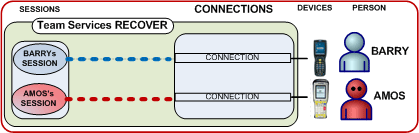
Figure 91: Before Team Service - RECOVER
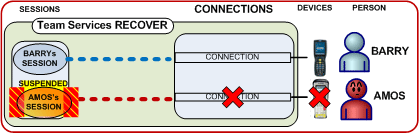
Figure 92: After Accident but before Team Service
-RECOVER
After Amos's device is
destroyed, his session is suspended but recoverable with TS. Barry has an extra
wireless mobile device. Amos obtains the wireless mobile device. On the mobile device
Amos enters Team Services Recover by pressing F7.
The mobile device display
shows a list of suspended sessions (Figure 94).
|
Wireless Mobile
Device
|
|
|
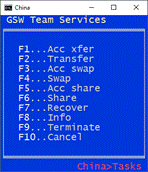
Figure 93: Enters Team Services (Ctrl-x)
|
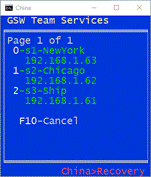
Figure 94:
List of Suspended Sessions (F7)
and select session.
|
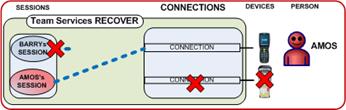
Figure 95: After Team Service - RECOVER
|
|
|
|
Amos is able to
identify his session as s0 by
the User Id and the IP Address. Amos presses number 0 to recover session 0
(s0). Amos can continue his work
exactly where he left off.
Often it is useful to obtain
Session Information about your current session. Team Services "Session
Info" can be viewed using the F8
key.
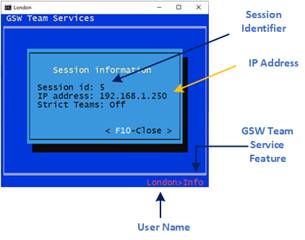
Figure 96: Team Services - Session Information
The session information displayed consists of:
The
Session Id is a unique number assigned to the session by GSW Team Services.
The
IP Address of the client device.
The User Id is displayed in the bottom right corner
of the screen. In Figure 96 the User Id is "london"
The GSW Team Services Tasks
menu provides the user access to the Team Services operations.
Enter GSW Team Services
by entering the hot key combination from the
device. The default key combination is Ctrl-x.
This can be changed to meet your requirements (see page 143).
To enter the hot key - depress Ctrl
then x, and then release
the keys. The Team Services Tasks menu is displayed.
Figure 97: Team Services Tasks Menu
|
Function Key
|
Team Service Operation
|
|
|
F1
|
Accept Transfer Mode
|
|
|
|
F2
|
|
Transfer
|
|
F3
|
Accept Swap Mode
|
|
|
|
F4
|
|
Swap
|
|
F5
|
Accept Share Mode
|
|
|
|
F6
|
|
Share
|
|
F7
|
Recover
|
|
F8
|
My Team Service
Information
|
|
F9
|
Terminate
my session
|
|
F10
|
Cancel Team
Service Operation
|
|
Configured hot key
|
Opens Team Services Menu
|
Table 30- Team Services Menu
Often with multiple users,
departments, locations, customers it is beneficial to organize users into distinct
teams for participation in Team Services. This strict team grouping prevents
users from accidently sharing, swapping, transferring or recovering sessions
with users outside their assigned group.
Configuration of
Strict Teams is performed through the tsgroups.txt
file.
The order of the fields
in the tsgroups.txt
file is as follows:
|
Field
|
Description
|
|
Team Name
|
Unique name assigned to a
team
|
|
User Domain Name
|
Domain Name. Exactly as
specified during logon
|
|
User Logon Name
|
Logon name. Exactly as
specified during logon.
|
Table 31
– Team Services - Strict Teams
Using a simple example, if you have seven (7) users
with three (3) in receiving and four (4) in shipping then you may want to have
two strict teams. Matt, David and Luke are in receiving and Diane, Naomi, Doug
and Phillip are in shipping. You want to create two teams with the names
Receiving and Shipping.
Team
Name User Domain Name User Logon Name
receiving highjumpserver_1 matt
receiving highjumpserver_1 david
receiving highjumpserver_1 luke
shipping highjumpserver_1 diane
shipping highjumpserver_1 naomi
shipping highjumpserver_1 doug
shipping highjumpserver_1 phillip
You would modify the tsgroups.txt file by adding the lines
as follows:
receiving,highjupserver_1,matt
receiving,highjupserver_1,david
receiving,highjupserver_1,luke
shipping,highjupserver_1,diane
shipping,highjupserver_1,naomi
shipping,highjupserver_1,doug
shipping,highjumpserver_1,phillip
The ‘#’ character in the first column designates a comment
line.
NOTE1: The team name must start in the first
column.
NOTE2: The ‘#’ character in the first column
designates a comment line.
Example - Strict Teams - Multiple
companies in an ASP environment
You are an Application
Service Provider and your customers want to use Team Services and it is critical
that they do not accidentally Share, Transfer, Swap or Recover sessions from
the other companies.
You can organize each
company as its own Strict Team and they will only be able to participate in
Team Services with members in their company. You can even organize multiple
Strict Teams within each company to further segregate team members.
Team
Name User Domain Name User Logon Name
acme_sprockets acme_server_1 acme_user_a
... ... ...
acme_sprockets acme_server_1 acme_user_z
army_complex1 army_intelligence army_user_1
... ... ...
army_complex1 army_intelligence army_user_1000
auto_factory sports_cars_7 emerson
... ... ...
auto_factory sports_cars_7 elliot
train_station public_trans_rr train_point_1
... ... ...
train_station public_trans_rr train_point_400
You would modify the tsgroups.txt
file by adding the lines as follows:
acme_sprockets,acme_server_1,acme_user_a
#Add a line for
each Team Members at Acme Sprockets
acme_sprockets,acme_server_1,acme_user_z
army_complex1,army_intelligence,army_user_1
#Add a line for
each Team Members at Army Complex
army_complex1,army_intelligence,army_user_1000
auto_factory,sports_cars_7,emerson
#Add a line for
each Team Members at the Automotive Factory
auto_factory,sports_cars_7,elliot
train_station,public_trans_rr,train_point_1
#Add a line for
each Team Members at the train station
train_station,public_trans_rr,train_point_400
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Team Services Global see page 379 , Per User - 414
Or
use legacy style below
|
In some environments it may not be appropriate for all
users to have access to all GSW Team Services. The system administrator may
configure the default access settings for each individual Team Service
operation using Registry parameters.
NOTE: For new installations of the GSW UTS the
Registry parameters enable all Team Services by default.
·
For upgrades from a pre-Team Services version (pre
v8.01) of the UTS, Team Services is disabled by default for security reasons.
You must enable Team Services for operation.
The registry key location is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\
The parameters, types and values are noted below:
|
Team Service
|
Registry Parameter
|
Type
|
Values
|
|
Transfer
|
TSEnableTransfer
|
DWORD
|
0=disable 1=enable
|
|
Swap
|
TSEnableSwap
|
DWORD
|
0=disable 1=enable
|
|
Share
|
TSEnableShare
|
DWORD
|
0=disable 1=enable
|
|
Recovery
|
TSEnableRecovery
|
DWORD
|
0=disable 1=enable
|
|
Other
Team Service Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
|
TSHotKeyCtrl
|
DWORD
|
0=disable 1=enable
|
|
Enter TS hot key
|
TSHotKeyVK
|
DWORD
|
See Section on page 143
|
|
Left Justify TS
Dialog/Text
|
TSLeftJustify
|
DWORD
|
0=disable 1=enable
|
Table 32 - Team Services
Registry Parameters Sizes and Values
These default settings can
be overridden using environment variables in global or per user logon scripts.
For example, you may want to have Team Services disabled
except for certain users. This can be accomplished by disabling each Team Service
with Registry parameters and then overriding them for specific users in their
logon scripts.
The environment variables for Team Services are shown
below.
|
Team Service
|
Environment Variable
|
Values
|
|
Transfer
|
gwtn_ts_enable_transfer
|
'Y' or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'
|
|
Swap
|
gwtn_ts_enable_swap
|
'Y' or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'
|
|
Share
|
gwtn_ts_enable_share
|
'Y' or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'
|
|
Recovery
|
gwtn_ts_enable_recovery
|
'Y' or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'
|
|
Other
Team Service Configuration
|
|
|
|
Enter TS hot key
|
|
|
|
Left Justify
TS Dialog/Text
|
gwtn_ts_left_justify
|
'Y' or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'
|
Table 33 - Team Services
Environment Variables
.
Team Services Recovery
Team Services Recovery works
together with Session Saver and thus Session Saver must be configured for Team
Services Recovery to operate.
The variable TSEnableRecovery is a registry key
value. This registry key sets the default behavior for all users.
0 disables
Team Services Recovery for all users.
1
enables Team Services Recovery for all users.
The key is: TSEnableRecovery
DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSEnableRecovery
An environment variable
may be set on either a Global or Per User basis to override the default
configuration specified by the Registry parameters described above.
The environment variable
for Team Services Recovery is:
gwtn_ts_enable_recovery
Possible values are Y
(or 'N', or 'y' or 'n')
This allows you to have
a set of users that can have different Team Services privileges than specified
in the Registry key value.
NOTE: No spaces are
allowed when setting environment variables.
For example: To enable
Team Services Recovery the following line should be present in the user's logon
script.
set
gwtn_ts_enable_recovery=Y is correct
set
gwtn_ts_enable_recovery = Y is not correct
The variable TSEnableTransfer is a registry key value.
This registry key sets the default behavior for all users.
0 disables
Team Services Transfer for all users.
1
enables Team Services Transfer for all users.
The key is: TSEnableTransfer
DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSEnableTransfer
An environment variable
may be set on either a Global or Per User basis to override the default
configuration specified by the Registry parameters described above.
The environment variable for Team Services Transfer is:
gwtn_ts_enable_transfer
Possible values are Y
(or 'N', or 'y' or 'n')
This allows you to have a set of users that can have
different Team Services privileges than specified in the Registry key value.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting
environment variables.
For example: To enable Team Services Transfer the
following line should be present in the user's logon script.
set
gwtn_ts_enable_transfer=Y is correct
set gwtn_ts_enable_transfer = Y is not correct
The variable TSEnableSwap is a registry key value.
This registry key sets the default behavior for all users.
0 disables
Team Services Swap for all users.
1
enables Team Services Swap for all users.
The key is: TSEnableSwap
DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSEnableSwap
An environment variable may be set on either a
Global or Per User basis to override the default configuration specified
by the Registry parameters described above.
The environment variable for Team Services Swap is:
gwtn_ts_enable_swap
Possible values are Y (or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n')
This allows you to have
a set of users that can have different Team Services privileges than specified
in the Registry key value.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example: To enable
Team Services Swap the following line should be present in the user's logon
script.
set
gwtn_ts_enable_swap=Y is correct
set gwtn_ts_enable_swap = Y is not correct
The variable TSEnableShare is a registry key
value. This registry key sets the default behavior for all users.
0 disables Team Services Share for all
users.
1 enables Team Services Share for all
users.
The key is: TSEnableShare DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSEnableShare
An environment variable may be set on either a
Global or Per User basis to override the default configuration specified
by the Registry parameters described above.
The environment
variable for Team Services Share is:
gwtn_ts_enable_share
Possible values are Y (or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n')
This allows you to have
a set of users that can have different Team Services privileges than specified
in the Registry key value.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example: To enable
Team Services Share the following line should be present in the user's logon
script.
set gwtn_ts_enable_share=Y is correct
set gwtn_ts_enable_share = Y is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Team Services see page 379
Or
use legacy style below
|
Team Services Left
Justify specifies the placement of the Team Services dialog information. If you
are not using the "mode con" command you may see some screens
displayed with part of the information hidden as show in Figure
98. This can be corrected using Left Justify as shown in Figure
99.
|
Figure 98:
Left Justify Disabled
|
Notice when
Team Services
Left Justify
is enabled the
dialog box
and the text at
the bottom
are in the
viewable display.
Note: this is usually not required
if
you are using the "mode con"
command
|
Figure 99:
Left Justify Enabled
|
Table 34 - Team Services Left Justify
The variable TSLeftJustify is a registry key value.
This registry key sets the default behavior for all users.
0 disables Team Services Left Justification
for all users.
1 enables Team Services Left
Justification for all users.
The key is: TSLeftJustify DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSLeftJustify
An environment variable
may be set on either a Global or Per User basis to override the default
configuration specified by the Registry parameters described above.
The environment
variable for Team Services Left Justify is:
gwtn_ts_left_justify
Possible values are Y (or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n')
This allows you to have
a set of users that can have different Team Services privileges than specified
in the Registry key value.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example: To enable
Team Services Share the following line should be present in the user's logon
script.
set gwtn_ts_left_justify=Y is correct
set gwtn_ts_left_justify = Y is not
correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Team Services see page 379
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Team Services menu
is entered by a hot key sequence. The default Team Services hot key sequence is
Ctrl-x, that is, depress Ctrl
then x, and then release the keys.
Both elements in the
sequence are configurable because your application may already have Ctrl-x defined
or there may be a more convenient key or key sequence for your environment.
TSHotKeyCtrl
You can configure the
TS hot key sequence to use the control key or not use the control key.
The variable TSHotKeyCtrl is a registry key value.
This registry key sets the default behavior for all users.
0 disables the requirement for the
CTRL key to be pressed to activate the TS Menu.
1 enables the requirement for the
CTRL key to be pressed to activate the TS Menu. (default)
The key is: TSHotKeyCtrl DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSHotKeyCtrl
TSHotKeyVK
You can configure the TS
hot key sequence to use a different key instead of x. The x
is represented in our settings by its virtual key code and the common values
are listed in the tables below. The values in the table are specified in hexadecimal.
In the registry editor when entering a value for TSHotKeyVK
be sure that the base is set to hexadecimal.
The variable TSHotKeyVK
is a registry key value. This registry key sets the default behavior for all
users.
The key is: TSHotKeyVK
DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\TSHotKeyVK
Default
Value: 0x58
|
Virtual Key
|
Code
|
|
Virtual
Key
|
Code
|
|
Virtual
Key
|
Code
|
|
Virtual
Key
|
Code
|
|
VK_SPACE
|
0x20
|
|
VK_0
|
0x30
|
|
VK_A
|
0x41
|
|
VK_N
|
0x4E
|
|
VK_PRIOR
|
0x21
|
|
VK_1
|
0x31
|
|
VK_B
|
0x42
|
|
VK_O
|
0x4F
|
|
VK_NEXT
|
0x22
|
|
VK_2
|
0x32
|
|
VK_C
|
0x43
|
|
VK_P
|
0x50
|
|
VK_END
|
0x23
|
|
VK_3
|
0x33
|
|
VK_D
|
0x44
|
|
VK_Q
|
0x51
|
|
VK_HOME
|
0x24
|
|
VK_4
|
0x34
|
|
VK_E
|
0x45
|
|
VK_R
|
0x52
|
|
VK_LEFT
|
0x25
|
|
VK_5
|
0x35
|
|
VK_F
|
0x46
|
|
VK_S
|
0x53
|
|
VK_UP
|
0x26
|
|
VK_6
|
0x36
|
|
VK_G
|
0x47
|
|
VK_T
|
0x54
|
|
VK_RIGHT
|
0x27
|
|
VK_7
|
0x37
|
|
VK_H
|
0x48
|
|
VK_U
|
0x55
|
|
VK_DOWN
|
0x28
|
|
VK_8
|
0x38
|
|
VK_I
|
0x49
|
|
VK_V
|
0x56
|
|
|
|
|
VK_9
|
0x39
|
|
VK_J
|
0x4A
|
|
VK_W
|
0x57
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VK_K
|
0x4B
|
|
VK_X
|
0x58
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VK_L
|
0x4C
|
|
VK_Y
|
0x59
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VK_M
|
0x4D
|
|
VK_Z
|
0x5A
|
Table 35 - Virtual Key Codes
|
Virtual Key
|
Code
|
|
Virtual Key
|
Code
|
|
VK_NUMPAD0
|
0x60
|
|
VK_F1
|
0x70
|
|
VK_NUMPAD1
|
0x61
|
|
VK_F2
|
0x71
|
|
VK_NUMPAD2
|
0x62
|
|
VK_F3
|
0x72
|
|
VK_NUMPAD3
|
0x63
|
|
VK_F4
|
0x73
|
|
VK_NUMPAD4
|
0x64
|
|
VK_F5
|
0x74
|
|
VK_NUMPAD5
|
0x65
|
|
VK_F6
|
0x75
|
|
VK_NUMPAD6
|
0x66
|
|
VK_F7
|
0x76
|
|
VK_NUMPAD7
|
0x67
|
|
VK_F8
|
0x77
|
|
VK_NUMPAD8
|
0x68
|
|
VK_F9
|
0x78
|
|
VK_NUMPAD9
|
0x69
|
|
VK_F10
|
0x79
|
|
VK_MULTIPLY
|
0x6A
|
|
VK_F11
|
0x7A
|
|
VK_ADD
|
0x6B
|
|
VK_F12
|
0x7B
|
|
|
0x6C
|
|
VK_F13
|
0x7C
|
|
VK_SUBTRACT
|
0x6D
|
|
VK_F14
|
0x7D
|
|
VK_DECIMAL
|
0x6E
|
|
VK_F15
|
0x7E
|
|
VK_DIVIDE
|
0x6F
|
|
VK_F16
|
0x7F
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F17
|
0x80
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F18
|
0x81
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F19
|
0x82
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F20
|
0x83
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F21
|
0x84
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F22
|
0x85
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F23
|
0x86
|
|
|
|
|
VK_F24
|
0x87
|
Table 36 - Virtual Key Codes -
continued
Team Services status
and state information is available in the GSW Session Administrator. The last
column in the Session Administrator is labeled TeamS for Team Services.
Figure 100: Team Services -
Session Administrator
The TeamS column indicates
the state or status of the session. Below are the various states and their
descriptions.
|
State
|
Description
|
Reason
|
|
Sel
|
User is in the
Team Services Menu
|
hotkey
|
|
|
|
|
|
AXfer
|
User has consented
to Accept a Transfer
|
F1
|
|
Xfer
|
User is
selecting the session for Transfer
|
F2
|
|
ASwap
|
User has
consented to Accept a Swap
|
F3
|
|
Swap
|
User is
selecting a session to Swap
|
F4
|
|
AShr
|
User has
consented to Accept a Share
|
F5
|
|
Shr
|
User is selecting
a session to partner
|
F6
|
|
Shr!
|
The originator
of a TS Share
|
(session is
shared)
|
|
Recov
|
User is selecting
a session to Recover
|
F7
|
|
|
|
|
Table 37 - Team Services State
Table
The System Administrator
can view the states of sessions as Team Service operations are occurring.
When
sessions are shared by Team Services the TeamS column and the Mon column are of
interest. The partnered (or shared) sessions will have the same Monitor ID. The
TeamS state of one session will be blank and the other will show Shr! The
session showing Shr! is the originating Team Service session (the one that
performed the F6)
and the
blank state is the session that performed the Accept Share (F5).
Figure 101: Team Services Session
Administrator - SHARE
The
Session Administrator may not have both partners of the share next to each
other like in the figure above. However, you can sort by Monitor ID as show
below which will group partners.
Figure 102: Team Services
Session Administrator - Sort
There are just a few
items to note when troubleshooting Team Services.
·
When you are performing Team Services Transfer, Swap or Share and
you are in the menu where you select the session - Only sessions in the
appropriate Accept Mode are displayed. For example, for Transfer, only sessions
in Accept Transfer Mode are displayed. For Swap, only sessions in Accept Swap
Mode are displayed, etc.
·
When you are performing Team Services Recover and you are in the
menu where you select the session to recover - Only suspended sessions are
displayed.
·
Check that the Team Services Registry settings are correct.
·
Check that the logon script’s Team Service environment variables
are correct.
There are some session
configuration items that must be the same for sessions participating in Team
Services.
- The
SSH settings must be the same (SSH in use or not in use)
- GSW
Encryption settings must be the same (GSW Encryption in use or not in use)
- FIPS
settings must be the same (FIPS in use or FIPS not in use)
Additionally, some
configuration items and/or requirements for sessions participating in specific
Team Services operations are:
Recovery
- Session
Saver must be configured (page 149)
- Session
must be in suspended state
- Client
types must match (GSW or 3rd Party)
- Unicode
Settings must match
Transfer
- Session
must be in Accept Transfer mode
- Client
types must match (GSW or 3rd Party)
- Unicode
Settings must match
Share
- Session
must be in Accept Share mode
- Session
must not already be monitored or shared
Swap
- Session
must be in Accept Swap mode
- Client
types must match (GSW or 3rd Party)
- Unicode
Settings must match
A quick way for the System
Administrator to identify the Client, Unicode and SSH settings for a given
session is to use the Session Administrator. Select the session and then use
the menu item Session->Details.
You will see a display similar to the one below.
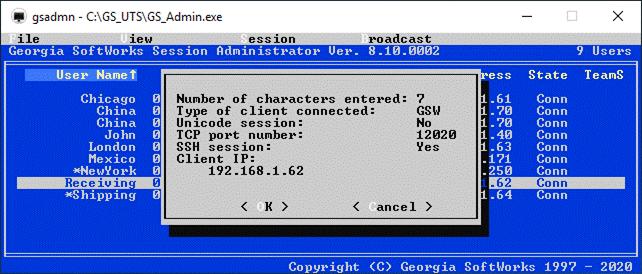
Figure 103: Team Services -
Session Details
You can identify if a client
is a GSW FIPS session by the '*' prepended to the User Name in the User name
column.
For Industrial applications
excellent failure detection and recovery is expected and required. This is one
area that separates the toys from the tools. Georgia SoftWorks pioneered
every feature listed on this page. Some have been copied but none have been
equaled. The ability to operate in industrial and commercial environments was a
design goal from the beginning not an afterthought. Commercial applications require
that remote link, PC and Client failures be detected and handled as to not
impact the other users of the system.
|
Failure/Recovery Pack
|
Configurable
|
Georgia SoftWorks
Client
|
3rd
Party Client
|
|
Session
Saver
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Complete
Session Cleanup
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Complete
NTVDM Cleanup
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Server-Side
Inactivity Timer
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Server-Side
Heartbeat
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Client-Side
Heartbeat
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Graceful
Termination of DOS Applications
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Termination
Scripts
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Termination
of Child Processes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Table 38
- Failure/Recovery Pack
Session Saver
Georgia SoftWorks has
again pioneered another outstanding feature for Windows 7/8/10/NT/XP/VISTA/2000/2003/2008/R2/2012/2016/2019
Servers. This feature Saves the Telnet/SSH Session in the event of a link or
client failure and allows users to reconnect to the same session the next time they
log in and resume the work in progress, exactly where they left off.
Extremely useful when connectivity is across the Internet or with Radio
Frequency Barcode/Scanner applications where it is important to continue work
in progress, even after a connectivity failure. If a reconnection is not
performed within a specified time period then Graceful Termination will
initiate. For the fastest reconnection and minimal prompting, you may want to
couple the Session Saver with AutoLogon (page 183). Especially useful in RF
Data collection applications.
Upon a client or link failure,
the SSH2/Telnet session and associated NTVDM are normally terminated
eliminating any orphaned sessions. This is the default behavior. However, there
are times when it may be desirable to Save the Session giving the user
the opportunity to reconnect to the session to resume work in progress. This
session is termed to be Saved or Suspended.
This feature can be enabled as described below.
Three methods exist to
connect to a Suspended session. They are the Session Reconnect Method and the Attach Method
and using Team Services Recover (page 131).
The Session Reconnect
Method is defined to automatically recognize when a User or User from a
specific IP address is Logging In and to determine if they have any Saved or
Suspended sessions. If so, then the telnet/SSH server will automatically
reconnect the user to their existing Saved Session.
The
Attach Method is defined to allow a User that is a member of the Gwtn
Monitors group to identify any Suspended sessions and to Attach (connect)
to that session. Please see the Session Monitor for more information on this
method (page 187).
The Session Reconnect method
can be configured on either a global or per user basis by utilizing Logon Scripts
(page 215).
The environment
variables for the Session Reconnect are:
gwtn_reconnect_timeout
Specifies the time that a broken session will wait
for the original user to reconnect. This variable does not have to be set, the
default value is 0. It must be set to non-xzero for Session-Reconnection to
operate.
gwtn_reconnect
Selects the criterial to use for a reconnect. There
are four possible values for gwtn_reconnect. The first two should be used with
version 8.09 and higher.
Possible values are:
·
auto_by_user_and_ip_always-
Reconnect
based on User ID and IP Address always.
Always
returns to the same session or process ID.
·
auto_by_user_
always
Reconnect based on User
ID always.
Always
returns to the same session or process ID.
·
auto_by_user_and_ip
Reconnect based on User Id and IP Address
·
auto_by_user
Reconnect based upon
User Id
Note: The User should be using the
same terminal emulation during a reconnect that they were using when the
failure occurred.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Failure Detection/Recovery see page 416
Or
use legacy style below
|
A system administrator
may not want Suspended sessions to stay around indefinitely. The amount of time
in minutes that a user's session can be available for Session Reconnection is
specified by the environment variable gwtn_reconnect_timeout. Once this timer has expired for a user then Graceful Termination
initiates.
This environment variable must to be set because the default
is 0 minutes, which is disabled. This environment variable is ignored if the gwtn_reconnect
environment variable is not set.
For example, to set the
Session Reconnection Time to 1 hour you would enter:
set gwtn_reconnect_timeout=60
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_reconnect_timeout=60 is correct
set gwtn_reconnect_timeout = 60 is not
correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Failure Detection/Recovery see page 416
Or
use legacy style below
|
Let’s look at an example.
User "Bob" is using a RF Hand Held terminal and is performing a multi-point
inspection of an item. Bob is navigating though many screens, logging data during
the inspection. Half way through the inspection the Hand Held terminal fails.
It would be great if Bob could simply grab a spare Hand Held Terminal, log in
and continue his work in progress.
This is possible with
Reconnection based on User ID. The SSH2/Telnet
server will determine if there are any Suspended sessions for user Bob. If
there are Suspended sessions then the SSH2/Telnet
server will automatically connect Bob to the existing session. The screen will
be exactly in the same condition as it was when Bob was previously connected
and Bob can continue work in progress!
For example, to enable
Session Reconnection you would enter:
set gwtn_reconnect=auto_by_user_always
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_reconnect=auto_by_user_always is
correct
set gwtn_reconnect = auto_by_user_always is not correct
Note: If there is a need
to make more than one Telnet / SSH connection using the same username, or if
using a version prior to 8.09.0001 use auto_by_user.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Failure Detection/Recovery see page 416
Or
use legacy style below
|
There may be times when
you have permanent IP addresses and you only want users from machines at those
locations to be able to reconnect to Suspended sessions for security or other
reasons. In this situation you may consider reconnection based on IP address
AND User Id.
Let’s look at an
example. User "Jane" is using a Medical Application from a secure
location. The medical application can only be used at this specific location for
security reasons. She is almost completed entering a new patient when a circuit
breaker trips. It would be nice if when the circuit breaker was reset, she
could login and automatically continue her work in progress.
This is possible with
Session Reconnection based on IP Address and User ID. The SSH2/Telnet server will determine if there are any Suspended sessions for user
"Jane" from the IP address from which she is connecting. If there are
Suspended sessions for that user AND that IP address then the SSH2/Telnet server will automatically connect Jane to the existing Saved session. The screen
will be exactly in the same condition as it was Jane was last connected and she
can continue her work in progress!
For example, to enable
this type of Session reconnection you would enter:
set
gwtn_reconnect=auto_by_user_and_ip_always
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_reconnect=auto_by_user_and_ip_always is
correct
set gwtn_reconnect = auto_by_user_and_ip_always is not correct
Note: If there is a
need to make more than one Telnet / SSH connection using the same username and IP,
or if using a version prior to 8.09.0001 use auto_by_user_and_ip.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Failure Detection/Recovery see page 416
Or
use legacy style below
|
When configured to use the
Session Saver Reconnect Method
it is important to make sure that the number of sessions purchased will accommodate
the Session Saver requirements. With Session Saver configured the UTS will save
a session that was abnormally disconnected and wait for the user to reconnect.
If the user reconnects during the configured window of time then the UTS will
present the user with his former session.
The UTS Session Saver
must temporarily use two (2) sessions, the one saved in memory and the new
session being connected in the reconnection process. Once the user is
reconnected to his former session then the UTS will close the second session and
return its associated license to the pool of available licenses. Please note
that each of the sessions counts towards the license count purchased, even
though the second session is used only for a temporary time. Once the user is reconnected
to his former session then the UTS will close the second session.
When using the Session
Reconnect Method the system administrator must ensure that there are enough
sessions available for Session Saver to have a session for the transitory logon
session used to reconnect to the saved session.
Please note that a one
(1) session license will not be able to use Session Saver with the Session Reconnect
Method because the suspended session will use the only license purchased.
The Georgia SoftWorks
UTS for Windows provides features that ensure that all SSH2/Telnet sessions are properly terminated, even during abnormal client and link failures. Many
internal session cleanup methods are automatic; others are configurable using the
different Inactivity and Heartbeat timers, termination strings and scripts.
Properly terminating telnet sessions ensure that all sessions are available for
use and that problems do not accumulate over a long term.
The Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Terminal Server has employed very complex and sophisticated
proprietary algorithms to detect, identify and eliminate “orphaned” NTVDM’s directly initiated
by applications when using SSH2/Telnet.
In many cases orphaned NTVDM’s or processes can consume all of the server’s
processing power rendering the server crippled or useless. Realizing that NTVDM
cleanup is essential in industrial, commercial and mission critical
applications, a great amount of design and development resources were expended
to ensure proper operation in this area.
Server-Side Inactivity Timer
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Failure Detection/Recovery see page
376
Or
use legacy style below
|
Server-Side Inactivity
Timer allows implementing an optional administrative policy to terminate
sessions after a period of inactivity.
Note: For RF Users
with devices that have Power Save or Sleep Mode enabled please
see page 245 for suggested settings.
For example; ACME Company
purchased Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server with a single session. User Bob connects
a session locks his office and goes home. No one else can connect due to the licensing limit.
If data (keyboard or
mouse events) is not received from a client within the specified server-side
inactivity time then the client session is terminated. This feature is useful
to ensure that an abandoned 3rd party client session is terminated
properly, releasing the telnet session for others to use. The Server-Side Inactivity
Timer is used only if the client-side heartbeat is not used.
This timer is a registry
key value and is in seconds. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\InactivityTimeout
The default value is
0xffffffff that is -1. (That is disabled.)
This is how to change
the registry key for the Server-Side Inactivity Timer.
Note: You must be on the
Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks UTS for Windows is installed. However,
you may connect to the Windows Registry from a remote location.
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\InactivityTimeout
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the InactivityTimeout
and click OK
The new
InactivityTimeout will take effect for all new connections that do not have a
client heartbeat configured.
The below variable can be defined within the User’s Logon
Script.
Example:
set gwtn_inactivity_timeout=7200
is correct
set gwtn_inactivity_timeout
= 7200 is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Failure Detection/Recovery see page
376
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Server-Side Heartbeat Timer is used for setting
the frequency in seconds which to poll the 3rd party client for presence.
If the client is not present then Graceful Termination is initiated.
This timer is a registry key value and is in seconds. The key
is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ClntChkTimeout
The default value is 30. (That is 30 seconds)
You may disable this timer by setting it to 0xffffffff.
Note: For RF Users with devices that have Power
Save or Sleep Mode enabled please see page 245 for suggested
settings.
This is how to change the registry key for the Server-Side
Heartbeat Timer.
Note: You must be on the Windows
system that the Georgia SoftWorks UTS for Windows is installed. However, you
may connect to the Windows Registry from a remote location.
1. Click
the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Click
RUN
3. Type
REGEDIT
4. Click
OK
5. Select
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ClntChkTimeout
6. Select
the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7. Enter
the new value for the ClntChkTimeout
and click OK
The new Server-Side Heartbeat
Timer will take effect for all new connections.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Local User Failure Detection/Recovery see
page 416
Or
use legacy style below
|
Server-Side Heartbeat Time by user functions identically
to Server-Side Heartbeat (Global), but supersedes any global setting allowing
more granular control. The Server-Side Heartbeat Timer is used for
setting the frequency in seconds which to poll the 3rd party client
for presence. If the client is not present then Graceful Termination is
initiated.
The below variable can be defined within the User’s Logon
Script.
Example:
set gwtn_serverside_heartbeat=15
is correct
set gwtn_serverside_heartbeat
= 15 is not correct
There may be situations
where a System Admin might want to assign a different value for Server-side
Heartbeat for a specific user or device. With the new user definable Gwtn_Serverside_Heartbeat
variable set in a user’s logon script; you can supersede the default globally
defined value so the client has its own Server-side Heartbeat.
This is extremely
useful in situations where a System Admin is testing a new device or has a
device that
they wish to test new values without affecting other devices.
Example:
gwtn_serverside_heartbeat=15
In the above setting the UTS server would send a Heartbeat pulse once every 15
seconds to test for the presence of the device.
To aid in the detection
of failed links or failed remote PC's the Georgia SoftWorks Client software
supports a Client Timeout value. The client will send a heartbeat to the server
at specified time intervals. At installation, this value is set to 30 seconds.
This can be changed using the shortcut properties.
If the server does not
receive data from the client in the specified time, the connection is terminated.
The data can be keyboard, or mouse input as well as the heartbeat. When keyboard
or mouse data is transmitted, or when a heartbeat detected the server's timer
is restarted.
The heartbeat time is
specified as an optional command line argument in seconds.
Example
- Set the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
CLIENT-SIDE heartbeat
Gs_clnt.exe /H1800
specifies a heartbeat
time of 30 minutes (1800 seconds = 30 minutes). Normally there is no need to
change this value. To disable the Client-Side Heartbeat set it to –1.
To change the Client Heartbeat
modify the command line parameter as described in the section on GSW Telnet and SSH Client command line options - Usage page 80.
Note: If an
Inactivity Timeout occurs and the Session Saver is active the Session will be
suspended; otherwise graceful termination will be initiated if specified.
Max Heartbeat Delay
MaxHeartBeatDelay registry value is the maximum delay the
server will wait for Georgia SoftWorks Clients to send the UTS server a client-side
heartbeat. If the server does not receive a heartbeat before this value is
reached it will suspend the client session when Session Saver is configured.
The default value is 60 seconds.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\MaxHeartBeatDelay
Graceful Termination of DOS Applications
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Local User Failure Detection/Recovery see
page 416
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Georgia SoftWorks Windows
Universal Terminal Server is outstanding in the case of a link or remote PC failure
we attempt to gracefully terminate the executing DOS application, therefore
saving important data that may otherwise be lost. Many applications are terminated
by sending a sequence of characters to the application such as ESC-ENTER.
Applications may have specific sequences. We allow a termination string to be
defined as an environment variable in the k_start.bat
or c_start.bat file. When a session
is to be terminated due the client heartbeat timer expiring or the server-side
inactivity timer expiring then the defined termination string will be sent to
the associated application. Approximately 3 seconds later the session is
terminated if still running.
The termination string
is a comma delimited list of keystrokes that you want to send to the shell (or
your application) before it is terminated due to either the Client Heartbeat
timeout or the Server-Side Inactivity timeout. No extra white space is allowed.
The string is not case sensitive. For example, you must specify 'shift-c' to produce a capital 'C'.
Note: Termination
String Syntax is also used with GSW Mobile
Client Macros when remapping function keys.
The following control key
designators are defined.
·
shift-
·
alt-
·
ctrl-
The following special
characters are defined.
·
ESC
·
ENTER
·
TAB
·
PGUP
·
PGDOWN
·
HOME
·
END
·
LEFT
·
RIGHT
·
UP
·
DOWN
·
DEL
·
BACKSPACE
·
COMMA
·
F1
·
F2 and so on through F12
Also, a special
operator is defined.
·
Sleepxx
This special operator will
pause the output to the shell for xx seconds. This gives the
application time to process the input. This is very useful when saving files to
disk and for applications that flush the keyboard buffer. By default, a
1-second pause is injected between keystrokes, however some specific cases may
require the use of the Sleepxx
operator to introduce additional delay.
To ensure graceful
termination you may want to enter the string "e,x,i,t,ENTER" to exit the shell. Once the specified
application is terminated by the user-specified string, the above string will
complete the graceful termination process. This string sends the command exit
and then enter which are
the commands to terminate a session. You must be sure that the user defined termination
string does indeed terminate the application before sending the "e,x,i,t,ENTER" string otherwise
unintended characters will be sent to the application.
Example
- Graceful termination: Amortization program - link failure.
We will continue to use
the amortization program from the previous example. However, we will assume
that a standard menu exists for the application. A File menu item exists
that is invoked by alt-f. The list of items in the File menu list
includes s for saving the work and alt-f for opening the file menu
list again and then x for exiting the application. Next follows the
",e,x,i,t,ENTER" to gracefully close the shell.
Step 1. Create batch file
c_start.bat
Step 2. Add this line
to c_start.bat
d:\amor\amortize.exe
Step 3. Add this line to
c_start.bat (note: there are no spaces in following the "=")
SET
LRA_TERMINATION=alt-f,s,sleep5,alt-f,x,e,x,i,t,ENTER
Step 4. Save file and
exit.
Now when the User ID
"bill" connects to the Windows
system via SSH2/Telnet the application amortize.exe will automatically be
executed. If the session is terminated due to system timeouts the termination
string alt-f,s,sleep5,alt-f,x will cause the following sequence of events
to occur.
First Alt-f to
be sent to the application (This opens the file menu).
Second s is sent
to the application (for saving the file).
Third, the Sleep5 causes
5-second pause to allow the application time to save the files,
Fourth alt-f to open
the file menu list again,
Fifth an x is sent
to the application to exit.
Finally,
",e,x,i,t,ENTER" is send to the shell which terminates the session.
Other examples of
termination string definitions are:
SET LRA_TERMINATION=alt-f,x,e,x,i,t,ENTER
SET LRA_TERMINATION=F2,alf-f,x,e,x,i,t,ENTER
SET LRA_TERMINATION=ESC,ENTER,e,x,i,t,ENTER
Termination
Scripts
Termination scripting
is analogous to the Logon Scripting except it is executed when the SSH2/Telnet
session is terminated. The commands within the file cleanup.bat are invoked upon termination of a SSH2/Telnet session. This is invoked with both normal and abnormal terminations. Cleanup
scripting is available on both a global and per user basis as with Logon Scripting.
NOTE: No
applications that require user input are allowed in the cleanup scripts.
It is especially useful
for properly un-mapping network connections such as drives. If you do not
un-map drives when terminating the session, you may be unable to connect to
them the next time you logon. The cleanup.bat file allows automatic un-mapping
of drives upon termination of the telnet session.
Example
- Termination
Script: Cleanup.bat file unmapping the “f” network drive
The system administrator
has setup user “Adam’s” logon script to map drive “f” as a network drive. In user “Adam’s” cleanup.bat
script the system administrator will un-map the drive when the session is
terminated.
Step 1. Create
directory
c:\gs_uts\scripts\Adam
Step 2. Create batch
file cleanup.bat
Step 3. Add the
following line.
net use f: /d
Step 4. Save file and
exit.
This will un-map the f
drive after the session is terminated.
NOTE: Please see the
section on logon scripting to determine the location for the cleanup script
files. (Page 218)
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Failure Detection/Recovery see page 416
Or use
legacy style below
|
You have the capability
to specify that all child processes started in the session will be terminated
when the session ends. Terminating child processes upon a session ending is the
desired behavior. However, scenarios do exist where you want the session to
terminate but you would like spawned child processes to continue. In either
case Graceful Termination is attempted first. This feature is not available in Windows
NT because the necessary operating system infrastructure did not exist until
Windows 2000 and later (Windows XP/VISTA/7/8/10/2000/2003/2008/R2/2012/2016/2019).
The environment
variable for controlling the termination of child processes for a session is:
gwtn_job_control
For example, to select
automatic termination of all child processes you would enter:
set gwtn_job_control=y
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
And to disable
automatic termination of all child processes started in the session you would
enter:
set gwtn_job_control=n
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
The default setting is
enabled.
Legacy Pack
The Georgia SoftWorks
UTS Server for Windows provides full support for DOS Legacy applications. When
you run DOS legacy applications using the GSW UTS it is as if you are running them
locally. We support DOS Character Mode Color graphics including the line and box
characters.
With our client you can
use the MOUSE just as you do locally. This was another feature pioneered
by Georgia SoftWorks. The function keys and special characters also work and display
as expected.
|
Legacy Pack
|
Configurable
|
Georgia
SoftWorks Clients
|
3rd
Party Client
|
|
Mouse
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes**
|
|
DOS Character Mode Color Graphics
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
Yes*
|
|
Function Keys
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes*
|
|
Special Characters
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes*
|
|
Screen Sizes other than 25 x
80
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes*
|
|
Alt key support for all
emulations
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Control-C Configuration
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes*
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 39 - Legacy Pack
*
As supported by the Terminal emulation mode
** If supported by the third-party client
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool - Emulations Summary (page 381 )
Or
use legacy style below
|
When using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Windows Clients the Mouse works as if you are sitting locally at the server. No
configuration is required.
The GSW also provides mouse support when using GSW
ConnectBot client for Android and other 3rd party ssh/telnet clients
that support mouse operation, e.g. PuTTY.
See page 177 to learn more about mouse operation with 3rd
party clients.
DOS Character Mode Color Graphics is fully supported.
This includes the full range of DOS Character mode Colors. All of the 256
possible background/foreground color combinations are supported.
The
function keys work as expected. With the Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal
Server for Windows the function keys operate as if you are sitting at
the server and running the application locally. For 3rd Party clients the
function keys are supported as per the emulation specified. Please note that
some function keys are not supported by various emulations.
All characters with character codes between 0x00 through
0xFF are supported and displayed properly when using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Clients and conforming third party client emulations.
You
may place the Mode command (as described
on page 298) in a logon script to
set screen sizes. Please note that most UNIX Telnet/SSH client’s default to 24 rows
while Windows and DOS applications default to 25 rows. Thus you may
have to adjust your UNIX SSH2/Telnet client row count settings to see all the rows of your
Windows or DOS application. Alternatively, you may need issue the mode con: lines=24 command. Note: if you
issue this command you will not see the last row of your application.
Alt keys are completely
supported. For 3rd party client Alt key operations see page 172.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Control-C see page 410
Or
use legacy style below
|
There are different expectations
as to the function of the behavior when <control-c> is depressed. The
Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server allows configuration of the
behavior for <control-c> by setting an environment variable in a logon
script.
The environment variable
for the <control-c> behavior is:
gwtn_ctrl_c_mode
The modes of control-c
behavior are:
·
key – <control-c> will be sent to the application as
a character value of decimal 3
·
event – <control-c> will be sent to the application
as a signal/event which can be trapped.
·
auto – The SSH2/Telnet
Server will attempt to get the application’s <control-c> settings and
send either event or key, whichever appears to be appropriate.
Sometimes the SSH2/Telnet server will make the wrong choice and you will have
to override with an explicit setting. This is the default setting
when the gwtn_ctrl_c_mode is not set.
For example, to select Event
Mode <control-c> behavior you would enter:
set gwtn_ctrl_c_mode=event
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_ctrl_c_mode=event is correct
set gwtn_ctrl_c_mode = event is not correct
Emulation
Pack
When using 3rd
party clients, comprehensive terminal emulations are a must. Not just offering
a wide range of terminal emulations but they are also correctly implemented!
|
Emulation Pack
|
Configurable
|
Georgia SoftWorks
Client
|
3rd
Party Client
|
|
SCO Console
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
DEC VT100/220/320/420
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
Wyse 50, Wyse 60
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
AT386
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
IBM 3101, IBM 3151
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
AlphaCom
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
PDCurses for VT-220/320/420
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes*
|
|
Perfect PC
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table
40 - Emulation Pack
*
As supported by the terminal emulation mode
3rd Party Clients
The Georgia SoftWorks
UTS for Windows will work with any RFC 854/SSH compliant 3rd party client.
Please see the vendor's instructions for configuration of the 3rd party client.
The procedure for connecting
with a 3rd party client is similar to connecting with the Georgia SoftWorks
client (see page 73).
Terminal Emulation
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Emulations - Terminal Emulations see
page 409
Or
use legacy style below
|
Upon connecting with a
3rd party client, you will be prompted to select a terminal emulation mode. Choose
the desired emulation by selecting the appropriate number. Be sure to set
the 3rd party client emulation mode to the same emulation as the one selected
on the server. The terminal emulation options available are:
|
·
DEC VT-100
·
DEC VT-220/320/420
·
SCO Console
·
AT386
·
Wyse 50
·
Wyse 60
|
·
IBM 3101
·
IBM 3151
·
AlphaCom - This is chosen when using the AlphaCommunicator
Telnet Client.
·
PDCurses for VT-220/320/420
|
Enter 0 for DEC VT-100 emulation, 1 for DEC VT-220/320/420, 2 for
SCO Console emulation, 3 for AT386, 4 for Wyse 50, 5 for Wyse 60, 6 for IBM 3101,
7 for IBM 3151, 8 for AlphaCom emulation, 9 for PDCurses for VT-220/320/420
If you do not want to
be prompted for the emulation mode each time you log on using a 3rd
party client then you may set an environment variable on a per user basis using
Logon Scripting (described later in the User’s Guide – Page 218).
The environment variable
for the terminal emulation is:
gwtn_term
For example, to select
SCO Console emulation you would enter:
set gwtn_term=2
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_term=2 is correct
set gwtn_term = 2 is not correct
Graphic
Characters
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Terminal Emulations see page 409
Or
use legacy style below
|
Third party clients do not always handle graphic characters and
commands as expected. The Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server for Windows
is flexible in providing options for handling graphic characters with 3rd
party clients. If you are unsure of which graphics mode to select then feel
free to experiment to determine the best mode for your 3rd party
client. Note that the typical progression is the order that the selections are
presented. The first works for all, the next is more specialized and so on.
Note: The graphics mode
prompts vary depending on the terminal emulation chosen.
|
Graphics Option Text
|
Description
|
|
Replace PC graphics characters with star characters:
|
This simply replaces PC graphics characters with the
"asterisk" character
|
|
Translate PC Graphics characters
|
For VT emulation's the system converts the PC Graphic Characters
to ACS and will temporally invoke Special Graphics character sets.
PC Graphics without ACS equivalents will be converted to the
"asterisk" character
|
|
SCO Console special handling
|
For SCO Console, the system will inject appropriate escape
|
|
Pass PC Graphics characters without changes
|
This will pass any characters >= 0x80 without any
changes
|
|
Pass all characters from PC Screen without changes.
|
This will pass ALL characters from the screen. Your client
software may have trouble handing ASCII values for some of the control characters
like 0x08 (backspace)
|
|
Georgia SoftWorks MSDOS Telnet Client
|
This is used when using the unsupported Georgia SoftWorks
modified CUTCU/CUTE (NCSA) utilities for MSDOS. For more details visit this
web page:
GSW - Other
Utilities
|
|
User Defined Character Translation
|
Used in conjunction with the file GS_Xchar.txt for character
translation. See page 183
|
|
Use UTF-8 encoded characters
|
All characters above and including 0x80 hex are encoded
using the UTF-8 standard. See page 251
|
|
Simplified Chinese - GB2312 (EUC)
|
Used when connecting using emulator configured to receive
and send Simplified Chinese.
|
|
Traditional Chinese - BIG5
|
Used when connecting using emulator configured to receive
and send Traditional Chinese
|
|
|
|
Table 41 - Graphics option choices.
If you do not want to
be prompted for the graphics mode each time you log on using a 3rd
party client then you may set an environment variable on a per user basis using
Logon Scripting.
The environment
variable for the graphics mode is:
gwtn_graphics
The value for the
environment variable will be the enumerated number associated with the graphics
option when prompted. For example, in the screen shot below the graphic options
are listed with enumerated values ranging from 0 to 8.
Figure 104: Select graphics
option for 3rd party client.
For example, to select star
graphics character substitution you would enter:
set gwtn_graphics=0
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables. For example, when setting the
environment variable to select “Pass PC Graphics characters without changes”
you would use the following syntax.
set gwtn_graphics=2 is correct
set gwtn_graphics = 2 is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Emulations - Terminal Emulations see page
409
Or
use legacy style below
|
Many times, programs
are developed to work with monochrome monitors or terminals. In this situation
you can choose between a color and monochrome presentation. After the graphics
mode options are presented the color or monochrome options are presented. The
prompt
Do you want ANSI
Colors? [Y/N]:
If you want a Color
presentation choose "Y". If you want a Monochrome presentation choose
"N".
If you do not want to be
prompted for the Color or Monochrome presentation each time you log on using a
3rd party client then you may set an environment variable on a per
user basis using Logon Scripting (Page 218). The environment variable for the Color
or Monochrome presentation is:
gwtn_color
For example, to select
a color presentation you would enter:
set gwtn_color=1
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
And to select a monochrome
presentation you would enter:
set gwtn_color=0
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations see page 389
Or
use legacy style below
|
If the monochrome mode
is selected, the color mapping is performed as described below. For each character
on the screen:
If background
intensity is set then the blink attribute is set.
If foreground
intensity is set then the bold attribute is set.
If the
character is blue then the underscore attribute is set.
If background intensity is greater than foreground
intensity then the inverse attribute is set as follows:
I
= .3 * R + .6 * G + .1B
The
intensity bit is not used in the above calculation. The attributes are
additive.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations see page 389
Or
use legacy style below
|
Certain color combinations displayed by the application
do not display in a satisfactory way when converted to monochrome. This may be
especially true when using monochrome RF devices. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server provides a mechanism to allow custom color mapping to monochrome
displays.
The SSH2/Telnet Server upon startup reads the file
“colormap.txt”. This file defines the color to monochrome mappings. The text file
contains 256 rows that represent all foreground and background color combinations
and associated default monochrome mappings.
You may edit the file and alter the monochrome mappings
to obtain the desired effects. You can then experiment to get the exact
mappings desired. The format of the text file follows.
Legend: I: Intensity R: Red, G:
Green, B: Blue
#Foreground Background Your monochrome(re)mapping
#I R G B I R G B BLINK INT UND INV
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
… and so forth for all 256 possible mappings ….
#Foreground Background Your (re)mapping
#I R G B I R G B BLINK INT UND INV
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0
The first and last 16 table entries are pictured above.
Please see the file colormap.txt to see all 256-table entries.
Alt Keys
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations – Character Emulation - see
page 382
Or use
legacy style below
|
Many applications take
advantage of the "Alt" key. However, many keyboards and terminal
emulations do not support the "Alt" key. The Georgia SoftWorks
Universal Terminal Server for Windows allows the "Alt" key sequence to
be transmitted to an application by providing a substitute key sequence (the
Alt Prefix) for the "Alt" key. The default Alt Prefix is
"Ctrl-b".
For example, in order
to transmit "Alt-f” you will
type:
Ctrl-b and then f.
(Depress
Ctrl then b, release the keys and then depress f).
In order to really type
in the AltPrefix character from the keyboard you will have to type it twice,
like Ctrl-b Ctrl-b to get the Ctrl-b.
A different Alt Prefix
can be configured using "AltPrefix" parameter in the registry editor.
The default value is set to two 0x02 which is the ASCII value of Ctrl-b, other values are as follows:
|
AltPrefix
Value
|
Key Sequence
entered by User
|
|
0x01
|
Ctrl-a
|
|
0x02
|
Ctrl-b
|
|
0x04
|
Ctrl-d
|
|
0x06
|
Ctrl-f
|
|
0x0e
|
Ctrl-n
|
|
0x0f
|
Ctrl-o
|
|
0x10
|
Ctrl-p
|
|
0x12
|
Ctrl-r
|
|
0x14
|
Ctrl-t
|
|
0x15
|
Ctrl-u
|
|
0x16
|
Ctrl-v
|
|
0x17
|
Ctrl-w
|
|
0x19
|
Ctrl-y
|
Table 42
- Alt Prefix values
This
is how to change the registry key for the AltPrefix.
Note: You must be on the
Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks UTS for Windows is installed. However,
you may connect to the Windows Registry from a remote location.
The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AltPrefix
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AltPrefix
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the AltPrefix
and click OK
The new AltPrefix will
take effect for all new sessions.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations – Character Emulation –
page 382
Or
use legacy style below
|
Third party clients will
send escape sequences on certain occasions. For example, when a function
or arrow key is depressed a sequence of data is transmitted that starts with the
escape character (0x1b). When
the escape character is received, the server must determine if this escape is
part of an escape sequence or simply an escape key. The server uses the ESC
Delay value to determine how long to wait for the next character after an
escape is received to consider it part of an escape sequence. If a character is
not received within this time then the escape is considered to be an escape
key, otherwise it is the start of an escape sequence.
The default value is 5 (500ms).
You may want to increase this value if you see that escape sequences are not
going through and being displayed on the screen rather than being interpreted. For
example, if you type F10 and see odd character starting with "]" or "[".
This is most likely to happen with terminal servers or other slow links like
RAS.
This is how to change the
registry key for the Escape Delay.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks UTS for Windows is installed.
However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ESCDelay
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ESCDelay
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the ESCDelay and click OK
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations - Character Emulation –
Negotiate Windows Size - see page 384
Or
use legacy style below
|
Enable Negotiate About Window
Size (NAWS) telnet option for 3rd party clients.
This registry parameter
EnableNAWS allows the NAWS option
to be enabled.
Default Value is 0 which disables
the NAWS option.
NOTE: This is a change from previous behavior when
NAWS was always on since Version 6.50.0035 of February 10, 2005. The change is
because some of the 3rd party telnet clients handle NAWS incorrectly
and cause endless looping.
The registry value is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableNAWS
Set this value to 1 to enable
NAWS option. The change of this value takes effect for the next session
connected.
NOTE:
The GSW SSH/Telnet clients handle window size automatically regardless of the
parameter value.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool - Emulations Summary (page 381 )
Or
use legacy style below
|
This feature is
available to work with GSW ConnectBot – SSH/Telnet client for Android.
When enabled, a number
of environment variables can be accessed by the application to obtain device and
client information. The device and client information can be used by the
application in any manner deemed useful. The uses range from reports to application
logic decisions based on device specific specifications such as display density
etc. This setting is configurable on a Global or User basis.
See how to use the GSW
Configuration GUI to enable Device and Client information. (See page 385
).
To manually enable 3rd
party mouse support, set the following environment variable in the user’s logon
script.
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_strings
Possible values are 'Y'
or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable 3rd
party Device and Client information strings
N – Disable 3rd
party Device and Client information strings (default)
For example, to enable support for 3rd party Device and Client information strings put the
following
set gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_string=Y
in the Logon Script. This can be done on a global or per
user basis.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting
environment variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_string=Y is correct
set
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_string = Y is
not correct
When enabled a variable
will be added to the users Logon Script as follows:
set gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_strings=y
The list of variables
enabled a variable will be added to the users Logon Script. The number of
variables provided is device dependent.
To find the list of
available variables you can use the command “set
gwtncl_” from within an SSH or Telnet session. See the example below.
Example output:
gwtncl_clnt_side_ip=192.168.1.205
gwtncl_device=sr6755_65u_m
gwtncl_display=MRA58K
dev-keys
gwtncl_display_density=xhdpi
gwtncl_display_dimensions=1280x720
gwtncl_error=0
gwtncl_gswcb_build_type=release
gwtncl_gswcb_version=2.4.1
gwtncl_host=android-build3
gwtncl_id=MRA58K
gwtncl_mac=E4-FB-8F-07-00-61
gwtncl_manufacturer=Mobiwire
gwtncl_model=RS50
gwtncl_product=full_sr6755_65u_m
gwtncl_serial=FD117A0014615
gwtncl_version=23
gwtncl_version_codename=REL
gwtncl_version_release=6.0
gwtncl_version_security_patch=2017-08-05
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool - Emulations Summary (page 381 )
Or
use legacy style below
|
Default: Enabled
The GSW UTS sends Screen Size information to 3rd
party clients.
Note: Supported by modern emulation clients, for example
GSW ConnectBot or PuTTY. Older clients will silently ignore this option.
The number of rows and columns used by the server and the client must be the
same or a severe misoperation may occur. This parameter ensures the number of rows
and columns used in the server-side session is passed to the 3rd
party client software automatically. This includes changes to the number of rows
and columns made dynamically by your logon script or application. This
parameter normally should be enabled.
See how to use the GSW Configuration GUI to enable global
Send Screen Size to 3rd Party Client by going to page 387
NOTE: The setting of
this environment variable OVERRIDES what is specified in the Configuration
GUI. This provides better granularity with respect to each client.
Possible values are 'Y'
or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable 3rd
party send screen size support (default)
N – Disable 3rd
party send screen size support
For example, to enable support for 3rd party send
screen size support put:
set gwtn_enable_send_screen_size_to_3rd_party=Y
in the Logon Script. This can be done on a global or per user
basis.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting
environment variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_enable_send_screen_size_to_3rd_party=Y is correct
set
gwtn_enable_send_screen_size_to_3rd_party
= Y is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool - Emulations Summary (page 381 )
Or
use legacy style below
|
Pseudoconsole support is a very powerful feature and brings many
of the capabilities presented by Microsoft in so called Windows Terminal to SSH
and Telnet. Microsoft is very enthusiastic about Windows Terminal (https://github.com/microsoft/terminal) but at the
time of this writing we have to treat our Pseudoconsole support as experimental
for the following reasons
1. Microsoft’s executable called conhost.exe located in the
System32 folder is fundamental to the correct operation of our Pseudoconsole
support but unfortunately, even with latest Windows Service Packs, it’s version
very seriously lags behind the version deployed with Windows Terminal and called
OpenConsole.exe. The conhost executable located in the System32 is
automatically used by the Command Prompt and consequently by SSH and Telnet.
For our development and testing we renamed OpenConsole.exe (from the Windows
Terminal folder) to conhost.exe and replaced existing conhost.exe in the
System32 folder. This procedure is neither recommended nor supported by
Microsoft.
2. Microsoft Windows Terminal download is supported only under
Windows 10 and no Windows Servers are officially supported. For our testing on Windows
2019 we replaced the conhost executable in the System32 folder of Windows 2019
and achieved correct operation.
3. Microsoft Windows Terminal is a fairly new product with
changing behavior/features. We may be unable to timely address potential future
problems without Microsoft’s help.
Default is disabled
Enables new console
features that are available in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019 also known as
Conhost V2. These new capabilities include support for 24-bit color, reverse video,
bold text, underscored text and applications sending (Unix style) escape
sequences to directly manipulate the screen. Please see Microsoft Windows
Terminal documentation for more details. Please make sure that this option is
disabled on Windows machines that do not support Pseudoconsole.
See how to use the GSW Configuration
GUI to enable Pseudoconsole global support by going to page 388
NOTE: This logon script
variable overrides the global setting found in the ‘Global per system” area.
To manually enable Pseudoconsole
support, set the following environment variable in the user’s logon script.
gwtn_enable_pseudoconsole
Possible values are 'Y'
or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable Pseudoconsole
support
N – Disable Pseudoconsole
support (default)
For example, to enable Pseudoconsole support put:
set gwtn_enable_pseudoconsole=Y
in the Logon Script. This can be done on a global or per user
basis.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting environment
variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_enable_pseudoconsole=Y is correct
set
gwtn_enable_pseudoconsole = Y is
not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool - Emulations Summary (page 381 )
Or
use legacy style below
|
The GSW UTS also provides mouse support when using GSW
ConnectBot client for Android and other 3rd party ssh/telnet clients
that support mouse operation, e.g. PuTTY.
When enabled, users using
a touchscreen/mouse capable device will be able to select and use the features
of the mouse enabled application as expected. In the case of touch screens,
touch events will be translated to mouse events. This setting can be configured
on a Global or per User basis. The per User basis can be used to easily handle
a mix of clients where some of them support mouse and others do not.
See how to use the GSW Configuration
GUI to enable 3rd Party Mouse support by going to page 388
To manually enable 3rd
party mouse support, set the following environment variable in the user’s logon
script.
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_mouse
Possible values are 'Y'
or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable 3rd
party client mouse support
N – Disable 3rd
party client mouse support (default)
For example, to enable support for 3rd party mouse
support put:
set gwtn_enable_3rd_party_mouse=Y
in the Logon Script. This can be done on a global or per user
basis.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting environment
variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_mouse=Y is correct
set
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_mouse = Y is
not correct
Please see the section 3rd Party Client - Default Domain Override on page 283 for further information.
This feature allows you
to re-map (or change) the colors the user will see when using the Georgia
SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server. Modify your application colors so they
are easy to read on a gray scale device without any source code changes. Also,
re-map your application colors to fit a customer’s look and feel without source
changes.
A text file is used for
specifying the colors to re-map. The name of the file is gs_color.txt and is installed in the
GSW UTS root directory. If you want different color mappings on a ‘per user’
basis then place the gs_color.txt file in the user’s directory in the Scripts
folder (see Logon Scripting on page 218). The first column lists the original
attribute bytes and the second column lists translated attributes. Attributes
not included in this file are left un-translated. The ‘#’ character in the first
column designates a comment line.
|
Attribute
|
Attribute Bit Value
|
Description
|
|
FOREGROUND_BLUE
|
0x0001
|
Text Color contains blue
|
|
FOREGROUND_GREEN
|
0x0002
|
Text Color contains green
|
|
FOREGROUND_RED
|
0x0004
|
Text Color contains red.
|
|
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY
|
0x0008
|
Text Color is intensified.
|
|
BACKGROUND_BLUE
|
0x0010
|
Background color contains
blue.
|
|
BACKGROUND_GREEN
|
0x0020
|
Background color contains
green.
|
|
BACKGROUND_RED
|
0x0040
|
Background color contains
red
|
|
BACKGROUND_INTENSITY
|
0x0080
|
Background color is
intensified.
|
Table 43
- Color Re-Mapping
Using the Attribute Bit Values from Table 43 we can create
all possible color codes.
|
Foreground Color Value
|
Description
|
|
Background Color Value
|
Description
|
|
00
|
Black
foreground
|
|
00
|
Black
background
|
|
01
|
Blue foreground
|
|
10
|
Blue background
|
|
02
|
Green
foreground
|
|
20
|
Green
background
|
|
03
|
Cyan
foreground
|
|
30
|
Cyan
background
|
|
04
|
Red
foreground
|
|
40
|
Red
background
|
|
05
|
Magenta
foreground
|
|
50
|
Magenta
background
|
|
06
|
Brown
foreground
|
|
60
|
Brown
background
|
|
07
|
White
foreground
|
|
70
|
White
background
|
|
08
|
Gray
foreground
|
|
80
|
Gray
background
|
|
09
|
Bright
blue foreground
|
|
90
|
Bright
blue background
|
|
0A
|
Bright
green foreground
|
|
A0
|
Bright
green background
|
|
0B
|
Bright
cyan foreground
|
|
B0
|
Bright
cyan background
|
|
0C
|
Bright
red foreground
|
|
C0
|
Bright
red background
|
|
0D
|
Bright
magenta foreground
|
|
D0
|
Bright
magenta background
|
|
0E
|
Yellow
foreground
|
|
E0
|
Yellow
background
|
|
0F
|
Bright
white foreground
|
|
F0
|
Bright
white background
|
Table 44 - All Possible Color Codes
Attribute
values are created by adding the foreground value to the background
value.
For
example: 93 means cyan text on bright blue background.
Example - COLOR translation table
entries:
Example
1: Change white on blue characters to red on white use this entry:
17
74
Example
2: To change white on black characters to bright white on black use this
entry.
07 0F
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Automatic Logon - see page 368
Or
use legacy style below
|
This feature allows you
to pre-configure a list of IP addresses that will be able to connect and log on
without any User ID, Password or Domain prompting when using 3rd
Party Clients.
AutoLogon is useful in
many situations; however the real power of this feature is realized when
coupled with the Session Saver (page 149) and/or used with RF Data collection devices
for fast and easy connection establishment. For example, when a connection is broken
due to a link failure you can reconnect without the time consuming UserID,
Password and Domain prompts and resume work exactly where you left off before the
link failure.
Please see page 111
for details on Automatic Logon and page 113 Automatic Logon with 3rd
Party Clients.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations see page 391
Or
use legacy style below
|
You may have a special
situation or advanced application where it would be useful to translate
characters sent to the terminal to a different character or string of
characters. Normally you do not need to get familiar with this section however
the capability is present for advanced requirements.
This feature allows you
to translate (or replace) the characters the user will see on 3rd
Party Clients and RF Terminals when using the Georgia SoftWorks Universal
Terminal Server. You may translate a single character to one or more
(up to 10 characters) other characters.
A text file is used for
specifying the characters to translate. The name of the global file is gs_xchar.txt and is installed in the SSH2/Telnet
server’s root directory. Each row in the file specifies a character to translate
and the replacement character(s). Characters not included in the file are left
un-translated. The specifications of the characters are byte values in
hexadecimal each separated by a single space. The ‘#’ character in the first
column designates a comment line.
The first value in each
row specifies the character to be translated. The character or list of characters
that replace the original character follows.
For example, the following entry in the file will replace
all lower-case letter ‘a” with upper case ’A’ when sent to the terminal.
61 41
Note: Remember that hex
61 is ASCII lowercase a
and hex 41 is ASCII uppercase A
Another example: The following entry in the file will
replace the PC bottom right corner character with the string using the DEC
Special Graphics character set.
bc 0e 6a 0f
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Emulations see page 392
Or
use legacy style below
|
You may have a special
situation or advanced application where you need to send a specific terminal
initialization sequence to a 3rd party client. Normally you do not need
to get familiar with this section however the capability is present for advanced
requirements.
This feature allows you to send an additional sequence of characters
to the 3rd party client at the start of each session. You may send
one or more (up to 10 per row) initialization characters to the 3rd
party client.
A text file is used for
specifying the initialization characters to send. The name of the global file is
gs_tinit.txt and is installed in
the GSW UTS root directory. Each row in the file specifies up to ten characters
to send to the 3rd party client. The specifications of the
characters are byte values in hexadecimal each separated by a single space. The
‘#’ character in the first column designates a comment line.
Each row must start in
the first column.
For example:
1b 2e 25
will
load the Portuguese character set into G2 for vt-220 terminal.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Emulations - see page 409
Or
use legacy style below
|
Configuration of whether a backspace is performed when a
delete key is used is done with the gwtn_backspace_on_delete
environment variable in your logon script (page 218).
The default setting is ‘N’ which means that the delete key
does not perform a backspace action, which is the standard delete key in
Windows.
The environment variable for specifying if a backspace is
performed on delete is:
gwtn_backspace_on_delete
Possible values are 'Y'
or 'N', or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Perform a
backspace on delete
N – Do not
perform a backspace on delete (default)
For example, to perform a backspace on delete:
set gwtn_backspace_on_delete=Y
in the Logon Script for a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces are allowed when setting environment
variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_backspace_on_delete=Y is correct
set
gwtn_backsoace_on_delete = Y is
not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Emulations - see page 409
Or
use legacy style below
|
Characters that occupy two-character
cells in Microsoft Windows command prompt will also occupy two-character cells
in third party clients is enabled by default.
This setting is
important when working with Far East versions of Microsoft Windows.
To enable/disable you
set the gwtn_two_cells_per_uc
environment variable in your logon script (page 218).
The environment variable
for specifying (enabling/disabling) that characters which occupy two-character
cells in Microsoft Windows will also occupy two-character cells in 3rd
party clients is:
gwtn_two_cells_per_uc
Possible values are 'Y' or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable occupying two cells in 3rd party
clients (default)
N – Disable occupying two cells in 3rd party
clients
For example, to enable
you would:
set gwtn_two_cells_per_uc=Y
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_two_cells_per_uc=Y is correct
set gwtn_ two_cells_per_uc = Y is not correct
Power Features Pack
As you would expect the
most powerful and useful features are standard with the Georgia SoftWorks
UTS for Windows. Everything from True Client-Side Printing, Logon scripting,
Session Monitoring and Session Shadowing to Programmatic access to the server.
These are not marketing or sales features but useful and powerful features requested
and used by SSH2/Telnet users around the world.
|
Power Features Pack
|
Configurable
|
GSW Clients
|
3rd Party Client
|
|
Session Administrator –
-
Observe/Sort client Sessions
-
Monitor client Sessions
-
Shadow client Sessions
-
Attach to client
Sessions
-
Terminate client Sessions
-
Send / Broadcast Message to
client Session(s)
-
Details - Get info on Session
-
Launch via Command Line
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Event and Activity Logging
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Logon
Scripting
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Programmatic Access to server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
True Client-Side Printing
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
- Enhanced Method
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
- Open Method
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
- Default Method
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Client
Identity Uniqueness
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Table 45 - Power Features Pack
Included with the
Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server for Windows
is a powerful administrative, development and training tool - the Session
Administrator. The session administrator is a standalone utility that allows
users within a certain group to perform many useful tasks associated with the active
SSH2/Telnet sessions on their system. You may Observe, Monitor, Shadow, Attach
and Terminate other SSH2/Telnet sessions. Observe the connection state, the Team
Services State, logon time. Etc.
Monitoring and Shadowing
are features pioneered by Georgia SoftWorks for SSH and Telnet Servers. With Monitoring
you can connect to existing SSH2/Telnet
sessions and observe the screen exactly as the client sees the screen. You may Shadow as session in the event you need interactive
input capabilities with that session. You may use this utility as a local Windows
user or as a user connected via SSH2/Telnet
.
To use the GS Administrator a user must belong to the local group Gwtn Monitors. The system administrator must
first create the group Gwtn Monitors. Next all users allowed to use the
Session Administrator must be added to the group. Windows does
not instantaneously update the group membership after the user manager is closed.
Windows will update the group memberships if you logoff/logon the desktop. In the
event that this does not work you may have to restart the Windows
server after creating the group and adding users.
The standard Windows
graphical User Management tools can be used to create the local group Gwtn
Monitors and add users to the group. Tools to perform these actions are also
available from the command line and you may find that they are faster and easier
to use.
To
add the group from the command line please log on as an administrator,
open a Command Prompt window on the server and run the following command:
net
localgroup "Gwtn Monitors” /ADD
To add a
user to the group, run the following command:
net
localgroup "Gwtn Monitors” username /ADD
(username parameter must be replaced
with the actual name of the user who will be allowed to run the GSW Session Administrator)
You
need to restart the server after this command completes successfully.
To find out who is allowed to run the GSW Session Administrator use the command:
net
localgroup "Gwtn Monitors"
The command
will provide the listing of the members of 'Gwtn Monitors'.
The name of the session
administrator utility is gs_admin.exe and resides in the UTS
installation directory. The Georgia
SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server program group has an entry to start the
Session Administrator. It may also be started from the command line locally or
via SSH2/Telnet.
When the session administrator
is executed a window is opened that dynamically displays all SSH2/Telnet sessions. For each session the Logon Id, the Logon time, the Process ID, the Monitor
ID, the IP address and the Connection State are displayed. The menu bar contains
the items File and Sessions. The bottom right corner of the Session
Administrator displays the number of SSH2/Telnet
Sessions that are currently active.
For each SSH2/Telnet
session the following information is displayed:
User
Name - Login ID of the Windows user
Logon Time
- Date and time the user logged on to the system via SSH2/Telnet.
Process
ID - Process ID assigned to the SSH2/Telnet
Session
Monitor ID - Process ID of the GS_Admin that is
monitoring the session. This indicates that this session is being monitored or
shadowed.
IP Address
- IP address of the computer where the client is located.
State
- Connection State of the SSH2/Telnet
session.
Defined States are:
Logon
- A User is in the process of logging in via SSH2/Telnet.
Conn - SSH2/Telnet session is Connected
Disc - A User is disconnecting
NoRsp - The Application has not responded to the data in its
input queue
Susp - A SSH2/Telnet Session is Suspended. That means the Session
Reconnect (page 149) feature is
enabled and the client or link has failed leaving the session Suspended. A Suspended
session can be reconnected to via the Auto-Reconnect feature or via the Attach
feature of the Session Administrator. A Suspended session can be terminated via
the Terminate feature of the Session Administrator or when the gwtn_reconnect_timeout
timer expires.
TeamS
- The GSW Team Services state.
Observing SSH2/Telnet
Sessions
Using the Session
Administrator allows observation of all telnet sessions on the SSH2/Telnet Server. Relevant information is displayed in an easy to read format.
Figure 105: GSW Session Administrator
- Observing Telnet Sessions
The
initial display is sorted by the Logon Time for each session (Note the
Arrow adjacent to the Logon Time heading). The session that has been logged on
the longest is displayed first and the most recent is displayed last. The
display may be sorted by User Name, Logon Time, Process ID, IP Address or
State. You can use the View menu item to select the column to sort on,
or you may click on the column heading.
Figure 106: GSW Admin - Menu
Sort Options
You
may also reverse the sort by re-checking the User Name menu item or by clicking
the column heading again. Click the heading to toggle between the ascending and
descending sort order. Again, note the arrow beside the column heading to
indicate the sort order.
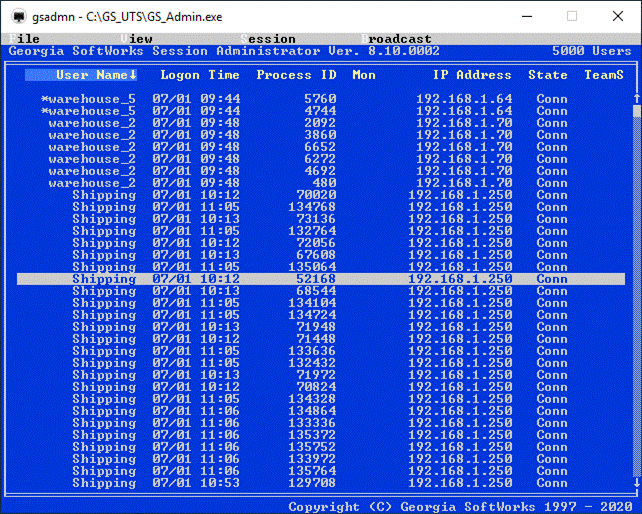
Figure 107: Session Administrator
- Descending Sort Order
Monitoring SSH2/Telnet Sessions
Session Monitoring is the
method used to locally observe the display on a remote SSH2/Telnet session. As the data displayed on the remote SSH2/Telnet
client, an exact copy is sent to the Session Monitor too. The display is exactly
the same as the display being presented to the remote session. Session Monitoring
is transparent to the client being monitored and does not impact their performance.
To select a SSH2/Telnet session to monitor first highlight the session to monitor. This is accomplished
either by moving the up/down arrow keys or clicking on the particular session.
Once selected either depress <ENTER> or click the menu item Session
(see Figure 108) to display the drop-down item Monitor. You may now
select Monitor.
You are now connected to
the other telnet session, observing the screen activity exactly is appears to
the other user. You may monitor only. No input is allowed to the other session.
To end monitoring the other telnet/SSH session depress <ESC>. You are returned
to the Session Administrator Screen.
Notice that the
graphics, the colors, the lines, checks and boxes are all displayed correctly.
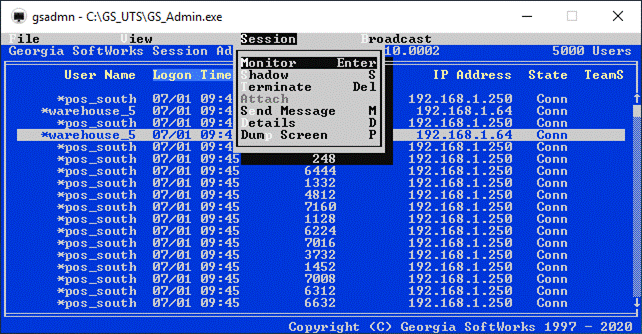
Figure 108: Session Administrator - Select Session to Monitor
If User John was using
Norton Command and his screen was displaying the following:
Figure 109: Session Administrator:
Client Session
Then the monitor screen
would look as follows:

Figure 110: Session Administrator
Monitor Session
Yes, the screen
displays look exactly the same and that is the way it is supposed to work. The
Monitor’s screen displays the screen activity exactly as it appears on the session
being monitored!
Shadowing SSH/Telnet Sessions
Shadowing is similar to
Monitoring except interactive input is allowed. This means that you can
provide input to another SSH2/Telnet session. This is a powerful training and
Quality Assurance tool. A user may need assistance in using their application and
you can shadow their SSH2/Telnet session providing input where they have difficulty.
To select a SSH2/Telnet session to Shadow first highlight the desired session. This is accomplished either
by moving the up/down arrow keys or clicking on the particular session. Once selected
click the menu item Session (see Figure 108) to display the menu drop
down items. You may now select Shadow. As a shortcut you may simply
press "S".
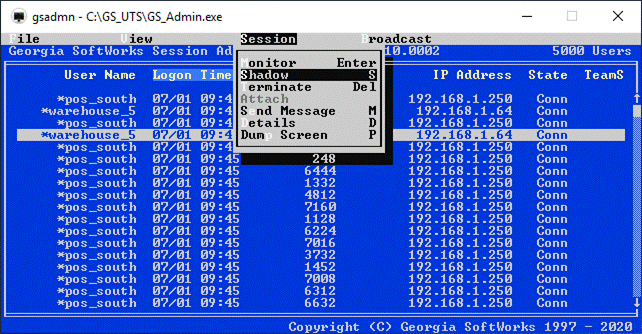
Figure 111: Session Administrator
- Shadowing
You are now connected
to the other SSH2/Telnet session, observing the screen activity exactly is
appears to the other user. Both you and the original user are now able to enter
data into the session. To end shadowing the other SSH2/Telnet session, depress <ctrl-z>.
You are returned to the Session Administrator screen.
The GSW SSH Server has
a FIPS 140-2 option available for purchase. The Session Administrator can be
used to verify that a GSW SSH FIPS 140-2 compliant client is connected to the
GSW SSH FIPS 140-2 compliant server. These connections are identified by an
asterisk “*” prepended to
the User Name in the Session Administrator as shown below.
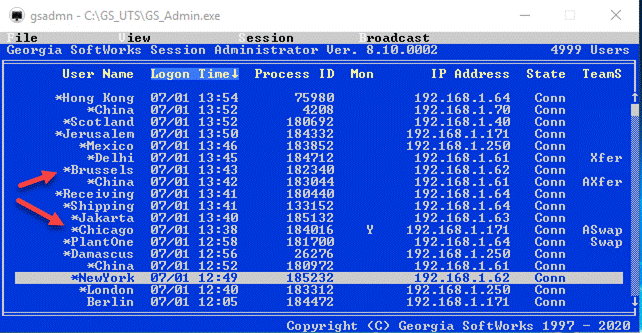
Figure 112: FIPS 140-2 compliant
connections
To select a SSH2/Telnet
session to terminate first highlight the session to terminate. This is accomplished
either by moving the up/down arrow keys or clicking on the particular session.
Once selected either depress <DEL> or click the menu item Session
to display the drop-down item Terminate. You may now select Terminate.
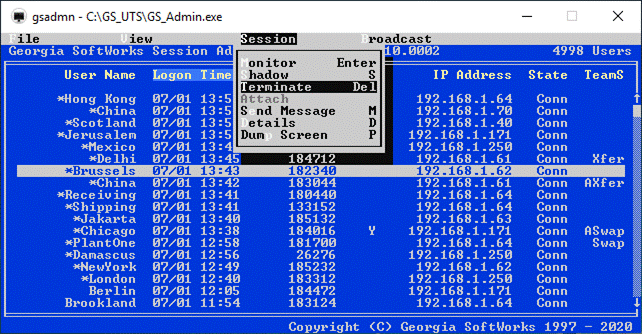
Figure 113: Session Administrator:
Terminate another session
You will be prompted to
make sure that you want to terminate the session. Graceful Termination (page 158)
will take place upon terminating the session.
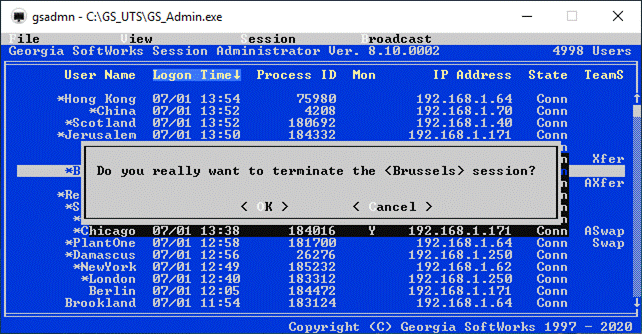
Figure 114: Session Administrator
Terminate another session verification prompt
As a member of the group
GWTN MONITORS you may need to know if there are any Suspended sessions. Suspended
Sessions are created when the Session Saver (see page 149)
feature is enabled and a client or link has failed, and the user has not yet
reconnected to their Saved session.
Using the Attach
feature of the Session Administrator tool you can Attach (or connect) to
a Suspended session and complete their work in progress. The Attach actually terminates
your current session and transfers control to you. You are now operating within
the Suspended Session. The Suspended session state changes back to “Conn” and
will no longer be suspended.
NOTE: For the
Attach to work you must be invoking the Session Administrator from a SSH2/Telnet
session.
To select a SSH2/Telnet session to Attach first highlight the desired Suspended session. This is
accomplished either by moving the up/down arrow keys or clicking on the particular
session. Once selected, open the Session drop down and select the menu item Attach.
Note: Attach
will not be available as a choice if the session selected in not in the
Suspended state or if you are not connected via a SSH2/Telnet
connection.
Select Attach. You
are now Attached to the Suspended session. You will observe the screen
exactly as the user was seeing it when their session was broken due to client
or link failure. Interactive Input capabilities are available to resume work in
progress.
When you exit the SSH2/Telnet Session, you are not returned to the Session Administrator tool, but are disconnected
just as the user of the original session would have been had they exited the SSH2/Telnet session.
The capability to send
a message to either a single or all SSH2/Telnet
sessions is available via the Session Administrator. This is useful in many
situations when the system administrator needs to communicate information to
one or all users usually regarding system status or maintenance. This saves the
system administrator time because the need to make multiple phone calls or
physically contacting the users is not necessary.
An example could be
that the system administrator would want to notify all users to be logged off
by a certain time due to system maintenance. Another example may be to send a
message to a specific user requesting that they help another user.
To send a message to
all currently active SSH2/Telnet sessions either depress <ALT-B> or click
the menu item Broadcast
to display the drop down item Send.
You may now select Send.
Figure 115:
Broadcast a message to all telnet sessions
Note: In the figure
above - even though a single session is highlighted the Broadcast message will
go to ALL SSH2/Telnet sessions.
Upon selecting the menu
item SEND you will see a
screen similar to the figure below.
Figure 116: Enter broadcast
message prompt.
Enter the text (up to a
max of 320 characters) that you would like to send to all active SSH2/Telnet
sessions.
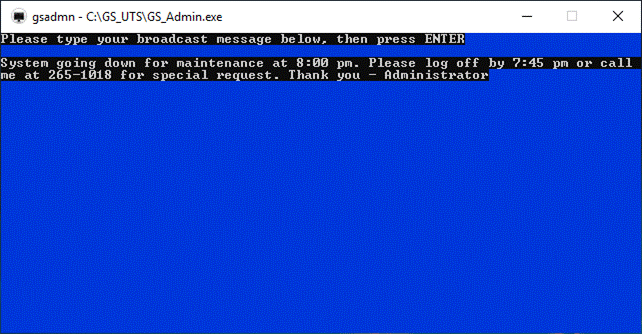
Figure 117:
Enter text of broadcast message.
Press <ENTER>
At this point you have
an opportunity to abort or confirm the sending of the broadcast message.
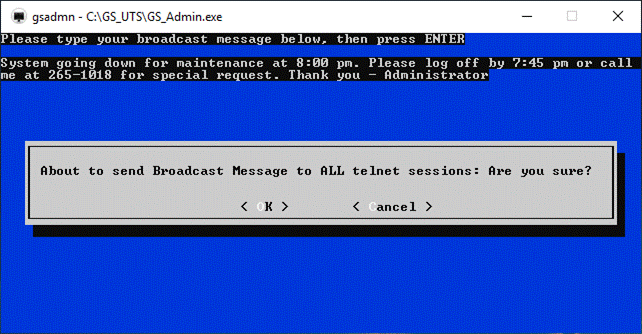
Figure 118: Send broadcast
message confirmation prompt.
Selecting <OK> will send the broadcast message
to all active SSH2/Telnet sessions. The message will
be displayed on the client terminal similar to the figure below.
(Selecting <Cancel> will
abort the broadcast message.)
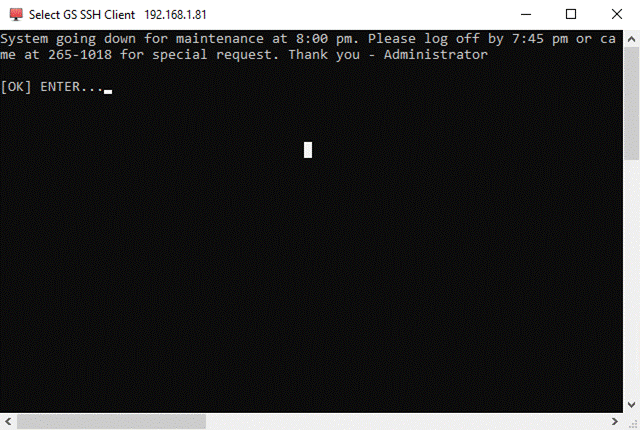
Figure 119: Broadcast message
display on client terminal.
The
exact display of the broadcast message will conform to the specific terminal
display characteristics in a typical manner. If the display has fewer columns,
then the message will wrap at the end of each row, etc.
The
broadcast message will remain on the client terminal until the message is
acknowledged. The SSH2/Telnet client terminal display will
return to the exact terminal display prior to the reception of the broadcast message
after the broadcast message is acknowledged the message by depressing
<RETURN> or <ENTER>.
If
multiple broadcast messages are sent before previous messages are acknowledged,
only the message acknowledged and the last broadcast message sent will be displayed
to that particular SSH2/Telnet client. The intermediate
messages will not be displayed to that session.
There will be times
that you will want to send a message to a specific SSH2/Telnet
session rather than to all the active SSH2/Telnet
sessions. To send a message to a single SSH2/Telnet
session you must first select the user to send the message.
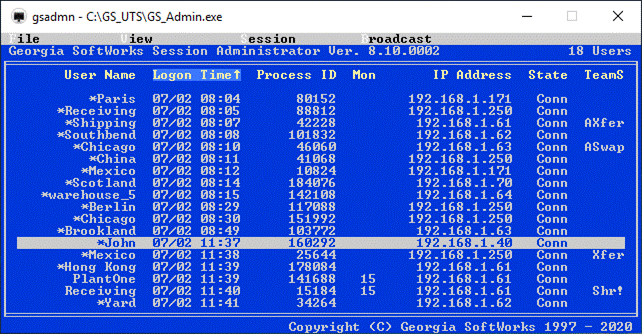
Figure 120: Select a specific
user to send a message.
In
the case above we are selecting the user name “doug” to send the broadcast
message. Once we have selected the user then we select the Session menu either
by entering <ALT-S> or clicking the menu item Session. This will display
the drop down which contains the item Send Message (See Figure
121 ).
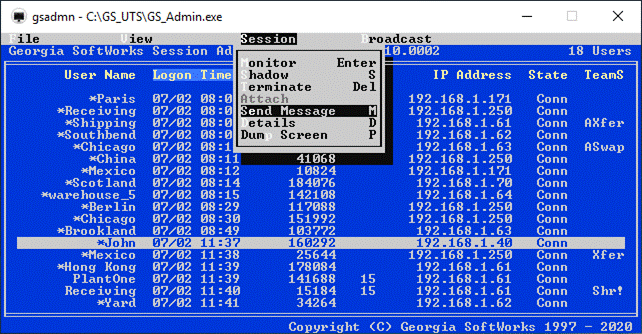
Figure 121:
Send a message to a specific user - Send Message dropdown.
 Upon
selecting Send Message you will
see a screen similar to the figure below allowing entry of the message
text. Note that the User Name (doug) of the user that will receive the
broadcast message is identified in the prompt.
Upon
selecting Send Message you will
see a screen similar to the figure below allowing entry of the message
text. Note that the User Name (doug) of the user that will receive the
broadcast message is identified in the prompt.
Figure 122: Enter broadcast message
prompt destined to a specific user.
Enter
the text that you would like to send to user doug and press enter when
the message is complete.
Figure 123: Entering the
broadcast message text to a single user.
At this point you have
an opportunity to abort or confirm the sending of the broadcast message.
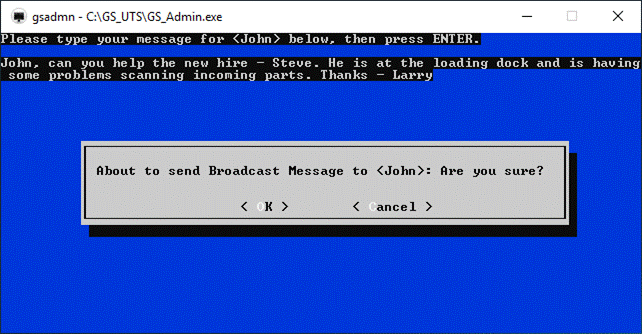
Figure 124: Send broadcast
message to a specific user confirmation prompt.
Selecting <OK> will send the broadcast message
to SSH2/Telnet user doug. Selecting <Cancel>
will abort the broadcast message. The message will be
displayed on the client terminal similar to the figure below.
You can schedule a
broadcast message using Georgia SoftWorks Broadcast command line utility and your
favorite scheduling program.
The GSW Broadcast utility
allows you to send a message to ALL active SSH2/Telnet
sessions or to a specific session. You can identify the specific SSH2/Telnet
session by User Name and/or IP Address. The text of the message that is sent is
specified in an ASCII text file.
GS_BCast [-iip_address] [-uuser_name]
file_path
Command: GS_BCast
Description: Command
line utility that Broadcasts (sends) a text message to one or all active SSH2/Telnet sessions.
Syntax: GS_BCast [-iip_address] [-uuser_name]
<file_path>
Arguments:
There are 2 optional arguments and 1 required argument.
1.
[-iip_address] The
–i parameter is followed by the IP
address corresponding to the SSH2/Telnet
session (or sessions) to send the broadcast message. (Optional)
2.
[-uuser_name] The
–u parameter is followed by the user name corresponding to the SSH2/Telnet
session (or sessions) to send the broadcast message. (Optional)
3.
<file_path> - the path to the ASCII text file that contains the broadcast
message. (Required)
If
the –i and –u arguments are omitted
then the broadcast will be sent to all active SSH2/Telnet
sessions. These arguments may be combined (as a Logical “OR” condition) to provide
more flexibility in choosing the destinations for the broadcast message.
Example – the GSW Broadcast Utility
(Schedule a Broadcast Message)
Send the
broadcast message contained in the ASCII text file “systemdown.txt:” which resides
in the directory “C:\mybroadcastmessages\systemdown.txt” to all telnet sessions.
GS_BCast C:\mybroadcastmessages\systemdown.txt
Example – the GSW Broadcast Utility
– to a Single User
Send
the broadcast message contained in the ASCII text file “givemeacall.txt:” which
resides in the directory “C:\mybroadcastmessages\givemeacall.txt” to user “doug”
GS_BCast -udoug C:\mybroadcastmessages\givemeacall.txt
The real power of the
GSW Broadcast utility is that you can use your favorite scheduling program to schedule
execution of the GSW Broadcast utility at a later time.
Georgia SoftWorks does
not support nor endorse any scheduling programs. The ones mentioned below are
listed as examples of scheduling utilities or programs that can be used to
launch the GSW Broadcast utility. Most any scheduling program can be used to
schedule the execution of the GSW Broadcast utility.
|
AT command – Native on Windows
|
|
|
The “AT” scheduling utility is available on
Windows NT/2000/XP from the command shell. The syntax of the AT command as
described in the “Help AT” on Windows XP:
The AT command schedules commands and
programs to run on a computer at
a specified time and date. The Schedule service
must be running to use
the AT command.
AT [\\computername] [ [id] [/DELETE] |
/DELETE [/YES]]
AT [\\computername] time [/INTERACTIVE]
[ /EVERY:date[,...] | /NEXT:date[,...]]
"command"
\\computername Specifies a remote
computer. Commands are scheduled on the
local computer if this
parameter is omitted.
id Is an identification number
assigned to a scheduled
command.
/delete Cancels a scheduled
command. If id is omitted, all the
scheduled commands on the
computer are canceled.
/yes Used with cancel all jobs
command when no further
confirmation is desired.
time Specifies the time when
command is to run.
/interactive Allows the job to interact
with the desktop of the user
who is logged on at the time
the job runs.
/every:date[,...] Runs the command on each
specified day(s) of the week or
month. If date is omitted,
the current day of the month
is assumed.
/next:date[,...] Runs the specified
command on the next occurrence of the
day (for example, next
Thursday). If date is omitted, the
current day of the month
is assumed.
"command" Is the Windows
NT command, or batch program to be run.
|
|
Graphical
Utility for Windows 2000
|
|
|
Windows 2000 provides a
graphical scheduling Wizard that gives you the options of scheduling tasks to
run one time only, daily, weekly, or monthly either when your computer boots up
or whenever you log on. The Wizard also gives you the option of setting a
time for the program to start. To run the Windows 2000 scheduling Wizard:
Step 1. Click on Start, Settings and then Control Panel.
Step 2. Double-click on Scheduled Tasks.
Step 3. Double-click on Add Scheduled Task to add
a new task.
Step 4. Windows 2000 will run the Scheduled Task
Wizard. The Wizard will walk you through scheduling a
program to run.
Note 1: Go to the Advanced Properties to specify the command
line arguments.
Note 2: This utility also exists on Windows XP.
The path to open the Wizard is slightly different.
|
Table 46 - GSW Broadcast Command Utility - Example Scheduling
Programs
You may exit the Session Administrator either by the File
then Exit Menu item or depressing the <ESC> key
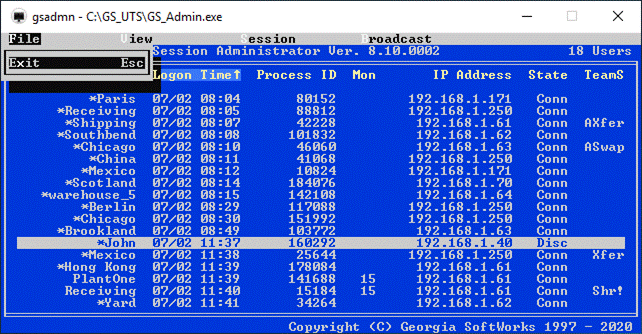
Figure 125: Session Administrator
– Exiting
Many of the Session Administrator
features are available from the command line. The features available include
Monitoring, Shadowing, and Terminating Session(s). Additionally, you can create
an ASCII text file on demand that will contain a snapshot of the information contained
on the Session Administrator main screen.
The GS_ADMIN command
line utility provides the capability to launch Session Monitoring or Session
Shadowing etc. from your own application. Command line arguments are used to specify
the operation (feature) and the session to perform the operation on.
Command: GS_ADMIN
Description:
Command line utility that performs GS_ADMIN functions.
The gs_admin command
line utility has three possible syntaxes.
Syntax 1:
GS_ADMIN [/m|/s|/t]
[/pPID]|[ [/iIP]|[/uUser] ] [/k]
Syntax 2: GS_ADMIN
[/T] [/k]
Syntax 3:
GS_ADMIN [/I[Infofilename]]
[/k]
Arguments: The
number of arguments depends on the operation selected.
/m is for monitoring
/s is for
Shadowing
/t is to terminate
a specific session
/T is to terminate
all sessions
/p select by
Process ID (PID)
/i select by
client’s IP Address
/u Select by
user’s name
/k keep
running gs_admin after completion of the operation
This argument
is valid with all 3 syntax formats.
/I is to create a snapshot of the SSH2/Telnet Status information in the file gs_ainfo.txt (default)
or specified filename.
Syntax 1 is used to Monitor,
Shadow or terminate a specific session
Syntax 2 is used to Terminate
ALL SSH2/Telnet sessions
Syntax 3 is used to
obtain a snapshot of the SSH2/Telnet server status information.
Note: Syntax
formats not listed have undetermined results.
Syntax
1 – Monitoring/Shadowing/Terminating a specific session
Choose
the operation (monitor, shadow, terminate) for the SSH2/Telnet
session.
Next
select one of the following [/pPID]|[
[/iIP]|[/uUser] ] to Filter the session.
/pPID Filter
based on Process ID (PID). Where PID is the Process Id of the desired session.
Each session will have a unique process id.
OR
/iIP Filter
based on the IP address
/uUser Filter
based on the User Name
Note: You may
use either or both of the IP Address and User Name filter arguments.
Example – the GSW GS_ADMIN Command
Line Utility – Syntax 1 - Monitor
The
following is the syntax to use the GS_ADMIN command line utility to launch the
Session Monitor for User “Doug”.
GS_ADMIN /m /uDoug
Example – the GSW GS_ADMIN Command
Line Utility – Syntax 1- SHADOW
The
following is the syntax to use the GS_ADMIN command line utility to launch the
Session Shadowing for User “david” with IP Address 10.110.244.103.
GS_ADMIN /s /udavid /i10.110.244.103
Example – the GSW GS_ADMIN Command
Line Utility – Syntax 1 - Terminate
The
following is the syntax to use the GS_ADMIN command line utility to terminate Session
with user name Doug.
GS_ADMIN /t /uDoug
Syntax
2 – Terminate All Telnet/SSH Sessions
The /T operation does not use any additional
arguments. This command terminates all SSH2/Telnet
sessions.
Example – the GSW GS_ADMIN Command Line
Utility – Syntax 2 - Terminate All Sessions
The
following is the syntax to use the GS_ADMIN command line utility to terminate
ALL SSH2/Telnet sessions.
GS_ADMIN /T
Syntax
3 – Obtain a snapshot of the SSH2/Telnet
Server Status
The /I operation
creates the file gs_ainfo.txt that contains the current status information for
the GSW SSH2/Telnet Server. The file is created
in the root GSW SSH2/Telnet Server
installation folder. The file contains similar information as displayed in the
Session Administrator main screen.
Example – the GSW GS_ADMIN Command
Line Utility – Syntax 3 – Status #1
The
following is the syntax to use the GS_ADMIN command line utility to create the
GSW SSH2/Telnet Server Status Information file.
GS_ADMIN /I
You
can also specify the filename and path for the information file.
Example – the GSW GS_ADMIN Command
Line Utility – Syntax 3 - Status #2
The
following is the syntax to use the GS_ADMIN command line utility to create the
GSW SSH2/Telnet Status information file and put it in the file folder c:\telnetstatus\time with
the filename mondaynoon.txt
GS_ADMIN /IC:\telnetstatus\time\mondaynoon.txt
Information File Layout
The file uses standard
Windows ini format rules.
[File Info]
Version=1.1
GSWTelnetServerVersion=8.09.0003
CreationTime=10/31/18 07:20:28
[Counters]
UserCount=4
[Users]
User0=HW-1,10/31/18 06:55:19,13200,0,127.0.0.1:62718,Conn,N
User1=HW-2,10/31/18 06:55:38,7660,0,127.0.0.1:62722,Conn,N
User2=HW-5,10/31/18 06:55:41,9644,12008,127.0.0.1:62723,Conn,N
User3=johnny,10/31/18 07:20:06,12300,0,192.168.1.56:0,Conn,Y
Note: User field layout meanings
Fields under [Users] are comma separated as follows:
User-name, Date Time , Client Process ID, Process ID of GS_Admin.exe if client
is being monitored or shadowed, IP-socket , state, FIPS Y/N
There are many uses for
session monitoring. A few are listed.
·
Quality Assurance - A supervisor can monitor data entry of employees.
·
Training - A senior application user can remotely help a trainee
understand and use an application.
·
Debugging - A developer can remotely observe an application phenomenon
that a user is describing.
·
Administrative - A system administrator can ensure that users are
using/setting up resources properly.
·
Security - Administrator monitor users that are using SSH2/Telnet.
·
Terminating Sessions that have been abandoned.
·
Terminating Sessions that are connected to applications which are
behaving abnormally etc.
·
Attaching to Suspended Sessions
·
Shadowing another Session
GSW
Event Logging
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server for Windows provides the System Administrator with useful SSH2/Telnet Server Activity information that can be used for generating reports. The System Administrator
can enable or disable various events that are logged. The logged information is
in an easy to import ASCII comma delimited format.
Two files are of
interest
1.
The log definition file: gsw_ldef.txt
and
2.
The actual log file gsw_elog.txt
The configuration file gsw_ldef.txt specifies the events that
are maintained in the log file. This file resides in the SSH2/Telnet server installation directory. Usually this is c:\gs_uts. Each event that can be
logged is listed together with its description.
The format of this file
is:
Event
ID <space> Group ID <space> Description of the event
The “#” character is
the comment symbol. Insert a "#" character in column 1 of a line to disable
the logging of a specific event. Enabling or
Disabling the logging of specific events are the only allowed modifications to
this file.
The Default configuration
for gsw_ldef.txt is:
1 100 Session Created
2 100 Session Suspended
3 100 Session Reconnected
4 100 Session Exited Normally
5 100 Session Exited Abnormally
6 100 Logon Failed
7 200 Print Job Redirected
8 400 File transferred (put)
9 400 Print File transferred (get)
10 500 Command execution event sent to client
If you do not want to log Print Jobs and Failed Logons you would insert
the # as the first character of those events.
1 100 Session Created
2 100 Session Suspended
3 100 Session Reconnected
4 100 Session Exited Normally
5 100 Session Exited Abnormally
#6 100 Logon Failed
#7 200 Print Job Redirected
8 400 File transferred (put)
9 400 Print File transferred (get)
10 500 Command execution event sent to client
NOTE: The event ids
and descriptions in the file cannot be changed.
The log file is a comma-delimited
text file where the activity events are actually stored. By default, the
maximum size of log file gsw_elog.txt
is 1 megabyte. Once the file has reached the maximum size the file is
renamed to gsw_elog.bak and
starts logging in a new gsw_elog.txt. This
actually provides up to 2 megabytes of log information to the administrator.
The size of the gsw_elog.txt can
be changed in the registry (See page 214).
The GSW Event Log resides
in the "Log" subdirectory of the Installation folder in a
comma-delimited file with the name gsw_elog.txt.
Georgia
SoftWorks Event Log File Name: gsw_elog.txt
The
format of the comma-delimited file is as follows.
|
Field Description
|
Data Type
|
Description
|
|
Event
ID
|
Integer
|
|
|
Event
Group ID
|
Integer
|
Useful for Filtering with
Reports
|
|
Login
Id
|
Text
|
Quoted Text Field
|
|
Domain
|
Text
|
Quoted Text Field
|
|
Session
ID
|
Text
|
Quoted Text Field
|
|
Time
Stamp
|
Date/Time
|
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
|
|
Client
Type
|
Integer
|
0 = 3rd Party, 1
= Georgia SoftWorks
|
|
Encrypted
Session
|
Integer
|
0 = Not Encrypted, 1 = Encrypted
|
|
Event
Specific Integer
|
Integer
|
|
|
Event
Specific Text
|
Text
|
Quoted
Text Field
|
|
IP
Address
|
Text
|
IP Address associated with
the event
|
Table 47 - GSW Event Log File
Format
An example of the data
in the gsw_elog.txt file may look like:
7,200,'Laura','.','1E339C27B99',2000-09-15
15:42:22,1,0,1326,’’,'192.168.1.186'
1,100,'Rebecca','.','1E439C27BCD',2000-09-15
15:43:09,1,0,0,'192.168.1.188','192.168.1.188'
6,100,'Joseph','.','5A39C27C2C',2000-09-15
15:44:52,1,0,1326,’’,'192.168.1.185'
1,100,'Anna','.','17F39C27C39',2000-09-15
15:45:03,1,0,0,’
'192.168.1.184’,'192.168.1.184'
1,100,'benjamin','.','12C39C27C66',2000-09-15
15:45:47,1,0,0,’
'192.168.1.183’,'192.168.1.183'
4,100,'John','.','1E439C27BCD',2000-09-15
15:46:07,1,0,0,’’,'192.168.1.180'
5,100,'Wally','.','12C39C27C66',2000-09-15
15:46:37,1,0,0,’’,'192.168.1.182'
1,100,'Luke','.','12C39C27C66',2000-09-15
15:46:51,1,0,0,'192.168.1.181','192.168.1.181'
2,100,'RaySpurg','.','12C39C27C66',2000-09-15
15:47:00,1,0,0,’’,'192.168.1.179'
3,100,'Doug','.','12C39C27C66',2000-09-15
15:47:12,1,0,0,’’,'192.168.1.178'
3,100,'Wanda','.','17F39C27C39',2000-09-15
15:47:20,1,0,0,’’,'192.168.1.189'
Defined Events are:
|
Event Id
|
Event Group ID
|
Name
|
|
1
|
100
|
Session Created
|
|
2
|
100
|
Session Suspended
|
|
3
|
100
|
Session Reconnected
|
|
4
|
100
|
Session Exited Normally
|
|
5
|
100
|
Session Exited Abnormally
|
|
6
|
100
|
Logon Failed
|
|
7
|
200
|
Print Job Redirected
|
|
8
|
400
|
File Transferred via
GS_PUT
|
|
9
|
400
|
File Transferred via
GS_GET
|
|
10
|
500
|
Command execution event
sent to client
|
Table 48
- Defined Log Events
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Power Features see page 380
Or
use legacy style below
|
This is how to change
the registry key for the size of the Log File. The size is specified in bytes
and the default is 1000000.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server is installed. However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ActivityLogFileLength
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ActivityLogFileLength
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the ActivityLogFileLength
and click OK
If users are already
connected the UTS service should be restarted for the new value to properly
take effect.
GSW
Session Logging
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Global Power Features – Event Logging - see page
380
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows provides a session log file that is used by GSW Technical Support
when troubleshooting is required. The file is not intended to be used by
customers and is formatted and uses special terms for engineering.
There are times when the
maximum file size may need to be adjusted due to resource or troubleshooting
reasons.
This is how to change
the registry key for the size of the Session Log File. The size is specified in
bytes and the default is 1000000.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server is installed. However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AgentLogFileLength
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AgentLogFileLength
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the AgentLogFileLength
and click OK
If
users are already connected the UTS service should be restarted for the new value
to properly take effect.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Power Features – Event Logging - see
page 415
Or use
legacy style below
|
An environment variable
is available on User - per session basis to enable brief or long format logging.
If enabled only system startup and tear down and some runtime events are logged
(such as user resizing window). Long format logging is the default.
The environment variable
for the brief or long format session logging is:
gwtn_enable_session_log
in the Logon Script.
Possible values are 'Y' or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable long format logging (default)
N – Disable long format logging
For example, to enable
long format session logging:
set gwtn_enable_session_log=Y
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
set gwtn_enable_session_log=Y is correct
set gwtn_enable_session_log = Y is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – User Power Features – Event Logging - see
page 415
Or
use legacy style below
|
An environment variable
is available on User - per session basis to enable/disable International
character translation of UTS-8, GB2312, and Big5 logging. This adds diagnostic
information to the log file gs_agnt.log and is available for diagnostic purposes
by GSW Technical support. It is disabled by default.
The environment variable
for International Character Translation logging is:
gwtn_log_char_xlat
in the Logon Script.
Possible values are 'Y' or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Enable International Character Translation Logging
N – Disable International Character Translation Logging
(Default)
For example, to enable
International Character Translation Diagnostic Data Logging:
set gwtn_log_char_xlat=Y
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces are
allowed when setting environment variables.
set gwtn_log_char_xlat=Y is correct
set gwtn_log_char_xlat = y is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – Users – per session - Logon Script - see
page 365
Or
use legacy style below
|
Logon Scripting is an
advanced feature that allows the system administrator unmatched control over the
user sessions. Associated with each User Login is a directory that will execute
batch files upon connection. Logon Scripting
provides automatic execution of the batch file upon the login of the user.
Logon scripts are often used to map drives, establish network connections,
change directories, set environment variables, run TSRs and launch applications.
When an application is launched via a logon script the User is automatically
deposited into the application upon successful logon.
One of two optional batch
files can be executed. One is named k_start.bat
and the other is c_start.bat.
Each batch file provides a unique behavior upon completion of the batch file.
·
k_start.bat - This
file runs upon connection and after its completion the user may get the system
prompt.
·
c_start.bat - This
file runs upon connection and after its completion the session terminates. This
can be used to restrict the user to a certain application. Even if the user
executes a control-c or something
similar this will not allow access other than what is specified in the batch
file on the Windows computer.
Logon Scripts can be defined
on a User, Global, or IP address basis. If a logon has IP Address based Logon
scripts defined then they are executed. Otherwise the GSW Universal Terminal Server
determines if a User ID based logon script exists. If so then it is executed.
Otherwise if a Global Logon scripts exists then it is executed.
A different Logon
script can be set up for each User Id. This allows Users to have individually
defined batch files to accommodate different requirements of Users. The batch
files are created and set up by the system administrator for each user
in the system. They must be in the directory
"InstallationPath\scripts\DomainUsers\UserLoginID or
"InstallationPath\scripts\LocalUsers\UserLoginID or
"InstallationPath\scripts\UserLoginID
Of course, InstallationPath
and UserLoginID are replaced with the actual values.
If both k_start.bat and c_start.bat exist then only c_start.bat is executed. You may call k_start.bat from c_start.bat. If the UserLogonID
script folder does not exist, then the GSW UTS will determine if a Global Logon
script exists.
The system administrator
must ensure that the directory permissions for the above files and directories
are correct. Remember the user and the SYSTEM must be able to read the batch
file. They are executed in the security context of the user.
Example
- Logon Scripting: Automatic Execution of a program upon
connection
Here is an example
script to allow automatic execution of a Physician’s Office Application
"medical.exe" upon connection for the user login id (nurse). The Physician’s
office application is in the directory c:\medical.
Step 1. Create directory
c:\gs_uts\scripts\LocalUsers\nurse
Step 2. Create batch
file k_start.bat
Step 3. Add line to
k_start.bat
c:\medical\medical.exe
Step 4. Save file and
exit.
Now when the User login
id "nurse" connects to the Windows
system via SSH2/Telnet the application medical.exe will automatically be started.
When the user exits the medical package, the Windows
Command line prompt is displayed allowing other activity to occur.
Example - Logon Scripting: User restricted to execute only a specific
program.
Here is an example script
that will allow the User login id (bill) only to execute the amortization
program amortize.exe. The amortization program resided in the directory d:\amor
Step 1. Create
directory
c:\gs_uts\scripts\DomainUsers\bill
Step 2. Create batch
file c_start.bat
Step 3. Add line to c_start.bat
d:\amor\amortize.exe
Step 4. Save file and
exit.
Now when the User Login
ID "bill" connects to the Windows
system via SSH2/Telnet the application amortize.exe will automatically be
executed. When the user exits the amortization package, the SSH2/Telnet session will terminate.
There are situations
where the system administrator may want to have the same logon script executed
by all the users upon connection. Instead of creating a logon script
for each and every user, a single logon script can be created that will
be executed by all users upon connection. The Global Logon script operates in
the same manner as a normal logon script except for the location of the script
files. The system administrator may put the k_start.bat
or c_start.bat file in the
subdirectory SCRIPTS (under the install directory). The server looks first for k_start.bat or c_start.bat in user's subdirectory and will not use the
global script if it can find user's script.
Example - Global
Logon Scripting: Automatic Execution of a program upon connection
by ALL users
Here is an example
script to allow automatic execution of a Physician’s Office Application
"medical.exe" upon connection for ALL users that do not have a
c_start.bat or k_start.bat in their logon script directory.
The Physician’s office application is in the directory c:\medical.
Step 1. Create batch file
k_start.bat in the SCRIPTS directory
(under the install directory).
Step 2. Add line to k_start.bat
c:\medical\medical.exe
Step 3. Save file and
exit.
Now when any user
(unless they have their own login script in their logon script directory)
connects to the Windows system via SSH2/Telnet
the application medical.exe will automatically be started. When the user exits
the medical package, the Windows command line prompt is displayed allowing
other activity to occur.
IP Address Based
Logon Scripts
The capability to
define different logon scripts based on the IP Address of the client logging on
is another advanced feature pioneered by GSW. System Administrators may have
specific mapping requirements or specific applications that must be launched
depending on the location of the User that is logging on. In many cases it is
easier to identify the location by IP addresses rather than User IDs. Another
case may be where a User is routinely working in different locations with
specific logon script requirements for each location. Another could be where
different devices access different applications, regardless of the user connected.
There are many other cases where IP Address based logon scripting can be used.
Associating the Logon
Script to use with the IP Address is configured using the gs_ip_rt.txt file. IP Addresses can be
specified as individual IP address or IP address ranges. Additionally, wildcards
can be used. For each entry in the gs_ip_rt.txt
file two fields are specified: The IP Address (or range) and the name of
the login script to use. A file gs_ip_rt.txt
is installed when the GSW UTS is installed. It contains examples that are commented
out to help you get started.
Notice the file in the
GSW UTS installation directory:
gs_ip_rt.txt
The file must reside in
the Georgia SoftWorks Windows Universal Terminal Server installation directory.
NOTE: The System
account must have permission to read the gs_ip_rt.txt
file.
The file gs_ip_rt.txt is used for configuration
of the association of IP Addresses and Logon Scripts.
The rules are simple
for setting up the gs_ip_rt.txt
file.
·
It
is a text file
·
The
# character is the comment character
·
Each
entry must start in the first column.
·
Each
entry consists of the IP Address (or IP Address Range) and the associated logon
script filename (page 222). The logon script file must
be located in the GSW UTS scripts folder.
·
The
IP Address and the Logon Script are separated by a single space.
IP Address Syntax. Use the industry
standard 4-part (dot-decimal) syntax: format nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
when specifying the IP Address.
Example: 10.1.1.1
An
example entry in the gs_ip_rt.txt
file would look like:
10.1.1.1 k_logon70.bat
The above
entry would instruct the system that when a user connects from the IP address 10.1.1.1 the logon script k_logon70.bat should be used.
IP Address Range Syntax: An IP address range
is specified as two IP addresses separated by the dash character '-'. No spaces are allowed. Below are
two examples.
Example A: 10.1.1.1-10.1.10.210
Example B: 192.68.22.10-192.68.22.99
An
example IP Address range entry in the gs_ip_rt.txt
file would look like:
192.68.22.10-192.68.22.99 k_buildingN.bat
The above entry would instruct the GSW UTS that when user
connects from any IP address that falls in the range from 192.68.22.10 to 192.68.22.99 the logon script k_buildingN.bat should be used.
IP Address Wild Cards: An IP address wild the
IP Address.
Example A: 10.0.0.*
Example B: 192.*.*.5
Example
C: *
Wild Cards can be used in IP Address Ranges too.
Logon Script Filename:
The logon script filename associated with the IP address can be any name
that you choose however it must start with either a k_ or a c_.
The ‘k_’ and ‘c_’ correspond to the analogous behavior
as the k_start.bat and c_start.bat (See page 215).
Example – IP BASED Logon Scripting
The ACME Company has a
New York location and a Mexico location. The New York location has a north
building that has a receiving dock, a manufacturing floor and a shipping dock.
Each area uses different applications to update a common database. The
Receiving dock uses fork lifts with vehicle mounted RF devices. The application
used by the receiving dock is a custom developed application. The ACME manufacturing
floor workers use hand held RF devices, mostly basic scanner guns. The Quality
Assurance Engineers on the manufacturing floor use Pocket PC 2003 devices to
enter comments and other information. The Quality Assurance Engineers use a
different application than the manufacturing floor workers. The New York Shipping
dock workers use hand held RF devices, again mostly basic scanner guns. Like
before they have yet another custom application. The shipping dock workers and
the manufacturing floor workers are multi-talented and can perform either duty.
The ACME Mexico location in Seaside ships partially assembled components to the
New York locations.
All the locations are
connected to a single server running the 100 session copy of the GSW UTS. The
system administrator needs to launch a different application for each group described
above.
This is can be
accomplished using GSW UTS Logon Scripting based on IP Addresses. We can start
editing the gs_ip_rt.txt file, but
first let’s make a chart of the locations, the IP addresses and the logon scripts.
The chart on the next
page contains the information needed to set up the IP Based Logon scripting.
|
Location Name
|
IP Address or Range
|
Logon Script
|
ACME New York North Building Receiving Dock |
164.10.15.1 164.10.15.211 164.10.15.212 164.10.15.213 164.10.15.214 164.10.15.215 164.10.15.216 164.10.15.217 164.10.15.218 164.10.15.219 |
164.10.15.220 164.10.15.221 164.10.15.222 164.10.15.223 164.10.15.224 164.10.15.253 164.10.15.226 164.10.15.254 164.10.15.228 164.10.15.229 164.10.15.255 |
c_nynrcv.bat |
ACME New York North Building Manufacturing Floor Guns |
164.10.16.1 164.10.16.10 164.10.16.11 164.10.16.12 |
164.10.16.23 164.10.16.23 164.10.16.24 164.10.16.25 |
c_nynman.bat |
ACME New York North Building Manufacturing Floor Quality Assurance Guns |
164.10.16.50 164.10.16.60 164.10.16.70 164.10.16.80 |
164.10.16.90 164.10.16.100 |
c_nynqua.bat |
ACME New York North Building shipping Guns |
164.14.12.210 164.14.102.211 164.14.245.212 164.14.246.213 164.14.247.214 |
164.14.15.220 165.14.19.1 165.14.150.222 165.14.151.223 165.14.178.224 |
c_nynsh.bat |
ACME Mexico Seaside Plant shipping Guns |
242.10.150.5 242.10.160.5 242.10.170.5 242.10.180.5 242.10.190.5 |
242.10.191.5 242.10.192.5 242.10.192.5 242.10.194.5 |
c_mexpl.bat |
Table
49 - IP Based Logon Scripting Information Table
This is how to set up the gs_ip_rt.txt
file to associate IP Addresses and Logon Scripts.
Edit the file gs_ip_rt.txt
and add the following lines.
#ACME North Building Receiving Dock
164.10.15.1 c_nynrcv.bat
164.10.15.211-164.10.15.255 c_nynrcv.bat
#
#ACME North Building Manufacturing Floor
164.10.16.1-164.10.16.25 c_nynman.bat
#
#ACME North Building Manufacturing Floor Quality
Assurance
164.10.16.50-164.10.16.100 c_nynqua.bat
#
#ACME North Building Manufacturing Floor Shipping
164.14.*.* c_nynshi.bat
#
#ACME Seaside Plant Shipping Guns
242.10.*.5 c_mexpl.bat
Each time a User Logs on,
the GSW Universal Terminal Server identifies the IP address of the User and executes
the associated logon script.
A sample gs_ip_rt.txt
file with examples is installed with the software. It can be easily modified
and used for your purposes. This is a copy of the file.
#
Georgia SoftWorks UTS IP-based selection of logon scripts
#
Copyright (C) 2004 Georgia SoftWorks
#
All Rights Reserved
#
#
This file allows you to map client IP addresses to logon scripts.
#
The order of fields is as follows:
#
#
IP address OR IP address range OR IP address with wildcards
#
k_logon_script_name OR c_logon_script_name
#
#
The 'k_' and 'c_' correspond to behavior analogous to k_start.bat and
#
c_start.bat respectively.
#
#
Each entry must start in the first column.
#
#
For example, the following entry below
#
(the comment ‘#’ character must be removed to activate the entry)
#
#63.80.112.70
k_logon70.bat
#
#
instructs the system that when a user connects from the IP address
#
63.80.112.70 he should use the logon script k_logon70.bat
#
#
#
IP address ranges
#
#
An IP address range is specified as two IP addresses separated by
#
the dash character '-'.
#
#
Examples of IP address ranges
#
#
10.1.1.1-10.1.10.210
#
192.68.22.10-192.68.22.99
#
#
#
IP address with wildcards
#
#
An IP address with wildcards is specified by using the star character
#
'*' instead of a number as one of four segments of an IP address or
#
all four segments.
#
#
Examples of IP addresses with wildcards
#
# 10.*.*.*
# 192.*.*.22
# fe80::5efe:192.168.1.*%2
# fe80::230:48fe:*:*%6
# *
#
# Note:
#
For security reasons this file's permissions should be set to allow only
#
#
SYSTEM - read access
#
#
No other accounts should be allowed to access this file.
Note: Programming skills may be required to understand the
following section.
Developers may take
advantage of the programmatic interface to the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server for Windows. Programmatic, language independent access to the SSH2/Telnet Server allows developers to write an application that (when run under the SSH2/Telnet Server environment) takes control of its input and/or output from/to the client.
This can be utilized to create a custom or highly specialized communications
application. The SSH2/Telnet Server still maintains critical functionality such
as logon, security, application launch and termination. Normally the application
before it terminates will release control to the SSH2/Telnet
server.
The SSH2/Telnet
Server communicates with the client through a WINSOCK socket. A protocol/mechanism
is provided that allows a custom application to take and release control of the
socket. Objects involved in taking and releasing control of the socket are passed
through environment variables as are described below.
·
GWTN_HSOCKET - This environment
variable holds the value of the handle of the open socket. Note: Never close or
otherwise destroy the socket.
·
GWTN_GET_I - This environment variable
holds the name of the WIN32 event that when signaled notifies the SSH2/Telnet server that
the custom application wants to take control of the input from
the client.
·
GWTN_RLS_I - This environment variable
holds the name of the WIN32 event that when signaled notifies the SSH2/Telnet server that
the custom application wants to release control of the input from
the client.
·
GWTN_GET_O - This environment variable
holds the name of the WIN32 event that when signaled notifies the SSH2/Telnet server that
the custom application wants to take control of the output to the
client.
·
GWTN_RLS_O - This environment variable
holds the name of the WIN32 event that when signaled notifies the SSH2/Telnet server that
the custom application wants to release control of the output to
the client.
·
GWTN_ACK - This environment
variable holds the name of the WIN32 event that when signaled notifies the
custom application that the request is granted.
Note1: All of the above-mentioned events are autoreset events.
Note2: The above environment variables are automatically injected into
the session's environment and will vary from session to session. Please do not
attempt to modify those variables or set them in the autoexec files or Control
Panel/System/Environment.
Please see the file interface.c included on
the installation disks for a code sample. interface.c
contains a short program that takes control of the input and output and echoes
characters to the client until a lowercase q is encountered.
True Client-Side
Printing - Printing the way you want it!
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows, True Client Side Printing allows documents to
be printed at locations that are easily accessible by each user. Traditionally,
default printing using SSH2/Telnet is always local to the server. This can be
inconvenient to the user. Georgia SoftWorks overcomes the traditional problem
by providing True Client-Side Printing - printing the way you want it.
Multiple (up to
9) printers may be used on a per user basis. Georgia SoftWorks offers several
printing methods for the SSH2/Telnet user that will address most printing
requirements. They are
·
Default - Works as if the SSH2/Telnet
user is sitting at the Windows server.
·
Enhanced - Printer output is sent to the printers accessible
by the client computer when using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
client. The printer is considered accessible if it is configured as one of your
printers visible in the Printers Applet in the Control Panel.
·
Open - allows SSH2/Telnet
user to configure the printing command used when printing.
·
Passthrough – allows print jobs to be redirected to RF
Devices supporting escape sequence-based printing.
·
SAP – Allows SAP print jobs to be redirected to RF Devices
(printer). See page 323 for details.
The Default Printing
method uses standard server printing facilities. When a SSH2/Telnet
user prints, the printer output destination is exactly the same as if the user
is sitting at the server and initiated the print. The destination may be local to
the server or any remote printer that has been captured by the net use command. No setup is required
for Default printing.
Enhanced Printing
Enhanced printing is an
advanced feature of the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
desktop clients that allows printers accessible to the user’s client computer to
be used when printing with SSH2/Telnet.
The Client computers default printer is used if no SSH2/Telnet client command line parameters are specified. The SSH2/Telnet
user can override the default printer using command line arguments when
initiating the client. Also, multiple printers can be utilized by configuring
additional client-side printers as described below.
Open Printing
The Open printing
method allows the SSH2/Telnet user to specify the printing command that SSH2/Telnet will use when processing print jobs. For example, if the user wants to send output
to a shared printer then the "print
/d" command can be configured. Another example is sending output to a printer
with an IP address that is on the network but is not shared or visible to the
server. In this case the SSH2/Telnet user would specify the "lpr" printing
command. Other valid print commands can be configured as the user’s requirements dictate. Please be knowledgeable with the printing
commands you select.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool – True Client Side Printing Global see page 378 , User see page 413
Or
use legacy style below
|
There are up to three
steps in setting up True Client-Side Printing.
·
Defining Virtual Printer(s) on the Server - This is the same for
all printing methods.
·
Adding the Georgia SoftWorks printer redirection commands to a
logon script. This is specific to the printing method chosen.
·
When using the Enhanced Printing method these steps must be performed.
o Provide command
line parameters when invoking the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client when using the Enhanced Printing method and
o Map the destination
printer using the Net Use LPT command on the client machine
A Virtual Printer(s) is
defined that redirects the output from your application. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server queries the Virtual Printer queue for new print jobs. When a print job enters
the Virtual Printer queue the originating user of the job is identified. Once
the user is known the associated printer is referenced and the print job is
redirected to the proper printer.
In creating a Virtual Printer,
the key information is the Printer Name, the Share Name and the Port.
Up to three (3) Virtual Printers may be defined on the server. (This will allow
up to three (3) printers to be used for each client.). A Printer Index is
used to identify and correlate the various printer setups. The printer indexes
are 1, 2 and 3. For the Virtual Printer Setup the Printer Name and Share
Name require printer indexes. The following setup is for a single printer
(Printer Index 1).
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Select Settings then printers.
3.
Double click on Add Printer. (The add printer window opens).
4.
Select My Computer and Click on Next
5.
Select one of the unused lpt or com ports. Do NOT
enable print pooling. Click Next.
6.
From the Manufactures list select Generic
7.
From the Printers select Generic/Text Only. Click
Next
8.
Name your printer GwtnPrinter1. NOTE: This name is required.
Click Next
9.
Select Shared and name the printer GwtnPrinterShare1. NOTE: This
name is required. Click Next
10. After
the printer is created, double click on the printer icon.
11. Pause
the printer by selecting the menu item Printer and selecting Pause
Printer. This printer must remain paused at all times. This printer cannot
be used by any other service except Georgia SoftWorks.
Now your virtual
printer is created and is ready for use by SSH2/Telnet
. However, you must be sure to set the redirection commands in logon scripts.
If you need to support more
than one client-side printer per user at a time then repeat steps 1 through 11
using the other two Printer Indexes. This involves replacing the printer
name in step 8 with GwtnPrinter2, GwtnPrinter3, GwtnPrinter4, GwtnPrinter5,
GwtnPrinter6, GwtnPrinter7, GwtnPrinter8 or GwtnPrinter9 and the share name
in step 9 with GwtnPrinterShare2, GwtnPrinterShare3, GwtnPrinterShare4,
GwthPrinterShare5, GwtnPrinterShare6, GwthPrinterShare7, GwtnPrinterShare8, or
GwthPrinterShare9.
For each user that is
using the Georgia SoftWorks True Client-Side Printing redirection commands must
be added to their logon script. First the Virtual Printer must be associated
with the printer device that the user wants to use. This is the device that the
application will select when printing. This can be accomplished with the
"net use" command. It is of the form:
net use lptx: \\servercomputername\GwtnPrinterSharey
Where
·
lptx is the printer port that the application sends
the printer output (typically lpt1 for Dos applications)
·
\\servercomputername\GwtnPrinterSharey is
the specification for the virtual printer. The printer share would be either
GwtnPrinterShare1, GwtnPrinterShare2, GwtnPrinterShare3 etc.
The next is an environment
variable that indicates the True Client-Side Printing method chosen. The
environment variable is:
GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD
and valid values are:
·
Open
·
Enhanced
The syntax is:
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Open or
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Enhanced
If the environment variable
does not exist then the True Client printing method is the Default printing method. This prints
as if the user is sitting local at the server. There is no setup required for the
Default printing method.
The Open print
method allows the administrator to determine the print command used by SSH2/Telnet
when printing. There are unlimited applications for this printing method.
Common uses involve printing to shared or network printers.
The
Enhanced print method allows any
printers accessible to the client system (for example the default printer) to
be easily used by SSH2/Telnet. A common use for Enhanced printing is when connecting to
the server across the Internet or via RAS.
The Enhanced Print
Method is very useful to users that connect across the Internet or via RAS.
Enhanced printing may also be used in many other scenarios. The Enhanced True
Client Side Printing Method is a feature of the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Clients and is not available with 3rd party clients. Print output is
sent to the client’s computer default or local printer(s). Client parameters
also exist that allow printers other than the default printer to be used with
Enhanced printing.
Note: It is
required that each user be logged in only once for the Enhanced Print method to
operate correctly. That means that each workstation/RF device must use a different
User Id when connecting to the server.
The first example
describes the basic Enhanced Printing setup and the second example describes
using multiple client-side printers and the third describes the override feature.
Example - Enhanced Printing: Printing to my local printer when connected across
the Internet or RAS
I have sales people
that SSH2/Telnet to the server to get reports from a variety of locations. They
carry laptops with portable printers and SSH2/Telnet
to the server either through the Internet or via RAS. They need to get customer
and shipping information printed. The sales application software that they use prints
to lpt3. How do they have printer output sent to their laptop portable printers?
This is an excellent
opportunity for the Georgia SoftWorks Enhanced True Client Printing Method.
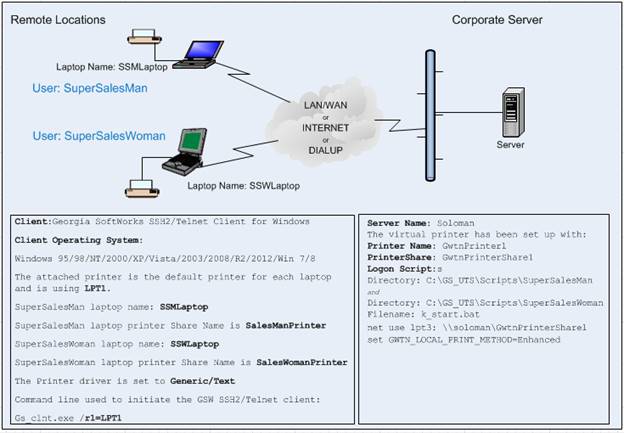
Figure 126: True Client-Side
Printing: Printing across the Internet or RAS
Note: The Logon
Scripts can be implemented in a variety of ways depending on the requirements.
For example, a global logon script could be created for all telnet users. In
the example above we used user specific scripts for each salesperson that might
use telnet.
Important Information
User Name(s):
SuperSalesMan and SuperSalesWoman
Server Computer Name: soloman
Telnet Client: Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client
Client Operating System: Windows
95 through Win Server 2019
The only requirement is
that the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client must be used. Of course, the Virtual printer must be defined as
described in the Virtual Printer section. The logon script for each user needs
to have the following commands:
On the Server edit the user’s
logon script k_start.bat and add
the following commands:
net use lpt3: \\soloman\GwtnPrinterShare1
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Enhanced
NOTE:
The above commands must appear in the logon script. It is not sufficient to set
these at the command prompt or in another batch file.
On the SuperSalesMan laptop
open a command shell and enter the command:
Net Use LPT1: \\SSMLaptop\SalesManPrinter
/persistent:yes
On the SuperSalesWoman
laptop open a command shell and enter the command:
net use LPT1: \\SSWLaptop\SalesWomanPrinter
/persistent:yes
Remember
we are using the laptops default printer.
The /persistent:yes retains the LPT port
mapping across reboots.
Initiate the Client
session as:
gs_clnt.exe /r1=LPT1
The portable printer
must be connected to the laptop and be the default printer for that system. It
is recommended that the printer driver for the default printer be set to Generic/Text.
When the salesman
prints to lpt3 the output will appear on the default printer connected to the
salesman's client computer. This same methodology is used for either a single
or multiple sales people. If the client needs to support more than one printer
at a time please read the section on Multiple Client-Side Printers - Carefully.
Example - Enhanced Printing: Multiple CLIENT-SIDE
Printers
Setting: remote Physician’s
office. They have a dot matrix printer that is used for insurance forms and a
laser printer for formal letters. The medical software application exists at
the main office on a Windows server and they are using SSH2/Telnet
to access the application. Here an office manager in a physician’s office needs
to be able to access two different printers from his client machine. The
Medical application is using LPT1 to print the forms and LPT2 for the formal
letters.
The main office configured
the server machine to have two virtual printers. One is named GwtnPrinter1 and
the other is named GwtnPrinter2 (As required by the virtual printer specifications.
(See page 227)).
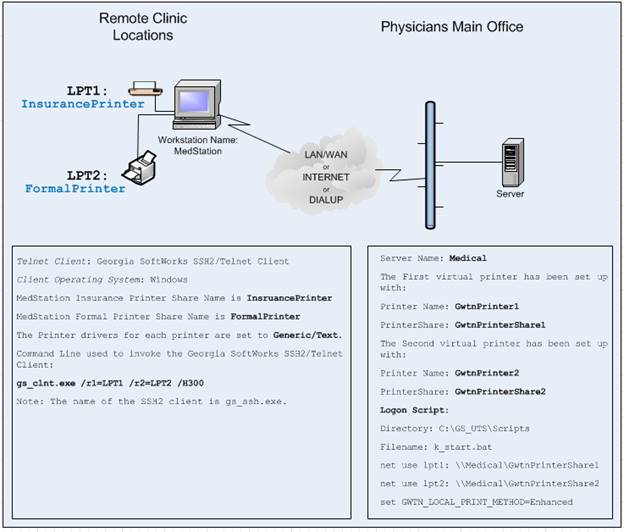
Figure 127: True Client-Side
Printing: Using Multiple Client-Side Printers per User
Note the correlation between
client-side command line parameters “/rx” and the Printer Share
and Printer names on the server.
Important Information
Server Computer Name: Medical
Telnet Client: Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
Client
Client Operating System: Windows 98-2008R2 and
Windows 7
Dot Matrix Printer Name: InsurancePrinter
Laser Printer Name: FormalPrinter
Virtual Printer to Use: 1 and 2
On the server in the user’s
logon script add the following commands:
net use lpt1: \\MedServer\GwtnPrinterShare1
net use lpt2: \\MedServer\GwtnPrinterShare2
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Enhanced
NOTE: The above
commands must appear in the logon script. It is not sufficient to set these at
the command prompt or in another batch file.
On the MedStation
workstation open a command shell and enter the command:
net use LPT1: \\medstation\InsurancePrinter
/persistent:yes
net use LPT2: \\medstation\FormalPrinter
/persistent:yes
The /persistent:yes retains the LPT port
mapping across reboots.
Initiate the Client session
as:
gs_clnt.exe /r1=InsurancePrinter /r2=FormalPrinter
/H300
Note: The name of the SSH
client is gs_ssh.exe.
Example
- Enhanced Printing: Override
This is a variation of
the previous examples. Here the salesman has access to a color printer. Our salesmen
carry laptops (running Windows 95/98) with portable printers and they SSH2/Telnet
to the server either through the Internet or via RAS. They need to get customer
and shipping information printed. The sales program that they use prints to lpt3.
A salesman is at the customer's office and wants to get a color printout of a
sales report. The customer has a color printer handy. They connect the color
printer and install the proper driver. It is not the default printer. How can
the salesman print to the non-default color printer?
This is an excellent opportunity
for the Georgia SoftWorks Enhanced True Client Printing Method with client
override. A command line parameter when initiating the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
client allows printers other than the default printer to be used.
The Parameter is:
On Windows 95/98
/rx=printername or
/rx=\\computername\printersharename
or
/rx=lpty:
/rx=comy:
On Windows
/rx=\\computername\printersharename
or
/rx=lpty:
/rx=comy:
Where x is (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
the Printer Index number and
Where y is
(1,2,3,4) the com port or lpt port number.
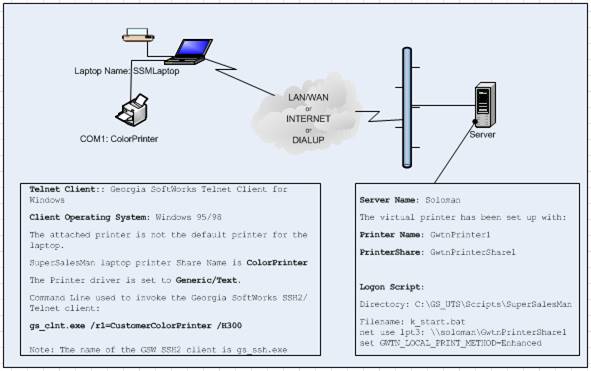
Figure
128: True Client-Side Printing: Enhanced Printing Override
Important Information
User Name: SuperSalesMan
Server Computer Name: soloman
Telnet Client: GSW SSH2/Telnet
Client for Windows
Client Operating System: Windows
95/98
Color Printer Name: CustomerColorPrinter
Color Printer Share: ColorPrinter
Virtual Printer to Use: 1
The only requirement is
that the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
for Windows client is being used. Of course, the Virtual printer must be
defined as described in the Virtual Printer section. The logon script for user
SuperSalesMan needs to have the commands described below. Edit the user’s logon
script k_start.bat and add the
following commands:
net use lpt3: \\soloman\GwtnPrinterShare1
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Enhanced
NOTE: The above
commands must appear in the logon script. It is not sufficient to set these neither
at the command prompt nor in another batch file.
On the SuperSalesMan laptop open a command shell and enter
the command:
net use COM1: \\SSMLaptop\ColorPrinter /persistent:no
Remember we are not using the
default printer but a customer printer.
The /persistent:no removes the COM port mapping at the next
reboot.
Initiate the client session as:
gs_clnt.exe /r1=COM1
/H300
When the salesman prints to lpt3 for user SuperSalesMan the
output will appear on the color printer.
Open Print Method
The Open Print Method is
extremely powerful allowing the user to configure any valid printing command to
be used when printing via SSH2/Telnet.
NOTE: It is required
that each user be logged in only once for Open Print method to operate
correctly. This means that each workstation/RF device must use a different User
Id when connecting to the server.
The printing command
and other parameters are configured by setting the print command environment variable.
The environment variables are:
GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD1
GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD2
GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD3
…
GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD9
They correspond to the
handling of print jobs sent to GwtnPrinter1, GwtnPrinter2, GwtnPrinter3 …
GwtnPrinter9
And the syntax of the command
is:
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMDx=PrintCommand
%s
Where
·
PrintCommand is
any valid printing command and arguments
·
%s is the Georgia
SoftWorks argument placeholder for the print job.
·
x is the printer index created on the server.
The print method and
capture is determined by setting the environment variable GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMDx.
The most commons commands are the "print
/d:" or the "lpr"
printing commands. Other printing commands may be used, as the user’s needs dictate.
If the client printer is a shared printer (that is visible from the server) then
you should use the "print /d:"
command. The lpr command should
be used when the host provides a lpd service. The user should be
knowledgeable of the print command selected. The syntax of the “print /d:” command could be:
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMDx=print /d:\\clientcomputername\sharename
%s
Note: the %s is
typed exactly as it appears. Do not replace the %s with a file name. The system
replaces the %s with the current NT-generated spool file as you print to your
printing port. Note: You are not printing to that temporary file from your
application - the system does this behind the scenes. Enhanced and Open
printing methods allow you to print to the printer port as you normally would.
Where
·
\\clientcomputername\sharename
is the network path to the destination printer.
·
%s is the Georgia
SoftWorks file placeholder
The syntax of the lpr
print command could be:
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMDx=lpr
-S Server -P printer %s
where
·
Server is the name
or ip address of the host providing the lpd service
·
Printer is the name
of the printer queue
·
x is the printer index
Other arguments are
available for the lpr
command. Please see the help for the lpd service that you are using.
Example
- Open Printing: Print to a client computer’s shared printer
In my office I have a
computer and a printer connected. I also am using a 3rd party SSH2/Telnet client. My system is on the network and my shared printer is visible to the
server. I use SSH2/Telnet to connect to the company server and I run accounting
applications. The accounting application uses LPT1 as the printer port. How can
I use the printer in my office when I print from the accounting applications?
Important Information
User
Name: Smarts
Client
Computer Name: SmartsComputer
PrinterShareName:
SmartsPrinter
Server
Computer Name: soloman
SSH2/Telnet
Client: Any - No Restriction
Operating
System: Any - No Restriction
The only requirement is
that the printer be visible to the server. In other words, the printer at the client
computer must be shared. Of course, the Virtual printer must be defined as described
in the Virtual Printer section. The logon script for user Smarts should have the
following commands:
Edit the user’s logon
script k_start.bat. and add the following commands:
net use lpt1: \\soloman\GwtnPrinterShare1
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Open
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD1=print /d:\\SmartsComputer\SmartsPrinter
%s
NOTE: The above
commands must appear in the logon script. It is not sufficient to set these at
the command prompt or in another batch file.
When the accounting
application prints to lpt1 the output will appear on the printer in Ms. Smart's
office. This same methodology can be used for as many users as you wish.
Example - Open Printing: Print to a Network Printer
In our building we have
two workgroups. Each workgroup has their network printer in a common area. Both
workgroups have 25 users that SSH2/Telnet
to the main server from UNIX workstations and run a database application. We
print reports on lpt2. How can we get the reports to be printed on the correct
network printer for each workgroup? This is an excellent case for the Open True
Client-Side Printing method using the lpr command.
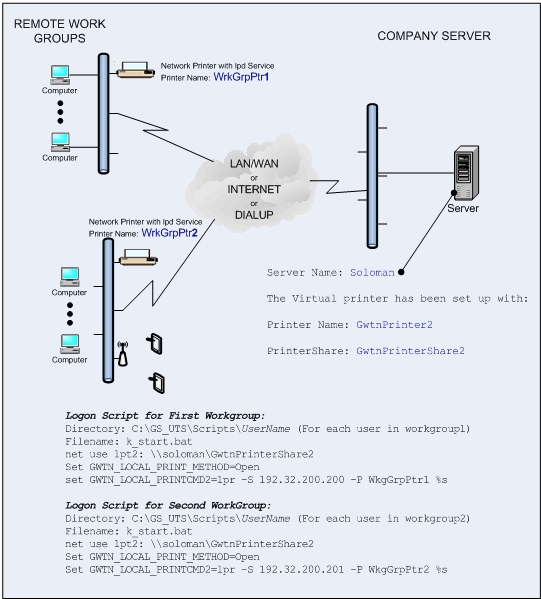
Figure 129: True Client-Side
Printing: Open Print Method
(Continued on next page)
Important Information
IP Address of the first Host providing
the lpd service: 192.32.200.200
Printer Name: WrkGrpPtr1
IP Address of the second Host
providing the lpd service: 192.32.200.201
Printer Name: WrkGrpPtr2
Server Computer Name: soloman
Telnet/SSH Client: Any
- No Restriction
Operating System: Any -
No Restriction
The only requirement is
that a lpd service exists for the printer to be used. In this case the
network printer provides the service. Of course, the Virtual printer must be defined
as described in the Virtual Printer section. The logon script k_start.bat for
users in workgroup 1 need to have the following commands:
net use lpt2: \\soloman\GwtnPrinterShare2
Set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Open
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD2=lpr -S 192.32.200.200
-P WkgGrpPtr1 %s
The logon script k_start.bat
for users in workgroup 2 need to have the following commands:
net use lpt2: \\soloman\GwtnPrinterShare2
Set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=Open
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_CMD2=lpr -S
192.32.200.201 -P WkgGrpPtr2 %s
NOTE:
The above commands must appear in the logon script. It is not sufficient to set
these at the command prompt or in another batch file.
When the database
application prints to lpt2 the output will appear on the correct network printer
for each workgroup. The logon script for each user in the Work Group will need
to be modified to contain the same commands. This same methodology can be used
for as many users as you wish.
Pass-through
printing is available for 3rd Party Clients that support Pass-through
printing. An example of a 3rd Party SSH2/Telnet
client that supports Pass-through printing is AlphaCommunicator. Most 3rd
party telnet clients for RF terminals also support Pass-through printing making
the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows
the ONLY SSH2/Telnet server that can accommodate Pass-through printing.
Note: It is required
that each user be logged in only once for the Pass-through Print method to
operate correctly. This means that each workstation/RF device must use a
different User Id when connecting to the server
Interested in printing
to portable printers when in SAPConsole? See page 323
The required Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server setup for Pass-through printing is exactly the
same as the Enhanced Print Method (page 226) with the following differences.
·
There is no client parameter setup
·
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=PASSTHROUGH
·
Optionally set GWTN_FF_IN_PASSTHROUGH
·
Optionally set GWTN_PP_PRINT_BUFFER_SIZE
Other than that, the
setup for Pass-through printing is identical.
Passthrough
Printing - FormFeed Control
NOTE: Some third
party SSH2/Telnet clients exhibit printing
problems when a form feed is sent at the end of the print job. The problems
may manifest by simply not printing and/or the form feed being converted to
NULLs. If you are experiencing this problem you can use the following environment
variable for controlling the trailing form feeds at the end of a print job when
using Pass-through printing.
The environment
variable for the enabling or disabling the trailing form feed in Pass-through
printing is:
gwtn_ff_in_passthrough
For example, to disable
the trailing form feed you would enter:
set gwtn_ff_in_passthrough=n
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
To enable trailing form
feeds in Pass-through printing you would set the environment variable to y or simply not include the
environment variable in the logon script as trailing form feeds are enabled by
default.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_ff_in_passthrough=y is correct
set gwtn_ff_in_passthrough = y is not correct
Passthrough Printing – Print Data
Buffer Size
The GWTN_PP_PRINT_BUFFER_SIZE
environment variable can be used to eliminate the condition where the user must
hit <ENTER> multiple times for a print job to complete due to some
clients prompting the user after each data block is received rather than just
printing the data.
The environment variable
for specifying the Print Data Buffer Size for passthrough printing is:
gwtn_pp_print_buffer_size
The default print data block
(buffer) size is 500 bytes.
For example, to specify
a Print Data Buffer Size of 2000 bytes you would enter:
set gwtn_pp_print_buffer_size=2000
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces are
allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_pp_print_buffer_size=2000 is
correct
set gwtn_pp_print_buffer_size = 2000 is not correct
Knowing the exact
identity of the client device connected is useful in many environments and
required in others.
Several mechanisms can
be used to obtain specific information about the client.
·
Client MAC Address.
·
Client IP Address
·
Client Answerback Text
·
Client IP Logon Scripting
·
User Logon Scripting
Using one or more of
the mechanisms listed above usually provides the capability to refine the client
identity to the granularity needed.
Client Media Access
Control (MAC) Address.
This is a hardware address
that uniquely identifies each client device in a network. The only way to
change the MAC address is to swap out or replace client hardware. The client
MAC Address of the client is available on the server within the session through
the environment variable gwtn_client_mac
(page 333 ).
Client IP Address
A unique IP Address is
defined for each device on a network. In many cases the System Administrator
can change the IP Address with Network Management Software. Regardless, the IP
address of the client is available on the server within the session through the
environment variable gwtn_client_ip
(page 333).
Client Answerback
Text
The GSW Desktop and
Mobile Clients (Pocket PC 2003, Windows CE .NET V4.2+) provide the capability
to pass a text string to the server. The Desktop clients use a command line
parameter and the GSW mobile clients provide a configuration field on the
client for defining the Answerback text (page 87). The Answerback text is
available on the server within the session through the environment variable gwtn_answerback (page 333
)
Client IP Logon
Scripting
This is a powerful
feature that allows different logon scripts to be launched based on the IP address
of the client connecting (page 220).
User Name Logon Scripting
This is a powerful feature
that allows different logon scripts to be launched based on the User Name of
the client connecting (page 218).
Compatibility Pack
The Georgia SoftWorks
Telnet Server allows connection with any RFC 854 compliant 3rd party
client. This includes generic UNIX, MAC, Windows CE, NT, XP, VISTA, 2000, 2003,
2008, R2, 2012, 2016, 2019 Wireless clients and more! Most telnet clients are RFC
854 compliant. Many Network Terminal and terminal servers are as well.
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH
Server allows connection with any SSH compliant 3rd party client.
This includes generic UNIX, MAC, Windows CE, NT, Wireless clients and more!
|
Compatibility Pack
|
Configurable
|
Georgia
SoftWorks Windows Clients
|
3rd
Party Client
|
|
RFC 854 Compliant
|
N/A
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from 3rd
Party Clients
|
Yes
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Unix
|
Yes
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Windows 3.1
|
Yes
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
|
Connect form Windows 95/98
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Windows Servers
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Windows CE
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Macs
|
N/A
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Wireless, RF Terminals and Scanners
|
|
Depends on RF Terminal
|
Yes
|
|
Connect from Terminal Servers
|
|
N/A
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table
50 - Compatibility Pack
RF Terminals – Bar Code Scanners
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows works well with RF Wireless systems, in particular hand held and
vehicle mounted units. By using SSH2/Telnet
the RF Wireless Hand Held application developer is able to create more generalized
applications that will easily work with a variety of manufactures hardware. In
addition to development and maintenance cost savings for application developers,
this added flexibility allows heterogeneous systems to exist allowing customers
to utilize existing hardware.
Encryption is available
with Telnet when using the GSW Telnet clients. GSW provides clients for the
PPC2003, Windows Mobile and many CE 4.2+ class devices (see 32).
Unmatched security
with the strongest encryption is available when using the SSH server with ALL SSH
clients.
Georgia SoftWorks is
committed to providing the best SSH2/Telnet
solution for the RF Wireless market. Some tailored features include:
·
Performance. Fast Fast Fast!
·
Logon Scripting to automatically launch your application upon connection.
See Page 218.
·
Session Saver – After client or link failures reconnect to
a Saved session and resume work in progress exactly where you left off! (See page
149)
·
Automatic Logon – Quickly re-establish the session by
pre-configuring the Host, Domain, User Id and Password. When coupled with Session
Saver you are back in operation with minimal time lost! (See page 183)
·
Environment variables to eliminate most prompting. See page 166.
·
Refresh the screen by entering “<ctrl> R.”. Many times, RF
systems may drop a packet of data and the screen will need to be refreshed.
·
Settable screen size to accommodate screens smaller than 25 x 80.
See section on Modes on page 298.
·
Extremely flexible Color to Monochrome mappings. See page 170
·
Extremely flexible Color to Grayscale mapping. See page 171
·
Multiple Levels of failure detection. Including configurable
timers. See Page 149.
·
Pass-through Printing. See page 241.
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows is industrial quality and is suitable for demanding RF Hand
held Terminal applications such as in warehousing, manufacturing, grocery stores
and more!
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global – Failure Detection/Recovery - page 376
Or
use legacy style below
|
If the RF devices are using a power save or sleep mode then the GSW SSH2/Telnet Server should be configured
such that the sessions associated with the ‘sleeping’ device are not
disconnected. Below are the registry changes you need to make if you have the
Power Save mode enabled on your RF devices:
1. Inactivity Timeout
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\InactivityTimeout
Please set to decimal 3600.
2. Server-Side Heartbeat.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\ClntChkTimeout
Please set to hexadecimal ffffffff.
The changes will prevent your RF devices from 'timing out' when left inactive.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –User - Windows see page 407
Or
use legacy style below
|
This parameter provisions
the maximum TCP receive windows size on a per session basis. The TCP Receive
Window specifies the number of bytes a sender may transmit without receiving an
acknowledgment. In general, larger receive windows will improve performance
over high delay, high bandwidth networks. For greatest efficiency, the receive
windows should be an even multiple of the TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS).
Some RF Terminals may
experience connectivity problems because they time out before data transmission
reaches them. In this scenario you may want to reduce the value of the TCP
Windows Size parameter. Reducing the value of TCP Windows Size causes an
acknowledgment for data received to be sent to the RF Terminal sooner. A
quicker acknowledgment lowers the possibility that the RF Terminal will time
out while waiting for an acknowledgment. However, it also increases the amount
of network traffic and causes slower throughput.
The environment variable for the TCP Window Size is:
gwtn_tcpwindowsize
For example, to set the TCP Windows Size to 5000 you would
enter:
set
gwtn_tcpwindowsize=5000
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set gwtn_tcpwindowsize=5000 is correct
set gwtn_tcpwindowsize = 5000 is not correct
To use the default value
(dependent on the network type) remove the environment variable from you logon
script.
Command: gs_tcp
Description:
Command line Utility that sets the TCP Retransmission Count
This utility provisions
the maximum retransmission count for TCP session data. This specifies the
number of times TCP will retransmit an individual data segment (not connection
request segments) before aborting the connection. The default value is 5. We
suggest that the value be increased to 8 when sessions are frequently disconnected
because of timeouts.
Syntax: gs_tcp [new_count|0]
Arguments: The number of retransmissions TCP will retransmit an
individual data segment (not connection request segments) before aborting the
connection. If no argument is provided then the current value is displayed.
Note: Administrative
privileges are required to run this command.
Warnings: The system
must be rebooted for the change to take effect.
Note: To restore the
system default (usually set to 5), invoke the utility with the TCP Retransmission
Count value equal to 0.
Example - Provision TCP Maximum Retransmission
Count
Provision the TCP Retransmission
Count to 8. At the command line enter:
Gs_tcp 8
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –User - Windows see page 407
Or
use legacy style below
|
This setting determines
system specific behavior in the situation where a user logs on and their HKEY_CURRENT_USER
registry key does not have a user specific registry hive to map to. The hive
will be created or not based on the value of gwtn_create_profile.
To specify you should set the gwtn_create_user_profile
environment variable in your logon script (page 218).
The environment variable
for specifying a user specific registry hive mapping is:
gwtn_create_user_profile
Possible values are 'Y' or 'N',
or 'y' or 'n'.
Y – Create a user specific registry hive mapping if the
HKEY_CURRENT_USER does not have a specific registry hive to map (default)
N – Do not create a user specific registry hive mapping.
Use HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT
For example, to enable a
user specific registry hive mapping in the case where HKEY_CURRENT_USER does
not have a specific registry hive to map to:
set gwtn_create_user_profile=Y
in the Logon Script for
a particular user.
NOTE: No spaces
are allowed when setting environment variables.
For example:
set
gwtn_create_user_profile=Y is
correct
set
gwtn_create_user_profile = Y is not correct
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –User - Windows see page 407
Or
use legacy style below
|
The UTS uses the Microsoft
command-line interpreter cmd.exe
(often called the “Command Prompt”) as the default shell.
You can override this
behavior and specify a path to a custom shell executable. For example, you may
want to use Windows Powershell as the default shell. In this case you would
enter the path such as:
C:\Windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
For those migrating
from cmd.exe to another shell please remember that each shell has its own
commands to interface with the operating system. Commands used to make or change
directories; launch applications, etc. in the cmd.exe
shell will not work when using the PowerShell or another shell.
You will need to use
new cmdlets or scripts that can be processed by your selected shell.
When you use a shell other
than cmd.exe, the UTS logon script
files (k_start.bat and c_start.bat) are still used but only
act as configuration place holders by the GSW UTS GUI. All other entries are ignored.
Power users can also automatically
launch an application instead of a shell with the Custom Shell Path such as SAPConsole,
QAD or HighJump by specifying the path to the executable.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global – Emulations – Character Emulation-
see page 382
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Refresh Character
will cause SSH2/Telnet to repaint the screen data. This is useful in
environments that may occasionally drop characters such as some RF Terminals. The
refresh character may be modified to suit your application. This is modified
through a registry key value.
This refresh character
is a registry key value. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\RefreshChar
The default value is 0x12 that is <ctrl-r>.
This is how to change
the registry key for the Refresh Character.
Note: You must be on
the Windows system that the Georgia SoftWorks Windows SSH2/Telnet
Server is installed. However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\RefreshChar
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the RefreshChar and click OK
The new RefreshChar will
take effect for all new connections.
The Unicode Standard is
a character coding system designed to support the processing and display of the
written texts of many international languages around the world. GSW offers UTF-8
encoding (UCS Transformation Format) for improved international
character set support when using the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Client and 3rd Party SSH2/Telnet
Clients. Of course, the 3rd party SSH2/Telnet
client must also support UTF-8 Encoding.
Below is an example of
the character sets supported with UTF-8 Encoding when using the Kermit 95 SSH2/Telnet
client with the GSW SSH2/Telnet Server.
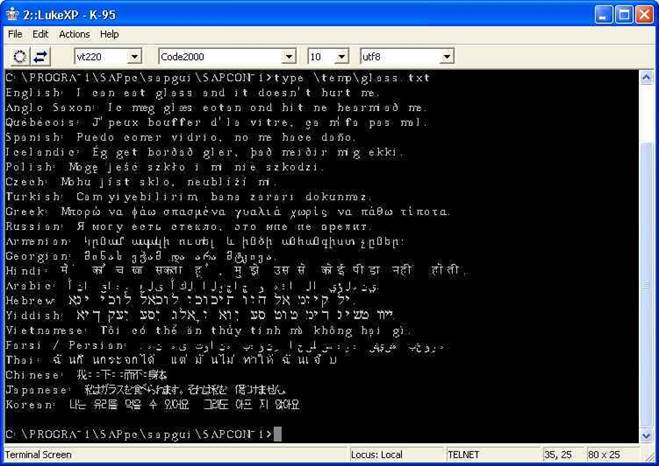
Figure 130: Unicode - UTF-8
Encoding with 3rd party telnet/SSH client.
It is easy to use
Unicode Character Support with the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Client. This feature is available on the Windows
platforms. It is not available on the lower end (Windows 3.1/95/98/ME)
platforms.
Follow the two steps
below to enable Unicode Character Support for the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Client.
1.
You must use the –U command line option to enable Unicode character processing
for input and output for the GSW Telnet/SSH Client. See page 80
for information on GSW SSH2/Telnet Client command line options.
2.
 Modify
the properties of the Command Prompt window to select a font which supports
Unicode characters, for example Lucida Console. Left Click and Select
Properties.
Modify
the properties of the Command Prompt window to select a font which supports
Unicode characters, for example Lucida Console. Left Click and Select
Properties.
Figure 131: Unicode - GSW Client
- Command Prompt Window - Properties
Upon selecting properties,
you will get a window similar to the below on the left. Select the appropriate
font for your application, for example. Lucida Console and click OK. Now you
can display Unicode characters.
Figure 132: Unicode - GSW Client - Select Font
You may need to add fonts to your Command Prompt properties. Fonts must meet
certain criteria to be available in the Command Prompt window. Details on
adding fonts to the Command Session (Command Prompt) can be found by reviewing Microsoft
Knowledge Base article - KB247815.
If we want to add the Everson Mono Terminal to the
Command Prompt, we follow the instructions as specified in the Knowledge Base.
The next time we view the Command Prompt Properties we observe that the Everson Mono Terminal is now available
for selection.
After selecting the Everson Mono Terminal font, the
following text can be displayed.
Figure 133: Unicode - GSW Client
with Unicode Screen Shot
UTF-8 Encoding is easy to configure for 3rd party clients.
Perform the following
steps to enable Unicode/UTF-8 encoding for 3rd party clients.
1.
Be sure that your 3rd Party client supports and is configured
for UTF-8 Encoding. Some examples of SSH2/Telnet
clients that support UTF-8 encoding are Kermit 95 version 2.0 and above, Anzio
or PuTTY.
2.
When connected to the SSH2/Telnet
Server select
One
of the following emulation modes.
DEC VT-220/320/420
or
DEC VT-100
and graphic option:
Use UTF-8 encoded characters
Now you are set up for
UTF-8 Encoding with 3rd Party Clients.

Figure 134: 3rd Party Client - UTF-8
Encoding Display
Telnet IP Protocol
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global - Protocols see page 394
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Telnet IP protocol version can be selected to either
use IPv4, IPv6 or both.
This Telnet IP Protocol is defined using a registry key
value. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\Protocol
Possible values are ‘ipv4’, ‘ipv6’ or ‘both’.
ipv4 – Use IP version 4
ipv6 – Use IP
version 6
both – Use both
IP version 4 and IP version 6 (default)
The default value is IPv4
This is how to change the registry key for the Telnet
Protocol.
Note: You must be on the Windows
system that the Georgia SoftWorks Windows SSH2/Telnet
Server is installed. However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
1. Click
the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Click
RUN
3. Type
REGEDIT
4. Click
OK
5. Select
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\Protocol
6. Select
the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7. Enter
the new value for the Protocol and click OK
The new Protocol will take effect for all new Telnet connections.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global - Protocols see page 394
Or
use legacy style below
|
The SSH IP protocol version can be selected to either use
IPv4, IPv6 or both.
This SSH IP Protocol is defined using a registry key
value. The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\szProtocol
Possible values are ‘ipv4’, ‘ipv6’ or ‘both’.
ipv4 – Use IP version 4
ipv6 – Use IP
version 6
both – Use
both IP version 4 and IP version 6 (default)
The default value is IPv4
This is how to change the registry key for the SSH
Protocol.
Note: You must be on the Windows
system that the Georgia SoftWorks Windows SSH2/Telnet
Server is installed. However, you may connect to the Windows
Registry from a remote location.
1. Click
the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2. Click
RUN
3. Type
REGEDIT
4. Click
OK
5. Select
Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\szProtocol
6. Select
the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7. Enter
the new value for the Protocol and click OK
The new SSH Protocol will take effect for all new SSH
connections.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global - Protocols see page 394
Or
use legacy style below
|
The UTS protocol can be
specified to use Telnet, SSH or Both. You must be registered to use SSH before
it can be selected.
The UTS Protocol is
defined using three registry key values. The keys are:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopbackOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\UseGSW_SSHD
As shown in the table below, set the registry key values
to obtain the desired protocol.
|
PROTOCOL
|
LsnOnLoopbackOnly
|
AllowTelnetWithSSH
|
UseGSW_SSHD
|
|
Telnet
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
SSH
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
Both
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
Table 51 - Registry Key Values for UTS Protocol Table
The default UTS
protocol is Telnet when SSH is not installed.
The default UTS protocol
is SSH when SSH is installed.
NOTE 1: Other combinations
are undefined and are not supported by the UTS configuration.
NOTE 2: Enabling Telnet
and SSH may compromise security goals. You must understand the ramifications if
you enable both Telnet and SSH.
The new UTS Protocol will
take effect for all new connections.
|
Utility Pack
|
Configurable
|
Georgia SoftWorks
Client
|
3rd
Party Client
|
|
Change Password
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Connection Banner
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Execute Command on Client
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
File Transfer
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Launch GUI Application
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Remote Reboot of Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Remote Shutdown of Server
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Remote Registration
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Special Bell Processing
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Special Bell Process for SAPConsole
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
TTY Name
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Table 52
- Utility Pack
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet server provides utilities for the users’ convenience. The utilities reside in the
installation directory. The utility names are not case sensitive. Arguments
such as Windows passwords are case sensitive.
Many times, a user
wishes to change their password. A convenient method is to use the Georgia
SoftWorks Change Password command line utility.
Command: GS_ChPwd
Description:
Command line utility that changes a user’s password
Syntax: Gs_ChPwd <user> <\\computer |
domain> <newpassword> <oldpassword>
Arguments: There
are 4 required arguments.
a.
<user id> The user
id for which to change the password
b.
<computer name or domain>
- The computer name or domain
c.
<new password> -
the new password
d.
<old password> -
the old password.
Example
- Utilities: Change Password
The user
"smith" wants to change his password on the computer "soloman"
from "fast" to "superfast".
Gs_ChPwd smith \\soloman superfast fast
A custom banner can be
displayed to the client upon connection to the host. The connection banner is
useful for displaying security and legal notices and other information that the
user should see BEFORE logging on to the host.
To enable a connection banner,
perform the following steps.
1.
Create the text of the banner in an ASCII text file.
2.
Save the file and name it banner.txt
3.
Place the file in the directory <telnet_server_root_path>
When a user connects,
the SSH2/Telnet server looks for the existence of the file banner.txt in the SSH2/Telnet root directory and displays the text before the LOGIN prompt is issued.
Please make sure that
the complete text can be displayed on a single console screen to ensure easy
readability.
Bridge the Gap
between GUI processing and a character-oriented protocol.
An incredibly powerful
utility that facilitates client-side processing of server-side files when using
the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server provides the capability to execute commands on the client computer while
in the SSH2/Telnet session. This is accomplished through a
utility:
gs_exec
client_side_command_line
This capability is fully
developed when coupled with the Georgia SoftWorks File Transfer Utilities
(gs_put and gs_get).
Execution of commands on
the client can be used to accomplish:
1.
Edit server files using a local GUI
editor like MS Word.
2.
Run programs on the client that prompts the user for data and transfers
the results back to the server.
3.
Automate file transfer from the server to the client, run program that uses
transferred file for input and then transfer the output data of the program
back to the server.
4.
Useful in situations where you want to do part of the processing on the
server and part on the client.
5.
Initiate program on client and transfer results to server when complete.
6.
Periodic initiation of client-side program processing transferred data and/or
transferring data when complete.
7.
View graphic images on the client using a program such as Corel Draw or
Microsoft Photo Editor when the image resides on the server.
8.
Run file or system level commands on the client synchronously with the server-side
script.
9.
AND MUCH MUCH MORE!
Command: gs_exec
Description:
Command line utility that executes commands on the client from within a SSH2/Telnet session.
Syntax: gs_exec <client_side_command_line>
Arguments: There
is 1 required argument.
a.
<client_side_command_line>
The command to execute on the client computer.
This
command is any valid command on the client computer. It can contain command arguments
just as if entered on the client.
NOTE:
Path information as argument data must be from the Clients perspective.
If the program selected
to run is a GUI program then a new Window is opened. If the program selected is
not a GUI program and has character output then the output data it is displayed
in the SSH2/Telnet Window for 2000 ms (two Seconds) or the time specified by
the /scmddelay gs_clnt.exe command line option (Page 78).
Typically, a script or
batch file is created that will transfer the server file to the client; run the
client-side command using the gs_exec command, and then transfer the file back
to the server when completed.
Example - Utilities: Execute program
on Client – Local Edit using GUI Editor
A company brochure that
resides in a file that contains graphic images and rich test exists on Server
that the user would like to edit using the client copy of Microsoft Word.
The file can be transferred
using the gs_put utility, then MS Word is invoked using the gs_exec utility,
and when the editing is complete, the file is transferred back to the server
using the gs_get utility. The following commands reflect the sequence of
commands that detail the steps.
gs_put d:\xfer\cbroch.doc c:\received\cbroch.doc
gs_exec winword c:\received\cbroch.doc
gs_get c:\received\cbroch.doc d:\xfer\cbroch.doc
These commands can be
included in a batch file such that the “Local Edit” capability is more
“generic” and easily invoked.
Create a batch file (let’s
call it ledit.bat)
gs_put d:\xfer\%1 c:\received\%1
gs_exec winword c:\received\%1
gs_get c:\received\%1 d:\xfer\%1
Assumptions:
File
on server is always in d:\xfer\ folder
File
to be edited on client is always in c:\received folder.
When
connected via SSH2/Telnet to the server; when in
the d:\xfer folder the user can simply type:
ledit cbroch.doc
to transfer the file to the client and run MS Word. When
completed in MS Word the file is automatically transferred back on the server.
Example - Utilities: Execute
program on Client –View Image on Client
A car dealership
headquarters has images of motor vehicles in the database. A local dealer can
easily display the images (pictures) to prospective buyers via SSH2/Telnet
.
The file can be
transferred using the gs_put utility, then the default image view can be
invoked allowing the image to be viewed without required knowledge of the graphics
display program. On the Windows OS the file type
extension will invoke a default executable. In the following two lines, the first
line transfers the file to the client and the second line will invoke the default
image display program, which will display the image.
gs_put d:\auto_database\corvette_1993.jpeg
c:\viewcar\corvette_1993.jpeg
gs_exec c:\viewcar\corvette_1993.jpeg
Again, these commands
can be included in a batch file such that the “View Image” capability is more
“generic” and easily invoked.
Create a batch file (let’s
call it vimage.bat)
gs_put d:\auto_database\%1 c:\viewcar\%1
gs_exec c:\viewcar\%1
Assumptions:
Image
files on server is always in d:\auto_database\ folder
Image
file to be viewed on client is always in c:\viewcar folder.
A
default image viewer exists for .jpeg extensions
When
connected via SSH2/Telnet to the server and
positioned in the d:\auto_database folder the user can simply type:
vimage corvette_1993.jpeg
to transfer the file to the client and display the image.

Example - Utilities: Execute
program on Client –Quick Directory Listing
The User needs to
transfer a file from the client to the server but does not remember the exact filename.
To quickly obtain a directory listing they can simply run:
gs_exec dir
This will display the
directory contents without having to open a new window on the client. The
contents of the directory (folder) are quickly displayed in the SSH2/Telnet Window for 2000 ms (two seconds) or the time specified by the /scmddelay gs_clnt.exe command line option
SSH2/Telnet
file transfer capabilities are available with Windows
when using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server and GSW Windows Clients.
File transfer via SSH2/Telnet is convenient as there is no need for an FTP server to be installed and you are
not limited by file sizes as with many email attachments.
Secure file
transfer with Telnet is possible with the GSW Telnet Server and GSW Windows
Clients. When encryption is enabled file, transfers are encrypted (see page 94)!
Secure file
transfer with SSH using very strong encryption is always enabled when
using GSW SSH clients.
Efficient file transfers
from the server to the client computer are easily accomplished when using the
Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client.
A utility called GS_PUT
is included in the SSH2/Telnet server installation directory.
Command: gs_put
Description: Command
line utility that copies a file from the Server to the Client device/computer.
Syntax: gs_put [/s]
[/e[<log_file_path]] <source_file_path> <destination_file_path>
Arguments: There
are 2 required arguments and 2 optional arguments.
Required Arguments
a.
<source_file_path> The
file path to the file on the server
(Uses
Server computer drive letters and directories)
b.
<destination_file_path>
The file path for the destination on the client
(Uses
Client computer drive letters and directories)
Optional
Arguments
c.
/s Silent mode
operation for GS_Put
Disables
the display of file transfer progress or other non-error information messages to
user
d.
/e[log_file_path] Silent
mode for error messages to the user
The /e argument is used to disable the
display of error messages to the user
If
the optional file path is included then the error messages are sent to the specified
file on the Server. Note: No spaces are allowed between the /e and the log file path.
Example - Utilities: File Transfer
Server to Client
gs_put f:\corba\hints\dealers.docx
c:\books\dealers.docx
This will copy the file
f:\corba\hints\dealers from the server
to the client computer and save it as c:\books\dealers.docx.
You will see the progress and completion messages.
Figure 135: File Transfer GS_Put
Progress Status
Figure 136: File Transfer GS_Put
- Transfer Complete
Example - Utilities: File Transfer
Server to Client – Silent Mode
gs_put /s f:\corba\hints\dealers.docx
c:\books\dealers.docx
When the silent mode
option is used the user will not see the progress or completed informative
messages. Below is an example.
Figure 137: File Transfer GS_Put
- Silent Mode
Even though /s silent mode option is used error
messages will still be displayed to the user. For example, the destination file
path was misspelled below and the error message is displayed to the user.
gs_put /s f:\corba\hints\dealers.docx c:\nooks\dealers.docx
Figure 138: File Transfer -
GS_Put - Error Message Displayed
Example - Utilities: File Transfer
Server to Client – Silent Mode Errors
In some cases, the administrator
may want to suppress displaying error messages to the user.
This can be accomplished
using the silent mode for errors /e
argument.
gs_put
/s /e f:\corba\hints\dealers.docx c:\nooks\dealers.docx
Using
the previous example with the /e
argument results in the display show below.
Figure 139: File Transfer - GS_Put
- Error Message Suppressed
Even though an error
occurred due to the misspelled file name, no error message is displayed to the
user.
Taking this example one
step further, the administrator can have the error messages sent to a log file
by including a file path to the /e
argument. The administrator must provide a log file name and path.
For example
gs_put /s /ef:transferlog\tlog.txt f:\corba\hints\dealers.docx
c:\nooks\dealers.docx
This will send any
error messages to the server file tlog.txt
at the specified path on the f: drive.
If the file does not exist it will automatically be created.
Figure 140:
File Transfer - GS_Put - Send Error Messages to a File
A screen shot of the
error message in the log file is shown below.
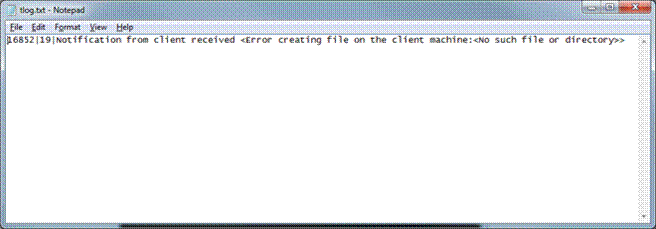
Figure 141: File Transfer - GS_Put - Error Message File
NOTE: You must use the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet client to use the GS_PUT file transfer utility.
The gs_put errorlevels
are described later in this section (page 271).
Efficient file transfers
from the Client to the Server computer are easily accomplished when using the Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client.
A utility called GS_GET
is included in the SSH2/Telnet server installation directory.
Command: gs_get
Description: Command
line utility that copies a file from the Client to the Server Computer.
Syntax: gs_get
<source_file_path> <destination_file_path>
Arguments: There
are 2 required arguments.
a.
<source_file_path> The file path to the file on the client
(Uses
Client computer drive letters and directories)
b.
<destination_file_path> The file path for the destination on the server
(Uses
Server computer drive letters and directories)
Optional
Arguments (Please see GS_Put for examples of the optional arguments)
c.
/s Silent mode operation for GS_Get
Disables
the display of file transfer progress or other non-error information messages
to user
d.
/e Disable the display of error messages to the user
e.
/e[log_file_path]
Disable
the display of error messages to the user but send them to the specified file.
Use server drive letters.
Example - Utilities: File Transfer
Client To Server
gs_get c:\books\dealers.doc d:\corba\hints\dealers.doc
This will copy the file
c:\books\dealers.doc from the
client computer and save it as d:\corba\hints\dealers.doc
on the server.
NOTE: You must use the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client to use the GS_GET file transfer utility.
The gs_get errorlevels are
described later in this section (page 273).
gs_put.exe uses the shell errorlevel variable to
report transfer results to the shell. The shell errorlevel variable reports transfer
results to the shell. The errorlevel variable is usually used in batch files in
automated processing environments.
|
Error
Level
|
ERROR VALUE
|
DESCRIPTION
|
|
0
|
|
Transfer Successful
|
|
1
|
ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
|
Transfer aborted: Internal shared memory could not be
accessed
|
|
2
|
ERROR_USAGE
|
Transfer aborted: Command line invalid.
|
|
3
|
ERROR_SOURCE_FILE
|
Transfer aborted: Source file could not be accessed.
|
|
4
|
ERROR_INFO_SLOT_ENV
|
Transfer aborted: Internal environment variable was not
found.
|
|
5
|
ERROR_INVALID_INFO_SLOT
|
Transfer aborted: Internal environment variable had invalid
value.
|
|
6
|
ERROR_SYNC_OBJECTS
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
7
|
ERROR_GET_MUTEX
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
8
|
ERROR_ABANDONED
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
9
|
ERROR_SET_EVENT
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
10
|
ERROR_OS1
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
11
|
ERROR_OS2
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
12
|
ERROR_WAIT
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
13
|
|
Transfer aborted: Unexpected notification from the agent
|
|
14
|
ERROR_SET_CONTROL_HANDLER
|
Transfer aborted: The CTRL-C handler could not be set.
|
|
15
|
UNDEFINED
|
|
|
16
|
ERROR_INVALID_CLNT
|
Transfer aborted: Client software is not the GSW Windows Client.
|
|
17
|
ERROR_GET_GSCLNT
|
Transfer aborted: Client type could not be determined.
|
|
18
|
ERROR_DISK_FULL
|
Transfer aborted: Disk is full on client.
|
|
19
|
ERROR_STDIO
|
Transfer aborted: Call to the standard C Library failed
|
|
20
|
ERROR_WIN32
|
Transfer aborted: WIN32 Subsystem Error
|
|
21
|
ERROR_SYNC
|
Transfer aborted: Session encountered unrecoverable synchronization
errors. User needs to establish a new session before a file transfer can be
used again.
|
|
22
|
UNDEFINED
|
|
|
23
|
ERROR_TCP_SEND
|
Transfer aborted: Connection broken during transfer.
|
|
24
|
ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
|
Transfer aborted: User pressed CTRL-C or CTRL-Break
|
|
25
|
ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
|
Transfer aborted: Session became suspended.
|
Table 53 - GS_PUT Error Levels
The usage of the errorlevel variable in an
automated file transfer batch file might have the form:
Example - Utilities: GS_PUT
Errorlevel Usage in batch file
@if errorlevel
25 goto ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
@if
errorlevel 24 goto ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
@if
errorlevel 23 goto ERROR_TCP_SEND
@if
errorlevel 21 goto ERROR_SYNC
@if errorlevel
20 goto ERROR_WIN32
@if errorlevel
19 goto ERROR_STDIO
@if errorlevel
18 goto ERROR_DISK_FULL
…
@if
errorlevel 3 goto ERROR_SOURCE_FILE
@if
errorlevel 2 goto ERROR_USAGE
@if
errorlevel 1 goto ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
@if errorlevel 0
goto ERROR_SUCCESS
@:ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
@echo ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
@goto exit
@:ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
@echo
ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_TCP_SEND
@echo
ERROR_TCP_SEND
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_SYNC
@echo
ERROR_SYNC
@goto exit
@:ERROR_WIN32
@echo
ERROR_WIN32
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_STDIO
@echo
ERROR_STDIO
@goto exit
@:ERROR_DISK_FULL
@goto exit
…
@:ERROR_SOURCE_FILE
@echo ERROR_SOURCE_FILE
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_USAGE
@echo
ERROR_USAGE
@goto exit
@:ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
@echo ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
@goto exit
@:ERROR_SUCCESS
@echo FILE TRANSFER
SUCCESSFUL
@:exit
NOTE: An expanded example template of the above example is located
in the SSH2/Telnet Server installation folder.
gs_get.exe uses the shell errorlevel variable to
report transfer results to the shell. The shell errorlevel variable reports
transfer results to the shell. The errorlevel variable is usually used in batch
files in automated processing environments.
|
Error
Level
|
ERROR VALUE
|
DESCRIPTION
|
|
0
|
|
Transfer Successful
|
|
1
|
ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
|
Transfer aborted: Internal shared memory could not be
accessed
|
|
2
|
ERROR_USAGE
|
Transfer aborted: Command line invalid.
|
|
3
|
ERROR_TARGET_FILE
|
Transfer aborted: Target file could not be accessed.
|
|
4
|
ERROR_INFO_SLOT_ENV
|
Transfer aborted: Internal environment variable was not
found.
|
|
5
|
ERROR_INVALID_INFO_SLOT
|
Transfer aborted: Internal environment variable had
invalid value.
|
|
6
|
ERROR_SYNC_OBJECTS
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
7
|
ERROR_GET_MUTEX
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
8
|
ERROR_ABANDONED
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
9
|
ERROR_SET_EVENT
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
10
|
ERROR_OS1
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
11
|
ERROR_OS2
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
12
|
ERROR_WAIT
|
Internal – report to GSW
|
|
13
|
|
Transfer aborted: Unexpected notification from the agent
|
|
14
|
ERROR_SET_CONTROL_HANDLER
|
Transfer aborted: The CTRL-C handler could not be set.
|
|
15
|
ERROR_INVALID_CLNT
|
Transfer aborted: The transfer software is not the GSW Windows
Client.
|
|
16
|
ERROR_GET_GSCLNT
|
Transfer aborted: Client software type cannot be determined.
|
|
17
|
UNDEFINED
|
|
|
18
|
ERROR_DISK_FULL
|
Transfer aborted: Disk is full on client.
|
|
19
|
ERROR_STDIO
|
Transfer aborted: Call to the standard C Library failed
|
|
20
|
ERROR_WIN32
|
Transfer aborted: WIN32 Subsystem Error
|
|
21
|
ERROR_SYNC
|
Transfer aborted: Session encountered unrecoverable
synchronization errors. User needs to establish a new session before a file
transfer can be used again.
|
|
22
|
UNDEFINED
|
|
|
23
|
ERROR_TCP_SEND
|
Transfer aborted: Connection broken during transfer.
|
|
24
|
ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
|
Transfer aborted: User pressed CTRL-C or CTRL-Break
|
|
25
|
ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
|
Transfer aborted: Session became suspended.
|
Table 54 - GS_GET Error Levels
The usage of the errorlevel variable in an
automated file transfer batch file might have the form:
An example for GS_GET
Example - Utilities: GS_GET
Errorlevel Usage in batch file
@:begin
c:\GS_UTS\gs_get %1
%2
@if
errorlevel 25 goto ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
@if errorlevel
24 goto ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
@if errorlevel
23 goto ERROR_TCP_SEND
@if errorlevel
21 goto ERROR_SYNC
@if
errorlevel 20 goto ERROR_WIN32
@if errorlevel
19 goto ERROR_STDIO
@if errorlevel
18 goto ERROR_DISK_FULL
@if errorlevel
16 goto ERROR_GET_GSCLNT
@if
errorlevel 15 goto ERROR_INVALID_CLNT
@if errorlevel
14 goto ERROR_SET_CONTROL_HANDLER
@if
errorlevel 13 goto ERROR_UNEXPECTED_NOTIFICATION
@if errorlevel
12 goto ERROR_WAIT
@if
errorlevel 11 goto ERROR_OS2
@if errorlevel
10 goto ERROR_OS1
@if errorlevel
9 goto ERROR_SET_EVENT
@if errorlevel
8 goto ERROR_ABANDONED
@if errorlevel
7 goto ERROR_GET_MUTEX
@if
errorlevel 6 goto ERROR_SYNC_OBJECTS
@if
errorlevel 5 goto ERROR_INVALID_INFO_SLOT
@if
errorlevel 4 goto ERROR_INFO_SLOT_ENV
@if errorlevel
3 goto ERROR_TARGET_FILE
@if errorlevel
2 goto ERROR_USAGE
@if errorlevel
1 goto ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
@if errorlevel 0
goto ERROR_SUCCESS
@:ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
@echo
ERROR_SESSION_SUSPENDED
@goto exit
@:ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
@echo ERROR_ABORTED_BY_USER
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_TCP_SEND
@echo ERROR_TCP_SEND
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_SYNC
@echo
ERROR_SYNC
@goto exit
@:ERROR_WIN32
@echo
ERROR_WIN32
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_STDIO
@echo
ERROR_STDIO
@goto exit
@:ERROR_DISK_FULL
@echo ERROR_DISK_FULL
@goto exit
@:ERROR_GET_GSCLNT
@echo ERROR_GET_GSCLNT
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_INVALID_CLNT
@echo
ERROR_INVALID_CLNT
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_SET_CONTROL_HANDLER
@echo
ERROR_SET_CONTROL_HANDLER
@goto exit
@:ERROR_UNEXPECTED_NOTIFICATION
@echo ERROR_UNEXPECTED_NOTIFICATION
@goto exit
@:ERROR_WAIT
@echo ERROR_WAIT
@goto exit
@:ERROR_OS2
@echo
ERROR_OS2
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_OS1
@echo ERROR_OS1
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_SET_EVENT
@echo ERROR_SET_EVENT
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_ABANDONED
@echo
ERROR_ABANDONED
@goto exit
@:ERROR_GET_MUTEX
@echo ERROR_GET_MUTEX
@goto exit
@:ERROR_SYNC_OBJECTS
@echo
ERROR_SYNC_OBJECTS
@goto exit
@:ERROR_INVALID_INFO_SLOT
@echo ERROR_INVALID_INFO_SLOT
@goto exit
@:ERROR_INFO_SLOT_ENV
@echo ERROR_INFO_SLOT_ENV
@goto exit
@:ERROR_TARGET_FILE
@echo ERROR_TARGET_FILE
@goto exit
@:ERROR_USAGE
@echo ERROR_USAGE
@goto
exit
@:ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
@echo ERROR_SHARED_MEMORY
@goto exit
@:ERROR_SUCCESS
@echo ERROR_SUCCESS
@goto begin
@:exit
@goto begin
The System Administrator
may need to reboot a Windows system remotely. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server provides a command line utility that reboots a Windows
computer.
Command: GS_Rbt
Description:
Reboot a Windows
computer. The computer will reboot about 40 seconds after the command is
executed. GUI users will receive a notification.
Syntax: Gs_Rbt [Computer]
Arguments: There
is 1 optional argument
[computer
name] - the name of the computer to reboot... If the computer name is omitted
then the Windows computer that the command is executed will reboot.
Notes: Administrative
privileges are required to run this command.
Warnings: The
system administrator must be sure that they want to reboot, as all user
sessions will be disconnected.
Example - Utilities: Reboot Windows
Reboot the computer soloman
Gs_Rbt soloman
You will then be
prompted with:
You have requested to shutdown soloman.
If you continue all applications with unsaved data will be
forcibly closed in 40 seconds.
Do you really want to continue? [Yes/No]
You must type either Yes or No and press
<enter>. "Y" or "N" is not valid.
In approximately 40
seconds the Windows computer will reboot.
The System Administrator
may need to shut down a Windows system remotely. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server provides a command line utility that will shut down a Windows computer.
Command: GS_Shutd
Description:
Shutdown a Windows computer. The computer will shut down in about 40 seconds after the command is
executed. GUI users will receive a notification.
Syntax: Gs_Shutd
[Computer]
Arguments:
There is 1 optional argument
[computer
name] - the name of the computer to shut down. If the computer name is omitted
then the Windows computer that the command is executed will be shutdown.
Notes: Administrative
privileges are required to run this command.
Warnings: The
system administrator must be sure that they want to shut down, as all user sessions
will be disconnected.
Example - Utilities: ShutDown Windows
System
Shutdown the computer
soloman
Gs_Shutd soloman
You will then be
prompted with:
You have requested to shutdown soloman.
If you continue all applications with unsaved data will be forcibly
closed in 40 seconds.
Do you really want to continue? [Yes/No]
You must type either Yes or No and press
<enter>. "Y" or "N" is not valid.
In approximately 40 seconds
the Windows Computer will shut down.
Remote Registration Utility
Apply the serial number
from a remote location via SSH2/Telnet
.
In some instances, you
may need to apply the serial number from a remote location. The Georgia
SoftWorks Remote Registration Utility provides the capability. This can be done
when upgrading to a new version or permanently activating a trial version of
the software.
Syntax is:
GS_RR serial_number
Where serial_number is the serial number is
obtained from Georgia SoftWorks.
NOTE: You must have SSH2/Telnet connectivity to the server, either during the trial period or an already registered
installed copy.
To run the Remote Registration
utility:
1.
Send the Product ID to Georgia SoftWorks as defined on page 16.
2.
Georgia SoftWorks will email or fax the serial number back to you. The
serial number will look something like: D25EEAF8AF1692EB0F9A5DE28520FD8407F8632CC5D8
3.
Connect to the Server via SSH2/Telnet
that you want to register.
4.
Change to the SSH2/Telnet installation root folder. This is the folder
where the SSH2/Telnet server was installed.
5.
Run the Remote Registration Utility.
Example
- Remote REGISTRATION via SSH2/Telnet .
At the
command prompt enter:
gs_rr D25EEAF8AF1692EB0F9A5DE28520FD8407F8632CC5D8
and press
<ENTER>.
You
will receive a Banner String followed by three dots. The text wait is displayed
while the serial number is being validated.
Upon completion the
message "Registration Successful" will be displayed.
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global Bell Control see page 393
Or
use legacy style below
|
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server can intercept a special character written to
the application's screen and send a bell character to the terminal (in the
place of the intercepted character). The number of times that the bell will
sound is also configurable. The default count is 1. The Special Character, Location
and Bell Count, are defined using Registry Values.
Usually the application can identify a normally unused position on the
screen that can be used for the placement of the special character.
This location is
specified in the registry as described below.
Registry Parameters are located:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters
BellX - column
of the bell character, initialized to 0xffffffff, which makes it inactive.
BellY - row of
the bell character, initialized to 0xffffffff, which makes it inactive.
BellChar - value
of the bell character, initialized to 0x87
BellCnt -
value for the number of times that the bell will sound, initialized to 0x01
All four parameters
work for all types of clients, including the gs_admin. In order to disable the feature: set BellX or
BellY to 0xffffffff.
NOTE 1: The Special Character will be automatically
replaced with a space character on the screen.
NOTE 2: The top left screen position is defined as
1,1.
Example - Confirm Operation of
Special Bell Processing
Perform
these steps for a quick test to verify that the Special Bell Processing is operating.
This example is useful for testing purposes.
Objective:
The Bell will sound when the character 5 is entered on the 15th column of the 3rd
row on the screen.
As
indicated above user the registry editor to set values for the BellX to 15
(0f), BellY to 3 (03) and BellChar to ‘5’ (35).
Next start a SSH2/Telnet session. At the command
prompt, clear the screen go to 3rd line and start typing character 5
until you get to column 15. When you get to the 15th column you should hear the
bell and the digit 5 will not be visible because SSH2/Telnet server will replace it with
space.
Special Bell processing
is available for SAPConsole users.
For expected Bell Operation
after Session Saver Reconnects the SAPConsole must be launched via the Gswbell
utility. Use the appropriate command for your UTS edition (32-bit or 64-bit)
Command: gswbell for x86 (32-bit) UTS edition
Command: gswbell_x64 for x64(64-bit)UTS edition
Description:
GSWBell is a command
line program that is usually entered in your GSW UTS logon scripts. Please review
Logon Scripting. A command line argument is used to specify the SAPConsole.
Gswbell will launch SAPConsole.
Syntax: Gswbell <sapconsole
file path>sapcnsl.exe
[Sapconsole arguments]
Arguments:
Optional arguments
Any
SAPConsole arguments are simply added to the command line in the format required
by the SAPConsole
Notes: Administrative
privileges are required to run this command.
Example - Utilities: GSWBell for
SAPConsole
Launch SAPConsole with
GSWBell utility
C:\gs_uts\Gswbell c:\sap\sapcnsl.exe
TTY
Name
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server creates a tty name on a per
session basis. This is available for viewing or use by customer created programs.
The environment variable
created is:
gwtn_tty
And is set to /dev/ttypmmm, where mmm
represents the socket
number (handle) for user's session.
You may enable scroll bars
on the Windows client window. This is accomplished by changing the buffer size
for the DOS window. You must be careful that the application can handle a modified
buffer size. Unpredictable display results will occur if this is not the case.
For GSW Mobile Client
scrollbar options please see page 45.
Setting a Default Domain
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –Global Emulations see page 383
Or
use legacy style below
|
In some instances the System
administrator may want to eliminate the prompting for a domain when the user is
connecting to the SSH2/Telnet server. This can be accomplished by setting the
default domain registry variable. This works for 3rd party clients
only. Use the command line parameters to set the default domain for the Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client. (See page 76)
This is accomplished as
follows.
The key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\Domain
1.
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your screen.
2.
Click RUN
3.
Type REGEDIT
4.
Click OK
5.
Select Registry Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\Domain
6.
Select the menu item Edit and then click on Modify
7.
Enter the new value for the Domain
and click OK
The new Domain will take
effect for all new sessions.
This registry value is
initialized to "UNKNOWN" which disables a default domain. The empty
string means the default domain. This is equivalent to pressing enter when
prompted. This will eliminate prompting for users of all clients.
The user may override
the default domain when using a 3rd party client when connecting via
Telnet or SSH. When a default domain is set the GSW UTS does not prompt for the
domain and automatically applies the domain set in the registry.
If the user needs to
override the default domain, then the optional syntax described below can be
used when logging on to the UTS to select a different domain.
The domain can be
specified (along with the username) when the user is prompted for the Windows
User Name. The domain override syntax is different depending if you are connecting
via Telnet or SSH.
TELNET
When connecting via Telnet
the syntax is the domain name followed by the backslash followed by the
username.
domainname\username
SSH
When connecting via SSH
the syntax is the username followed by the “AT” sign followed by the domain
name.
username@domainname
The default port for
telnet is port 23 and NO configuration is required unless you want to change or
add telnet ports.
Note: These
features are available for the Telnet Server only.
To use a different
telnet port (other than the default) for the GSW Telnet Server you need to
create an entry like:
gstnet 55555/tcp
in the Services
file on the server and restart the GSW Telnet Server. Replace the 55555 with
another port number if necessary. You will have to explicitly specify the
alternate port number when starting the connection from 3rd party clients and
the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client (page 77).
On Windows
the services file is located in the directory:
<Windows Root>\system32\drivers\etc
The file is named Services.
The
capability exists to configure up to 100 ports for the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
Server to listen on. Use the etc/services file to configure port names gstnet1 through gstnet100.
The
following example will configure 5 Telnet Ports.
Edit the file Services
file as described above. Add the following entries. Notice that you may use any
of the one hundred port names and that they do not have to be in order.
gstnet1
23/tcp
gstnet2 14002/tcp
gstnet5
14005/tcp
gstnet6
14006/tcp
gstnet10 14010/tcp
Telnet
will now listen on the above five ports.
To
further take advantage of this feature you can use the environment variable:
gwtn_server_port
to access the port number associated with your current session.
To
view the port number associated with your session at the command prompt enter:
echo %gwtn_server_port%
If you have multiple
telnet ports configured you may want to have a different task process the information
that comes in on each port. Here is an example of a logon script
which uses the port information to branch to different tasks based on the port
number.
@if %gwtn_server_port%==23 goto label23
@if %gwtn_server_port%==14002 goto label14002
@if %gwtn_server_port%==14005 goto label14005
@if %gwtn_server_port%==14006 goto label14006
@if %gwtn_server_port%==14010 goto label14010
@echo port not found
@pause
@goto labelend
@:label23
@echo About to run app23
@pause
@rem Put your code to run23 app here
@goto labelend
@:label14002
@echo About to run app14002
@pause
@rem Put your code to run14002 app here
@goto labelend
@:label14005
@echo About to run app14005
@pause
@rem Put your code to run14005 app here
@goto labelend
@:label14006
@echo About to run app14006
@pause
@rem Put your code to run14006 app here
@goto labelend
@:label14010
@echo About to run app14010
@pause
@rem Put your code to run14010 app here
@goto labelend
@:labelend
Note: This feature applies to the Telnet Server only.
The
Georgia SoftWorks Java Client (GSJC) is an applet that allows you to add web-based
capabilities to your MS DOS or Win32 Console application. Leverage platform
independence for remote access to the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server by
providing access from the most popular browsers such as MS IE and Netscape.
Allow
telnet connectivity from any platform with TCP/IP based connectivity and a Java
1.1 (or higher) enabled browser. This can include platforms ranging from RF Terminals
to mainframe computers.
Many
of the powerful features found in the standard Georgia SoftWorks telnet client
such as Mouse support, DOS Character Mode Color Graphics, excellent keyboard support
and client-side printing are now available in the GSJC.
This
section contains information which webmasters need to create web pages including
the Georgia SoftWorks Java Telnet Client.
Java
language 1.1 or higher enabled browser.
The
above includes Internet Explorer 4.0 and higher, Netscape Communicator 4.7 and
higher.
The
Georgia SoftWorks Java Client may be distributed as a .jar file, .cab file, or
a set of class files.
- gsjc.jar - This is the
Java archive file for all browsers supporting .jar files. For example: Netscape
Communicator or Internet Explorer with the Java Plug-In (JRE 1.2)
OR
- gsjc.cab - This is the
cabinet file used for Internet Explorer Browsers when Java Plug-In is not
used.
Client-side printing requires the Java 1.2 Plug-In
(JRE 1.2)
(Unless you are using IE 4.0+)
- Java 1.2 Plug-In - This is required for client-side printing.
If you are using Internet Explorer 4.0 or higher you
can simply use the gsjc.cab file INSTEAD of the gsjc.jar and the Java 1.2 Plug-In
is not required.
Client-Side Printing is implemented through the print
command applet parameter. This parameter specifies the print command that is
used locally (client machine) to print the spool file. The print command specified
depends on the printing facilities available to your client machine.
For example:
AIX UNIX will use the
"lpr" command and
Windows 98 will use the "copy"
command and
Windows will use the "print"
command.
If the print commands parameter is not specified the
behavior is as follows.
Windows will print on the default printer using the
print command. Other operating systems will attempt to print using the Java
graphics engine (which does not always produce expected results).
The full capabilities that exist with the standard
Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client are available.
Applet
parameters are provided to supply configuration information to the telnet
server just as with the standard Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client. The
parameters include:
NOTE:
The syntax provided is an example and is different based on the type of browser
interpreting the commands.
Description:
host’s port to connect to. (see page 296)
Default:
Port 23
Syntax : <PARAM NAME=port
VALUE="23">
Description:
NT/2000/XP User ID
Default:
No default. The user will be prompted (see page 78)
Syntax: <PARAM NAME=user
value="Smith">
Description:
Password for NT/2000/XP User ID
Default:
No default. User will be prompted (see page 77)
Syntax: <PARAM
NAME=password value="mypassword">
Note:
Security may be compromised if this parameter is used.
Description:
NT/2000/XP Domain for the user (see page 77)
Default:
No Default, user will be prompted
Syntax: <PARAM
NAME=domain value="mydomain">
""
uses the default domain.
Description:
Indicates the address of the host computer to connect.
Default:
No default. User will be prompted (see page 73)
Syntax:
<PARAM NAME=address value="Host IP Address">
Description:
Places the work area in the top left corner of the rectangle specified for the
applet.
Default:
The default value is FALSE indicating that the work area is centered inside the
applet’s rectangle.
Syntax:
<PARAM NAME=useTopLeftLocation value="True|False">
Description:
Specifies if the classic MSDOS frame will be drawn around the work area of the
applet.
Default:
The default value is TRUE.
Syntax:
<PARAM NAME=useMSDOSFrame value="True|False">
Description:
Specifies if borders will be drawn around the applet. FALSE specifies that no
boarders shall be drawn and all non-work areas of the applet will be eliminated.
Default:
The default value is TRUE.
Syntax:
<PARAM NAME=useBorders value="True|False">
Description:
Tells the applet to use the bold font.
Default:
True
Syntax: <PARAM NAME=useBoldFont value="True|False">
Description:
Background color for the area around the GSJC Window.
Default:
000080 (This is blue)
Syntax:
<PARAM NAME=bkgColor value="000080">
The
format is RRGGBB in hex.
Description:
Heartbeat Time in seconds. (see page 156)
Default:
20
Syntax: <PARAM
NAME=HBTime value="20">
Description:
Enables Encryption and forces Login Encryption. (see page 95)
Default:
FALSE
Syntax: <PARAM
NAME=useEncryption value="true">
Additionally,
Complete Date Stream Encryption can be enabled via the logon scripts as per our
standard method. (see page 93).
Description:
Specifies the print command used by the client computer in conjunction with Enhanced
printing.
Default:
NT Systems will use print.exe
Non-NT
systems will use java printing through the graphics engine.
Syntax: <PARAM NAME=printCommand value="command.com
/C copy ??? lpt1:">
the ??? is a wildcard which will be replaced during printing by the actual
print file name. The above example assumes a printer on lpt1. The example
works on Win95/98. Please see the Enhanced printing (Page 226
) documentation
for further examples and details.
Provisioning
of the User, Password and Domain parameters by the applet will eliminate prompting
for these values by the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server.
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<META
NAME="GENERATOR" Content="Microsoft Visual Studio 6.0">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<OBJECT
classid="clsid:8AD9C840-044E-11D1-B3E9-00805F499D93"
WIDTH=640
HEIGHT=520
codebase="http://java.sun.com/products/plugin/1.2/jinstall-12-win32.cab#Version=1,2,0,0">
<PARAM NAME=JAVA_CODE
VALUE=GSJC.class >
<PARAM NAME=CABBASE
VALUE=GSJC.CAB >
<PARAM
NAME="type" VALUE="application/x-java-applet;version=1.2">
<PARAM NAME=port
VALUE="23">
<PARAM NAME=user value="test1">
<PARAM NAME=password
value="test1">
<PARAM NAME=domain value="">
<PARAM NAME=bkgColor
value="008000">
<PARAM NAME=HBTime
value="20">
<PARAM NAME=useEncryption
value="false">
<COMMENT>
<EMBED
type="application/x-java-applet;version=1.2"
WIDTH=640
HEIGHT=520
CODE=GSJC.class
archive=gsjc.jar
port="23"
user="test1"
password="test1"
domain=""
bkgColor="000080"
HBTime="20"
UseEncryption="false"
pluginspage="http://java.sun.com/products/plugin/1.2/plugin-install.html">
<NOEMBED>
</COMMENT>
No Java support for
applet.
</NOEMBED>
</EMBED>
</OBJECT>
</BODY>
</HTML>
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<META NAME="GENERATOR"
Content="Microsoft Visual Studio 6.0">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<!-- Insert HTML here
-->
<applet
code=GSJC.class
name=GSJC
width=640
height=520 >
<param name=cabbase
value=gsjc.cab>
<param name=port
value="23">
<param
name=user value="test1">
<param
name=password value="test1">
<param
name=domain value="">
<param
name=bkgColor value="008080">
<param
name=HBTime value="20">
<param
name=useEncryption value="false">
</applet>
</BODY>
</HTML>
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<META
NAME="GENERATOR" Content="Microsoft Visual Studio 6.0">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<!-- Insert HTML here
-->
<applet
code=GSJC.class
name=GSJC
archive VALUE=gsjc.jar
width=640
height=520 >
<param name=port
value="23">
<param name=user
value="test1">
<param
name=password value="test1">
<param
name=domain value="">
<param
name=bkgColor value="008080">
<param
name=HBTime value="20">
<param name=useEncryption
value="false">
</applet>
</BODY>
</HTML>
The
page below may be needed for browsers, which do not support cab files and jar files.
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<META NAME="GENERATOR"
Content="Microsoft Visual Studio 6.0">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<!-- Insert HTML here
-->
<applet
code=GSJC.class
name=GSJC
width=640
height=520 >
<param name=port
value="23">
<param
name=user value="test1">
<param
name=password value="test1">
<param
name=domain value="">
<param name=bkgColor
value="008080">
<param name=HBTime
value="20">
<param name=useEncryption
value="false">
</applet>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Applet
uses size specified through the width and height parameters. The telnet window
uses Java's “courier” font of size, which gives best fit for the applet dimensions,
specified. Some experimentation may be necessary to get desired appearance.
Note: This feature applies to the Telnet Server only.
The
Georgia SoftWorks Java Telnet Client (GSJC) is a standalone application that allows
telnet connectivity to the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server without a browser.
Using
the Georgia SoftWorks Java Client provides many of the powerful features such
as Complete Data Stream Encryption, Mouse support, DOS Character Mode Color
Graphics, excellent keyboard support and client-side printing. Additionally,
this is accomplished without any web server setup. The client-side parameters are
passed from the command line or menu options at the client computer.
Java
language 1.1 or higher.
The following files
should be installed in a directory or folder.
Writer.class
Console.class
GetOpt.class
GS_Crypt.class
GS_NullCrypt.class
GS_CryptixCrypt.class
GS_Print.class
GSJC$1.class
GSJC$2.class
GSJC$dlgConnectCancelHandler.class
GSJC$dlgConnectOKHandler.class
GSJC$mniConnectHandler.class
GSJC$mniDisconnectHandler.class
GSJC$mniExitHandler.class
GSJC$mniUseEncryptionHandler.class
GSJC.class
Reader.class
SpChars.class
Telnet.class
Console$1.class
buttons.gif
msdos.gif
Additionally, a path must be set to give access to the JavaSoft\Jre\1.2\bin directory or
folder.
For
Example: java GSJC -utest1 -ptest1 -d.
-c -h209.86.40.83
Command
lines parameters are the same as with the standard Georgia SoftWorks Telnet
Client. (See page 77)
Encryption
requires the use of JRE 1.2 (Java 2) and Cryptix libraries. These are available
from Cryptix, which is an international volunteer effort to produce robust, open-source
cryptographic software libraries. Cryptix products are free, both for commercial
and non-commercial use and are being used by developers all over the world.
www.cryptix.org
The
product required is called Cryptix. JCE was planned for official release in
February 2000.
Download
the cryptix-jce-20000211.zip from http://www.cryptix.org/products/jce/
After
you unzip the cryptix files, copy these two files:
cryptix-jce-api.jar
cryptix-jce-provider.jar
to your jre/lib/ext
directory.
My MSDOS applications execute very slow, even on a high-performance
system. Is there anything I can do?
Yes, you can use the Georgia
SoftWorks DOSBOSS to boost the performance of your MSDOS application when running
under NT. (Page 109)
Can I use a port other than port 23
for the Telnet Server?
Yes, you can use an
alternative port for the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server.
Note: This feature applies to the Telnet Server only.
You will need to create
an entry like:
gstnet 55555/tcp
in the Services
file on the server and restart the GSW Telnet Server. Replace the 55555 with
another port number if necessary. You will have to explicitly specify the alternate
port number when starting the connection from 3rd party clients and the Georgia
SoftWorks Telnet Client (page 77).
On Windows
the services file is located in the directory:
<Windows
Root>\system32\drivers\etc
The file is named Services.
Can I SSH2/Telnet
to the SSH2/Telnet server and then SSH2/Telnet
to another server?
The short answer is
Yes. If you SSH2/Telnet to the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server and you then want to SSH2/Telnet
to another GSW SSH2/Telnet server you simply run the gs_clnt.exe/gs_ssh.exe
program at the DOS command line. However if you want to SSH2/Telnet
to a non-Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
server you will need a 3rd party DOS client that can be executed
from the command line.
Very interesting
opportunities exist with this capability. For example, a user may want secure access
to their corporate network from remote locations such as a customer site or
hotel. They can connect to the GSW SSH Server from the remote site. Once the secure
connection has been established to the SSH server, they can now telnet to a telnet
server on the corporate network. There are many possibilities mixing and matching
this type of arrangement. Remember that you can only use a Telnet client to
connect to a Telnet Server and only use a SSH client to connect to a SSH
Server.
I can't logon fromSSH2/Telnet,
what should I do?
The typical rule is
that if you can log in locally to the Windows
machine then you can logon from SSH2/Telnet.
Make sure that you can logon locally. Users must have "log on
Locally" access permissions. From "User Manager" or "User
Manager for Domains" choose the menu item "Policies" which is a
drop down. From the drop down choose "User Rights". A "User Rights
Policy "dialog appears allowing you to add the "Log on Locally” Right
for the group.
However, if the local
group Gwtn Users exists you must be a member of this group to logon via SSH2/Telnet
. If you continue to have trouble please see the technical support (page 424) section of this User’s Guide to expedite resolution of the issue.
I am the Administrator but gs_admin.exe says I do not have
permission to run Session Administrator.
To use the GSW Session
Administrator a user must belong to the local group Gwtn Monitors. The
system administrator must first create the group Gwtn Monitors. Next all
users allowed to use the Session Administrator must be added to the group. Windows
does not instantaneously update the group membership after the user manager is
closed. Windows will update the group memberships if you logoff/logon the desktop.
In the event that this does not work you may have to restart the Windows
server after creating the group and adding users.
I want to set the background color on the client Window
and make it distinct from the standard MSDOS Windows.
You need to use the
COLOR Command in a logon script. Here is the syntax:
COLOR [attr]
Sets the default
console foreground and background colors.
attr Specifies color
attribute of console output
Color attributes are specified
by TWO hex digits -- the first corresponds to the background; the second the
foreground. Each digit can be any of the following values:
0 =
Black 8 = Gray
1 =
Blue 9 = Light Blue
2 =
Green A = Light Green
3 = Aqua
B = Light Aqua
4 =
Red C = Light Red
5 =
Purple D = Light Purple
6 = Yellow E
= Light Yellow
7 =
White F = Bright White
If no argument is
given, this command restores the color to what it was when CMD.EXE started.
This value either comes from the current console window, the /T command line
switch or from the DefaultColor registry value.
The COLOR command sets
ERRORLEVEL to 1 if an attempt is made to execute the COLOR command with a foreground
and background color that are the same.
Example: "COLOR fc"
produces light red on bright white
I want to change the size of
the window. The client is set to 80x40 but when it connects to the server it
reverts back to 80x25.
The mode command will
address this issue.
Mode con[:] [cols=c] [lines=n]
Try putting
mode con: LINES=40
in your logon script.
How do I eliminate prompting for the various settings when
using 3rd party clients?
Environment and
registry variables exist such that when defined will be used as defaults eliminating
the prompting for those values when connections are established. The environment
variables can be set in either Global or Per User Logon Scripts. For a list of
the environment variable please see the section on 3rd party clients
(page 166) in the User’s Guide and/or the section on Environment (page331)
and Registry variables (page 334).
Can I eliminate prompting for the Host, UserID and
Password?
When using the Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client the Host, User ID and Password can be specified as
a command line options. You can modify the command line options by editing the
file GS_SClnt.bat. Please see
page 76 for the section in the User’s Guide on
Georgia SoftWorks Desktop Client Command line options.
Can I eliminate prompting for the Domain?
Yes. For all 3rd
party clients, a registry variable can be set that will contain the default
domain for all connections. This is described on page 282.
When using the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
client you may use command line options to set the default domain to eliminate
prompting. This is described on page 77.
Can I connect from older systems with DOS or Windows 3.1?
Yes, however you must
have a 16-bit client. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client is 32 bit and requires Windows 95/98 or Windows
. Several 16-bit clients can be found on the Internet.
Can I have the user
deposited into a specific directory upon connection?
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –User – Login Script see page 406
Or
use legacy style below
|
Yes. You may set the
environment variable gwtn_home_dir
in the logon script on either a global or per user basis.
set gwtn_home_dir=d:\users\tom
Can I restrict user access to
specific directories?
In order to restrict user’s
access to specific directories you must first make sure that all of your drives
use NTFS. Next use Windows Explorer|File|Properties|Security|Permissions to grant
or deny access to specific drives, directories, or files.
Is there any way to get the bell to sound on the client?
For customers that have
control over the development of their own applications the answer is yes.
Please see page 278 for detailed instructions.
Is there any way to get the bell to sound on the client
when using SAPConsole after a reconnect?
Please see page 280
for special bell processing utility Gswbell.exe when using SAPConsole.
Can I start and stop services when connected via SSH2/Telnet
?
Yes. The commands “net start” and “net stop” provide this ability. Please
execute the “net start ?” or
“net stop ?” from a Windows command prompt for the details on the “net” commands and parameters.
Can I configure user
information when connected via SSH2/Telnet
?
Yes. The commands “net user …”, “net account …” etc. provide this capability. Please
execute the “net user ?” or “net account ?” from a Windows
command prompt for the details on the “net”
commands and parameters.
Control-C is not working as expected. What can I do?
Several valid behaviors
exist for Control-C. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server allows explicit configuration of the behavior for control-c on either a
global or per user basis by using the environment variable gwtn_ctrl_c_mode (see
page 164).
I changed the IP Address of my Server and SSH2/Telnet does not work anymore.
After changing the IP address,
you should stop and start the SSH2/Telnet
Server. This can be done through the Windows
Control Panel. If this does not help you must reboot the server.
I get extra form feeds when printing from certain applications
when using the Enhanced Print mode. What can I do?
The client-side printing
option -f may help suppress additional form feeds. Please see page 80.
How can I print to Portable Printers when I am using
SAPConsole?
Using the GSW True Client-Side
Printing you CAN print to portable printers when in SAPConsole. Please see page
316.
Why do my print jobs print on somebody else’s printer?
It is required that each
user be logged in only once for the Enhanced, Open and Pass-through Print methods
to operate correctly. That means that each workstation/RF device must use a
different User Id when connecting to the server. When a print job for one of
these print methods is redirected, the redirection is based on the owner of the
print job. The owner is the same as the User Id, thus if more than one User Id
is connected then the print job is redirect and the destination selected will
at best be random.
I want to modify the polling
interval that the gs_agent polls the GwtnPrinerx print queues. Is this possible?
|

|
Use
the GSW GUI Configuration Tool –User – Power Features - Printing see page 406
Or
use legacy style below
|
Yes. You may set the
environment variable gwtn_local_print_poll_interval
in the logon script on a per user basis.
set gwtn_local_print_poll_interval = x
Where x specifies the poll interval in seconds with which the gs_agent
polls the GwtnPrinterx print queues. Values range from 1 to 10 seconds where the
default is 5 seconds.
I am using FoxPro and my system is running out of memory.
Upon inspection of the Task Manager I can see that my NTVDMs are consuming all
available memory. What should I do?
The solution for many
customers is to limit the memory which FoxPro can use per instance. This can be
done via the config.fp or config.fpw file. The memory may be limited
using the MEMLIMIT command. More information can be found by view Microsoft Knowledge
Base article 123281. There is abundant information on this topic on the internet
using search engines.
One or more keys are not working properly under VT220
Emulation. Please Advise.
VT220
Terminal Emulators from different vendors may not have standard key mappings.
For
each key that does not work please verify that the escape sequence programmed
in your terminal emulator matches the table below. Most of the emulators (the
program running on your RF device, client PC or terminal) provide
the capability to edit the escape sequence sent when a specific key is pressed.
The table below shows
the escape sequences that the GSW SSH2/Telnet Server expects to receive from the terminal running the
VT220 emulation.
|
Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server
https://www.georgiasoftworks.com/
Industry Standard VT220 Key
Mapping
|
|
|
Key
Code
|
Action
|
|
Key
Code
|
Action
|
|
|
ESC [ D |
Cursor left |
|
ESC O P |
F1 |
|
|
ESC O D |
Cursor left |
|
ESC O Q |
F2 |
|
|
ESC [ B |
Cursor down |
|
ESC O R |
F3 |
|
|
ESC O B |
Cursor down |
|
ESC O S |
F4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ A |
Cursor up |
|
ESC [ M |
F5 |
|
|
ESC O A |
Cursor up |
|
ESC [ 1 5 ~ |
F5 |
|
|
ESC [ C |
Cursor right |
|
ESC [ 1 7 ~ |
F6 |
|
|
ESC O C |
Cursor right |
|
ESC [ 1 8 ~ |
F7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESC O l |
Keypad STAR |
|
ESC [ 1 9 ~ |
F8 |
|
|
ESC O m |
Keypad MINUS |
|
ESC [ 2 0 ~ |
F9 |
|
|
ESC O M |
Keypad ENTER |
|
ESC [ 2 1 ~ |
F10 |
|
|
ESC O n |
Keypad DELETE |
|
ESC [ 2 3 ~ |
F11 |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ 2 4 ~ |
F12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESC O p |
Keypad 0_INS |
|
ESC [ 2 5 ~ |
SHIFT-F1 |
|
|
ESC O q |
Keypad 1_END |
|
ESC [ 2 6 ~ |
SHIFT-F2 |
|
|
ESC O r |
Keypad 2_DOWN |
|
ESC [ 2 7 ~ |
SHIFT-F3 |
|
|
ESC O s |
Keypad 3_PAGEDOWN |
|
ESC [ 2 8 ~ |
SHIFT-F4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESC O t |
Keypad 4_LEFT |
|
ESC [ K |
SHIFT-F5 |
|
|
ESC O u |
Keypad 5 |
|
ESC [ 3 1 ~ |
SHIFT-F6 |
|
|
ESC O v |
Keypad 6_RIGHT |
|
ESC [ 3 2 ~ |
SHIFT-F7 |
|
|
ESC O w |
Keypad 7_HOME |
|
ESC [ 3 3 ~ |
SHIFT-F8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESC O x |
Keypad 8_UP |
|
ESC [ 3 4 ~ |
SHIFT-F9 |
|
|
ESC O y |
Keypad 9_PAGEUP |
|
ESC [ 3 5 ~ |
SHIFT-F10 |
|
|
ESC [ U |
Page down |
|
ESC [ 3 6 ~ |
SHIFT-F11 |
|
|
ESC [ 6 ~ |
Page down |
|
ESC [ 3 7 ~ |
SHIFT-F12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ H |
Home |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ 1 ~ |
Home |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ V |
Page up |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ 5 ~ |
Page up |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ 2 ~ |
Insert |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ 3 ~ |
Delete |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ 4 ~ |
End |
|
|
|
|
|
ESC [ Z |
Tab Backward |
|
|
|
Table 55 - VT220 Industry Standard Key Mapping
Discussion: Orphaned NTVDM's and Windows
SSH2/Telnet Servers
NTVDM's
are Windows Virtual DOS Machines. For Windows to run DOS programs, Windows
creates a Windows VDM that provides a DOS environment for the DOS program to reside.
When
DOS applications are executed a NTVDM is created. A normal SSH2/Telnet scenario is to connect to a Windows system and run a
DOS application. Windows will create a NTVDM. This is all fine and normal.
Normally
during a SSH2/Telnet session running a DOS application, upon completion of
the application the user will exit the application properly. In this situation
the NTVDM is properly terminated.
However,
problems occur when a SSH2/Telnet session running a DOS application abnormally
terminates.
The
SSH2/Telnet session will normally terminate however the NTVDM
will not terminate. This leaves what is called an orphaned NTVDM. Some term
this rouge or phantom NTVDMs or processes.
These
orphaned NTVDM's are a serious
problem to the Windows System. They will start consuming all the processing
resources of the Windows system that results in the severe degradation of all other
processes on the system. This is not just a slight slowing down of the system
but a slowing down to the point of the system being useless by most users’ standards.
The most common way to clear the NTVDM is to reboot the Windows system. However,
if you are skilled you can kill the orphaned processes.
Any
abnormal termination of a client can cause an orphaned NTVDM. One easy way to
create an NTVDM with SSH2/Telnet simply to power off the Client PC while running a DOS
program via SSH2/Telnet. For example:
1. SSH2/Telnet from a remote Client PC to a Windows System.
2. Run a DOS application.
(Such as Edit, Norton Commander etc.).
At this point a NTVDM is created.
You can observe this on the SSH2/Telnet Server by:
a. Typing Ctrl-Alt-Delete on the server and select
the Task List
1.
Select processes and observer the NTVDM that was created.
3. Power down the Client
PC.
4. On the SSH2/Telnet Server, observe that the NTVDM is still running. In
many cases you will notice that after a few minutes the processing percentage
will increase to 90+%.
Having
multiple SSH2/Telnet sessions connected running DOS applications when an
abnormal termination occurs can exacerbate this problem.
Frequent scenarios for abnormal terminations
1.
Power Failure for Client PC.
1. Power Hit in building
2. Breaker trip, Client PC
or Power strip accidentally unplugged
2. Client PC powered down without
properly exiting the DOS application
3. Client PC OS locks up
4. Link Failure
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server for Windows automatically provides advanced detection and elimination
for orphaned NTVDM's. Unlike others that claim to handle this serious problem,
the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server actually detects and eliminates these
process consuming tasks in a remarkably quick time minimizing the impact on
other users and tasks on the system. The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client accomplishes detection via the configurable heartbeat timer and third
party SSH2/Telnet clients utilize the configurable Server Side Heartbeat Timer.
Upon detection sophisticated algorithms are used to identify orphaned NTVDM and
eliminate them.
Information derived and extracted from the Microsoft
Knowledge base.
Windows provides a fully integrated command prompt that
enables you to launch both Windows-based and MS-DOS-based applications.
Although the concept of running an MS-DOS-based application in a Windows-based
environment may be familiar to you, Windows handles this somewhat differently than Windows
(16-bit) does.
The
essential difference lies in the command prompt itself; under Windows, the command prompt is
a 32-bit Windows based application, not the virtual MS-DOS machine you would
expect from Windows. Under Windows, until you start an
MS-DOS-based application, no virtual MS-DOS machine is created. Furthermore,
once you start an MS-DOS-based application, its virtual MS-DOS machine is used
for all subsequent MS-DOS-based applications started from the same command
prompt.
As in Windows, each MS-DOS-based application can have a
program information file (PIF). If there is no PIF for a particular application,
the default PIF, _DEFAULT.PIF, is used. Because Windows
only uses the PIF from the first application started in any given command
prompt, you may need to take special care in the way you start your applications.
For example, if you design a PIF that allocates some EMS memory, it is important
that you start the associated application first; otherwise, the EMS memory may
never be allocated. You may start a Windows
command prompt and then run the MS-DOS command, MEM, to see how much memory you
have free. Because MEM is another MS-DOS-based application, Windows creates a virtual MS-DOS machine, probably using _DEFAULT.PIF. After MEM finishes, you
start the application you created the PIF for. Unfortunately, because _DEFAULT.PIF
doesn't instruct Windows to allocate EMS memory, your application reports that it
can find no EMS memory. Rechecking the PIF you created does not solve the
problem. You need to start another command prompt and then make sure to start
your EMS-requiring application first, before you start any other MS-DOS-based
applications.
There is one more difference to be aware of: each PIF
contains a pointer to AUTOEXEC and CONFIG files. Usually these default to the Windows versions, AUTOEXEC.NT and CONFIG.NT. If you want to change environment variables for
your MS-DOS-based applications, you need to point their PIFs to different files
or modify the default ones. (To see these files and their locations, run PIF
Editor and choose Windows NT.)
If
you are not satisfied with the performance of your MS-DOS-based applications on
Windows NT, try the following:
Windows keeps the same setting
in the property (right click) of the MS-DOS-based applications.
•
If the application is in a window and the video display performance is slow, try
full-screen mode. Windows “screen folder”
provides this setting.
•
Disable the Compatible Timer Hardware feature in the _DEFAULT.PIF or the
application's program information file (PIF) under the NT-specific section of
PIF Editor. Since this feature causes a decrease in performance, it should be
used only if it is required to make an application to run with Windows NT. Windows “program folder” under
“Windows” section provides this
setting.
•If the application is in a window and seems to pause
periodically, try disabling Idle Detection in the Advance section of that
application's PIF. Windows “misc folder” provides this setting in a form of a slider
bar called “idle sensitivity”.
•If the MS-DOS-based application can be configured
for printing, choose LPT1, LPT2 over parallel
port. Most of the applications use Int17 to print when
configured for LPT<x>. If you select parallel port mode, these applications
print directly to printer ports. Parallel mode is significantly slower in Windows compared to Windows 3.1.
Note: Vangard Voice
AccuSpeech® (Mobile) software must be installed and verified to be operational
prior to any attempt to configure GSW Windows Clients to use it. Additionally,
Vangard Voice AccuSpeech® (Mobile) should be configured to operate in the Half-Duplex
mode. Please contact Vangard Voice or authorized party to ensure proper
installation and configuration of AccuSpeech® for the application you intend to
voice enable. Assistance with Vangard Voice AccuSpeech ca® (Mobile) n be found at
949.435.1001.
|
Configure
Voice Vangard AccuSpeech Recording Mode to Half Duplex
|
|
Figure 142: Open VVTools
|
|
Figure 143: VVTools - Select Half Duplex
|
|
Figure 144: VVTools - Click Register Mode
|
|
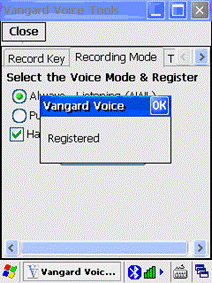
Figure 145: VVTools - Done, Click Close
|
GSW UTS Mobile clients
support Vangard Voice Systems, Inc AccuSpeech® Mobile on Windows CE and Windows Mobile Operating Systems. Support
is enabled by simple GSW Windows Client configuration steps described below.
UTS and GSW Mobile client’s version 8.04 or higher is required for Vangard Voice
AccuSpeech support.
When using Windows CE,
you will navigate to the correct configuration screen, enable Vangard Voice support
and provide the path to the Vangard Voice AccuSpeech® Mobile XML file.
Step 1: Enable Vangard
Voice AccuSpeech® Mobile support in the GSW mobile client for Windows CE
On the Windows CE
device open the GSW Mobile Client and using the dropdown
select Session -> Settings.
|
GSW
Mobile Client for Windows CE
|
|

Figure 146: Open GSW Mobile Client for Win CE
|
|
Figure 147: Select Settings to enable Vangard Voice
support
|
Scroll right with
arrows and you will see the Vangard Voice Tab. Check enable Vangard Voice
|
GSW
Mobile Client for Windows CE
|
|
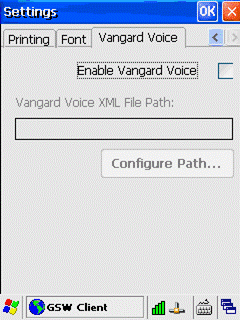
Figure 148: Vangard Voice tab on GSW Mobile Client
for Win CE
|
|
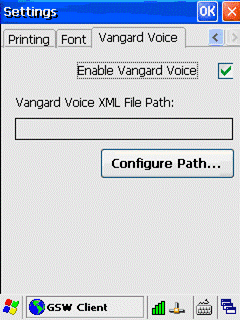
Figure 149: Click the Checkbox to enable
|
Step 2: Configure the path to the Vangard Voice AccuSpeech® Mobile XML file
Click on Configure Path button.
Browse to the folder where the Vangard Voice AccuSpeech® Mobile XML file is located, specified by Vangard
Voice installation. In the example below it is in the Program Files folder and
named SamplApp.xml. Select the file and click OK.
|
GSW Mobile Client for Windows CE
|
|
Figure 150: Navigate to the
Vangard Voice XML file
|
|
Figure 151: Select the file
and click OK
|
.
Be sure to save the GSW Mobile client configuration.
|
GSW
Mobile Client for Windows CE
|
|
Figure 153: Be sure to save
your GSW Windows Client configuration
|
|
Figure 154: Select “Save As”
|
|
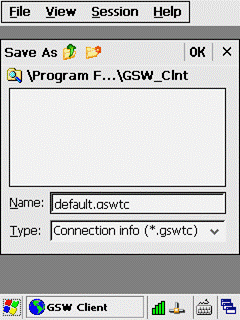
Figure 155: Select GSW configuration
file name, Click OK
|
The configuration is completed. Simply connect to the UTS and start talking!
To enable Vangard Voice
when using the GSW Windows Mobile Client is simply modifying a line in the GSW
Windows Mobile configuration file. This is accomplished by first copying the
configuration file to a workstation (PC) where editing is easier than on a
device. Next, add the Vangard Voice Enabling configuration line. This is done
by setting the environment variable VVPath to the path of the Vangard Voice XML
configuration file. Then save the file and copy it back to the device.
Step 1: Make
sure the GSW mobile client is not running
·
Close the client.
·
On the Windows Mobile Device – Open Task Manager and stop the GSW
Windows Client.
Step 2: Copy the
GSW Windows Mobile client configuration file to a workstation.
On the
Windows Mobile device open File Explorer and copy the GSW Mobile Client
configuration file (which has a .gswtc
extension and identified by the Globe Icon) to a workstation (PC).
Step 3: Edit the file (in this example it is named default.gswtc) using an editor
such as notepad.exe to add the path to the Vangard Voice AccuSpeech Mobile XML file
(that is located on the device)
The path
to the Vangard Voice AccuSpeech Mobile XML file is added to the configuration
file in the Session Section identified
by the word Session enclosed in
square brackets is [Session].
Add the line anywhere in the [Session] section. The path is specified by Vangard
Voice installation.
Use
the syntax as follows:
Syntax :VVPath=<file_path>
Example: VVPath=\SamplApp.xml
|
GSW
Mobile Client for Windows Mobile
|
|

Figure 156: Select the GSW Windows Mobile client configuration file. Note the Globe Icon.
|
Copy the file to a workstation for editing.
|
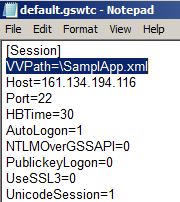
Figure 157: Edit the GSW Mobile Client configuration file.
|
Copy the file back to
the device to the appropriate folder on the device.
The configuration is completed.
Simply make a connection
with the GSW Mobile client to the UTS and start talking.
Configuration of the
desktop client is easy and requires the addition of a command line parameter that
specifies the path to the Vangard Voice XML file. (Learn more about desktop
client parameters on page 77)
Notes:
·
The UTS and Desktop client version must be 8.04 or greater.
·
Vangard Voice runtime must be installed and XML file must reside on
the client machine.
Step 1: Open the
desktop client batch file
Following is an example
for specifying client command line parameters. The GS SSH2/Telnet Client shortcut invokes the batch file GS_SClnt.bat (for Telnet) or GS_SSSH.bat (for SSH) which
in turn launches the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Client. The GS_SClnt.bat and GS_SSSH.bat files reside in the GS_UTS installation
directory. The contents of the batch files look as follows.
@echo off
:start
@if exist once1.bat do call once1.bat
@if exist once1.bat do del once1.bat

 @gs_clnt.exe
@gs_clnt.exe
@if errorlevel 2 goto copy
@exit
:copy
@copy gs_clnt.new gs_clnt.exe > gsnull.txt
@if exist once2.bat do call once2.bat
@if exist once2.bat do del once2.bat
@goto start
The
line @gs_clnt.exe
is the
line that launches the Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Client. For SSH the
client name is gs_ssh.exe.
Step 2: Add the
command line parameter and save the file
The Command Line Parameter
used is:
Add
the parameter –vxml_file_path
Where
v
is
the command line parameter to enable Vangard Voice AccuSpeech Mobile support for
GSW desktop clients
xml_file_path
is
full path to the Vangard Voice AccuSpeech XML file
And thus the GS_SClnt.bat
file will be modified as shown below adding the command line parameters.
@echo
off
:start
@if
exist once1.bat do call once1.bat
@if
exist once1.bat do del once1.bat
@gs_clnt.exe -v"c:\Program
Files\Vangard Voice\grammar\testGrammar.xml"
@if
errorlevel 2 goto copy
@exit
:copy
@copy
gs_clnt.new gs_clnt.exe > gsnull.txt
@if
exist once2.bat do call once2.bat
@if
exist once2.bat do del once2.bat
@goto start
Save the file and desktop client configuration is complete.
SSH2/Telnet Connectivity for SAPConsole is not
just a Good solution it is the Best Solution!
The speed and efficient bandwidth utilization for telnet/SSH
connectivity to Windows cannot be beat! If SAPConsole and SSH2/Telnet Connectivity are important to your business then your only choice is the Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server.
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server IS the Industrial Grade SSH2/Telnet
Server for your SAPConsole RF Application.
The reliability, consistency, performance and features of
the GSW SSH2/Telnet Server are unequaled and requirements for today’s commercial
RF Applications.
Works great
out the box with SAPConsole
Use the 3rd
SSH2/Telnet Client for your hardware
If you have
Windows Pocket PC 2003 devices then you can use the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client for Pocket PC 2003 class machines.
Easy to install
The Georgia SoftWorks
Industrial Grade SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows
is installed on every continent on the planet (..except Antarctica )
)
You can also obtain the GSW Telnet/SSH
Server from SAP/SAPConsole Experts who
can assist with your decision process. See our web site for more information.
This special section contains information on:
Using the GSW
SSH2/Telnet client for Pocket PC 2003, Windows Mobile class devices (Page 32).
How to Print
Labels on a Portable Printer using SAPConsole (Page 323 )
How to
automatically launch SAPConsole from a SSH2/Telnet
Session (Page 321 )
SAPConsole
and the Georgia SoftWorks Rocket Terminal Engine. (Page 330)
SAP User Name
displayed when using gs_admin. (Page 322 )
SAP Special
Bell Processing when used with SAPConsole (page 280)
If you
are using the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client for Pocket PC 2003,
Windows Mobile class machines then the following configuration steps may be
helpful. Installation of the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client on Pocket PC 2003 class is
described on page 33 .
- On
the Pocket PC device select one of the following depending on the class of
device.
For
Pocket PC 2003: Start|Programs|GSW SSH2/Telnet
This selection will launch the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet client.
- When
your run the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet client you will be
prompted for the connection info as on the picture left below:
|
Figure 158: SAPConsole - PPC
2003 Configuration. Host Prompt
|
Figure 159: SAPConsole - PPC
2003 Configuration - Options Screen
|
- Click
the Options button to verify the connection options.
- Press
the OK button to leave the Options screen.
- Press
the OK button again to accept the connection info and connect to the server.
- Wait
for the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client to connect to the
server.
You should
see the SAP logon screen similar to one on the picture below left.
|
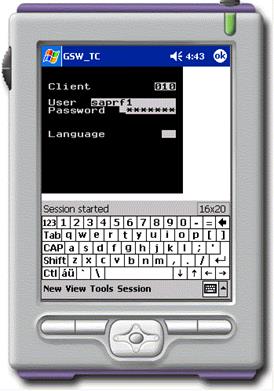
Figure 160: SAPConsole - PPC
2003 Configuration. Logon Screen
|
Figure 161: SAPConsole - PPC
2003 Configuration - Save Changes
|
….Continued
on next page
- Use
SAP.
Below is an example of the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client for Pocket PC 2003/Windows Mobile class
devices. Notice that the function keys are available as well as proper placement
of the text and fields.
Figure 162: SAP - GSW SSH2/Telnet Client for PPC 2003 - Function Keys
- Quit
SAP application.
- The GSW
Pocket Windows Mobile SSH2/Telnet Client will prompt you to
save your connection settings so you will not need to reenter them for the
next connection. See picture on the right above.
- Click
the ‘Yes’ button.
- You
will be prompted to select the file name
|
Figure 163: SAPConsole - PPC
2003 Configuration File Name Prompt
|
Figure 164: SAPConsole - PPC
2003 Select Configuration Prompt
|
- Next time
you use the GSW Pocket PC 2003/Windows Mobile SSH2/Telnet Client you will be presented with the
screen like the figure on the right above.
- Simply
click on the connection info file and you will get connected.
In most instances you will want SAPConsole to
automatically launch when the SSH2/Telnet
session is connected. This is easily done via the GSW Logon Scripts.
For SAPConsole 64-bit:
c:
cd “\Program
Files\SAP\Console”
sapcnsl
For SAPConsole
32-bit:
mode con: lines=16 cols=20
c:
cd “\Program Files
(x86)\SAP\Console”
sapcnsl
If your screen size is not 16x20
then adjust the mode statement
to correspond to your screen size.
When using the GSW Rocket Engine (version 1.39.0002 or
later), the SAP User Name will be displayed in addition to the Windows
user name when using the GSW Session Administrator.
 Windows
User Name: luke
Windows
User Name: luke

 SAP
User Name : lbatko
SAP
User Name : lbatko
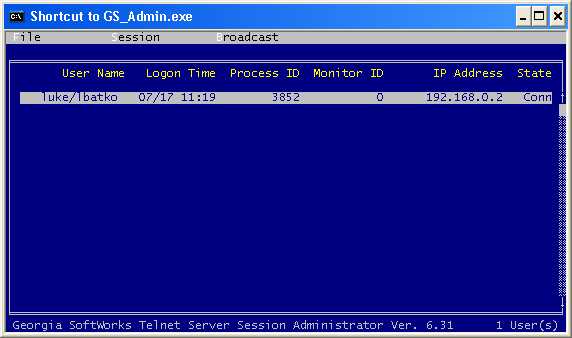
Figure 165: SAP User Name displayed in GSW Session Administrator
One of the limitations of using SAPConsole is an
ability to utilize local printers attached to an RF device. Georgia SoftWorks
provides a native method of printing to serial (or tethered) printers. Using SAPConsole
and the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server, printing to tethered printers from
R/3 becomes possible.
Some important aspects of this solution include:
- No
special software is required on the RF device. Most RF emulation clients already
support pass though printing.
- No
special software is added to SAPConsole or R/3.
- This
solution only works with the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server.
- To
utilize mobile printing, a user must have the same username for R/3 andSSH2/Telnet .
- The
SSH2/Telnet Server can support each
user type, mobile printing and non-printing clients. A different server is
not required for RF users that do not require mobile printing.
- Mobile
printers are seen by R/3, but are not controlled by R/3 (e.g. offline,
paper out, etc.)
- The
SAP printing application SAPLPD is required, and should be configured to
run as a service on the SAPConsole machine.
- The
capability to design labels and the R/3 business logic to print the labels
are not part of this particular solution.
- All
labels are created using sapscript (or 3rd party software that integrates with
sapscript).

- SAPConsole
Standard
SAPConsole installed from SAPGUI CD.
- Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server
·
Configured for local printing.
- SAPLPD
·
A known method of printing to local client printers that is supported
by R/3. SAPLPD is installed by default with SAPGUI on SAPConsole machine.
- Sapscript
·
All labels printed on a tethered printer are in fact, a sapscript
form. Newer methods, such using BAR-ONE for R/3 from Zebra, allow WYSIWYG label
designs to be uploaded into a sapscript form. Creating labels this way does not
require learning the printer’s command language.
- R/3 Printing
·
Utilizes standard R/3 printing capabilities. All setup is completed
in transaction SPAD. To R/3, a tethered printer appears like a local printer
attached to the SAPConsole machine.
- Install and Configure Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Ser ver
- Configure SSH2/Telnet
Server for Mobile printing
- Configure each SAPConsole user for local printing
- Install and configure SAPLDP on SAPConsole machine
- Configure mobile printers in R/3
- Modify RF device configuration to allow printing
- Create sapscript form containing barcode label for mobile
printer
- Determine or create R/3 printing logic. (e.g. an R/3
transaction to print label using the proper sapscript form)
1. Install
SSH2/Telnet Server as per instructions in the User’s Guide. There are no
special installation options for mobile printing.
2. Create
a Windows account for each user that will utilize mobile printing. The username
MUST match the user’s SAP R/3 login name.
3. Create
“script” subdirectory (e.g. C:\GS_UTS\script\rfuser for user rfuser) and create
the k_start.bat (login script) file for each user
Configure SSH2/Telnet
Server for Mobile printing
1. Create a “virtual printer” on the
SAPConsole machine.
In creating a “Virtual Printer” (or local mobile printer) the
key information are the Printer Name, the Share Name and the Port.
The following steps are required to setup the printer:
·
Click the Start button at the bottom left corner of your
screen.
·
Select Settings then printers.
·
Double click on Add Printer. (The add printer window opens).
·
Select My Computer and Click on Next
·
Select the lpt1 port. Do NOT enable print pooling. Click
Next.
·
From the Manufactures list select Generic
·
From the Printers select Generic/Text Only.
Click Next
·
Name your printer GwtnPrinter1. NOTE: This name is required.
Click Next
·
Select Shared and name the printer GwtnPrinterShare1.
NOTE: This name is required. Click Next
·
After the printer is created, double click on the printer icon.
·
Pause the printer by selecting the menu item Printer and
selecting Pause Printer. This printer must remain paused at all times.
This printer cannot be used by any other service except Georgia SoftWorks Telnet/SSH
Server.
1. Add
the following line to each login script (k_start.bat) file for each user
requiring mobile printing:
set GWTN_LOCAL_PRINT_METHOD=SAP
5. SAPLPD
is installed automatically when SAPGUI is installed. If it is not already on the
SAPConsole machine, it must be installed.
6. Using
instsrv.exe and svrany.exe utilities from Windows resource kit configure SAPLPD
to run as a service. Two steps are required to run saplpd as a service.
a.
The syntax for using these utilities is as follows:
instsrv saplpd.exe c:\path\srvany.exe
Note: the instsrv.exe and saplpd.exe
should be in the current directory.
7. Add
a registry key. In registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SAPLPD
create a new sub-key named Parameters. In the Parameters key, create a new
entry name Application. The value of this field is the part to the saplpd.exe
file (e.g. c:\sappc\saplpd.exe).
Figure 166: SAPLPD service,
properties dialog window
If all the users use the same printer only one mobile
printer needs to be created in R/3. If multiple printers are desired, each
printer should use the same “host spool access method” and “destination host”
values specified below.
1. Create
the mobile printer in R/3 using transaction SPAD
·
The device type should be ASCIIPRI or other device type for the
particular printer being used.
·
The “Host spool access method” is set to “Print using SAP protocol”
(type S).
·
The “Destination host” is set to the machine running the Georgia
SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server (This can be network name or IP address). Note: SAPLPD will need to be running on the host, or the
SPAD transaction may not allow creation of the printer.
·
Set the “Host printer” to GwtnPrinter1
·
Leave all other fields as the default. Do not select cover page
or specify tray information
Figure 167: Sample SPAD transaction
screen
Each RF device and terminal emulation client has its own configuration
to allow printing. Some devices allow more control over printers. For this
application, the printer should be “dumb” and the RF device should not
intercept or interpret any control characters. Lastly, the serial port parameters
must be configured to match the printer’s settings.
Create SAPScript form for label(s). Either manually or with
BAR-ONE for R/3, create sapscript form(s) that represent labels to be printed
on mobile printers.
This section varies and is left up to each individual
organization. At a basic level, a SAPConsole transaction outputs data to a mobile
printer defined in R/3. This can be accomplished with or without sapscript.
Maximize your SAPConsole and GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server performance while adding important features by obtaining the Georgia SoftWorks
Rocket Terminal Engine.
What is the GSW Rocket
Terminal Engine?
Answer: The
Rocket Terminal Engine is a HIGH-Performance replacement for the SAPConsole
VTIO Terminal Engine.
Why do I need a replacement?
Answer: Performance,
Savings and Features
Sounds like Sales Talk?
Answer:
The benefits are truly outstanding!
Performance:
Very Large number
of sessions with expected performance.
Reduce the
number of systems required for your application
Enable Application
where not possible before
Savings:
Save the price
of extra computer(s) hardware.
Save the
price of extra computer(s) software
Save the
continuing maintenance cost of hardware and software
Powerful and Useful Features
such as:
Adjusted
Logon Screen Size
Adjusted Logoff
screen size
Configurable
screen size
Capability to
adjust the “Off Screen Fields” back on to the screen
Flexible
translation of screen attributes with powerful new options not available in the
SAPConsole VTIO Terminal Engine.
Full Support
of SAPConsole Profiles
Contact
Georgia SoftWorks for more information on the Rocket Terminal Engine!
Contact GSW Sales
Or
call
Tel: 706.265.1018
Many environment
variables exist for the user’s convenience. They are available to use in local
and global login scripts to set defaults to eliminate prompting as well as setting
values for special uses. The details are described it the appropriate section
in the User’s Guide however we have included a quick reference list here.
gwtn_backspace_on_delete – Specifies if the delete
key performs a backspace action (page 185).
gwtn_color - Sets Color or Monochrome presentation
for 3rd party clients (page 170).
gwtn_create_profile – Specifies if a user specific
registry hive will be created (page 247).
gwtn_clnt_no_x – Specifies if the GSW Desktop
clients display the ‘x’ in the top-right corner (page 86
).
gwtn_ctrl_c_mode - Sets <control-c> behavior
(page 164).
gwtn_enable_pseudoconsole–Enables/Disables
the “new” Microsoft pseudoconsole. (Global or Per User)
(page 178).
gwtn_enable_send_screen_size_to_3rd_party – Enables/Disables
sending screen size to 3rd party clients (Global or Per User) (page 177).
gwtn_enable_session_log – Enables/Disables long
format session logging (Global or Per User) (page 216).
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_strings – Enables/Disables
GSW ConnectBot Device and Client information strings (Global or Per User) (page
385).
gwtn_enable_3rd_party_mouse – Enables/Disables support
for 3rdparty mouse operation (Global or Per User) (page 388).
gwtn_encrypt_session – Activates Data Stream Encryption
for the session (Global or Per User) (page 93).
gwtn_ff_in_passthrough – Enables/Disables the
trailing form feed in pass-through printing (page 241)
gwtn_graphics - Sets the graphics mode for 3rd
party clients (page 168).
gwtn_home_dir – Selects the home directory that the
User will be deposited into upon connection (page 299).
gwtn_inactivity_timeout – User defined inactivity
timeout (page 153).
gwtn_job_control – Specifies to automatically terminate
all child processes when a session ends (page 162).
gwtn_log_char_xlat – Log International character
translation of UTS-8, GB2312, and Big5 (page 217).
gwtn_local_print_poll_interval – Specifies the poll interval with which the
gs_agent polls the GwtnPrinterx print queues. Values range from 1 to 10 seconds
where the default is 5 seconds. (page 301 )
gwtn_local_print_cmdx - Indicates the printing
command/index used by the Open Print Method (page 236).
gwtn_local_print_method - Indicated the True Client-Side
Printing method chosen (page 226).
gwtn_pp_print_buffer_size – Specifies the print
data buffer size for passthrough printing. (page 242).
gwtn_reconnect - Enable Session Saver (page 149).
gwtn_reconnect_timeout - Specifies how long a
session will exist in minutes before Graceful Termination will initiate when it
is enabled (page 151).
gwtn_serverside_heartbeat – User defined server-side
heartbeat for 3rd party clients (page 155).
gwtn_show_console_title – Displays application title
on the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Client Window (page 85).
gwtn_term - Sets terminal emulation for 3rd
party clients (page 166).
gwtn_tcpwindowsize - Sets the TCP Receive Window
Size (page 246).
gwtn_ts_enable_recovery - Sets Team Service Recovery
override (page 138).
gwtn_ts_enable_share - Sets the Team Service Share override
(page 141).
gwtn_ts_enable_swap - Sets the Team Service Swap override
(page 140).
gwtn_ts_enable_transfer - Sets the Team Service
Transfer override (page 139).
gwtn_ts_hotkey - Sets the HotKey to enter Team
Services (page 143).
gwtn_two_cells_per_uc – Specifies if characters that
occupy two-character cells in MS Windows command prompt will occupy two-character
cells in 3rd party clients (page 186).
lra_termination - Define the termination string that
is sent to an application upon detected failures (page 158).
Many environment variables
are set by the SSH2/Telnet server and are available to the User or Programmer.
gwtn_agntpid - Process id of the Agent Process
handling the user session.
gwtn_answerback – Answerback text passed from the GSW
Client (page 87).
gwtn_client_ip - IP address of the client computer/device.
gwtncl_clnt_side_ip – Client’s IP address as seen
by the client’s device.
gwtncl_var_name – Where var_name
is the name of the variable. GSW ConnectBot for Android Device and Client
information strings (pages 175, 385).
gwtncl_hal_uuid – Hardware Abstraction Layer
Universally Unique identifier. No two devices will have the same gwtncl_hal_uuid.
gwtn_client_mac – MAC (Media Access Control) address
of the client computer/device.
gwtn_gsclnt – Set to 1 or 0 depending if a GSW or 3rd
Party client is connected. If GSW then the value is 1 otherwise the value is 0
gwtn_hsocket - Socket handle of client session
gwtn_server_port –SSH2/Telnet
Port associated with the session (page 284 )
gwtn_tty - The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server creates a tty name on a
per session basis (page 281).
gsw_uts_root - The installation path for the GSW
UTS.
Many registry variables
exist for provisioning the system. Registry variables are an excellent method for
the system administrator to configure software as to utilize already learned skills
by the system administrator. There is no need to learn yet another interface to
provision the software. Here is a list of the registry variables and a brief description
of their use. Please see the appropriate section in the User’s Guide for
complete descriptions.
Almost all Registry values used by the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows are stored in the following Registry path. If the registry path
is different it will be noted. For SSH Specific Registry settings please see the
GSW SSH Server User’s Guide.
·
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters
ActivityLogFileLength - Set the Session Activity
Log File Size – For use by GSW Tech Support (page 214).
AgentLogFileLength - Set the Event Log File Size (page
215 ).
AllowTelnetWithSSH – UTS Protocol selection (page 258)
AltPrefix - Configure a different Alt Prefix (page 172)
BellX - column of the bell character, initialized
to 0xffffffff, which makes it inactive (page 279).
BellY - row of the bell character, initialized to 0xffffffff, which makes it inactive.
BellChar - value of the bell character, initialized to 0x87 (page
279)
BellCnt – number of times the bell will sound, initialized to
0x01 (page 279 ).
ClntChkTimeout - Server-Side Heartbeat. Set the
frequency in seconds which to poll the 3rd party client for presence
(page 154).
Domain - Set the default Domain for 3rd Party
Clients. This is used to eliminate the prompting for the domain (page 282).
dwLogonTimeout – The maximum time a client is allowed
to complete authentication.
Enable3rdPartyCursorSize–
Allows applications to control Windows Cursor Size for 3rd party
clients.
EnableEncryption – Enables the ability to activate
Data Stream Encryption (page 94).
EnableRFC854Clients - Allows/Disallows connection
from 3rd Party Clients. (page 100)
EnableNAWS – Enables Negotiate about Windows Size
telnet option (page 175).
EnablePseudoconsole – For Windows systems with
Windows Terminal installed. Enables Pseudoconsole. Data: 0 is disabled, 1 is enabled.
Default is disabled. (page 178)
EnableSendScreenSizeTo3rdParty–
Allows applications to send the screen size to 3rd party clients. Data:
0 is disabled, 1 is enabled. Default is Enabled.
(page 177)
ESCDelay - Determine how long to wait for the next
character after an escape is received to consider is part of the escape sequence
(page 174).
InactivityTimout - Server-Side Inactivity Timer. Set
the time in seconds that defines the maximum allowed inactivity period (page 153).
LogonInactivityTimeout – Specifies how long a
telnet session will wait for a user to provide credentials before the session
is disconnected. The value is in seconds and the default is 150.
LsnOnLoopbackOnly – UTS Protocol selection (page 258)
Max3rdPartyLogonAttempts – Specifies the maximum
number of Telnet logon attempts before the session is disconnected. The default
is 3.
MaxHeartBeatDelay – Adjusts time interval that the
server will wait for the GSW client heartbeat (page 157).
MaxSessions – Limit the total number of sessions for
the SSH2/Telnet server (page 101)
Path – Contains the installation path of the UTS. Please
note the registry path below.
·
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Georgia
SoftWorks\Georgia SoftWorks UTS
Protocol – Defines the Telnet IP protocol (page 256)
RefreshChar - Defines a character that refreshes
the screen. The default is 0x12 (page 250)
RequireEncryptedSession - Restricts connection
to only encrypted sessions (page 107)
szProtocol – Defines the SSH IP protocol (page 257)
TSEnableRecovery - Enables/disables Team
Services Recovery (page 138)
TSEnableShare - Enables/disables Team
Services Share (page 141)
TSEnableSwap - Enables/disables Team
Services Swap (page 140)
TSEnableTransfer - Enables/disables Team
Services Transfer (page 139)
TSLeftJustify - Enables/disables Left
Justification for Team Services dialogs / text (page 142)
TSHotKeyCtrl - Enables/disables
requirement for CTRL KEY Team Services Menu (page 143)
TSHotKeyVK - Defines the virtual key
code for the Team Services Menu (page 143)
UseGSW_SSHD – UTS Protocol selection (page 258)
Version – Contains the version of the UTS. Please note
the registry path below.
·
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Georgia
SoftWorks\Georgia SoftWorks UTS
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
server utilizes several ASCII text files for configuration.
banner.txt – Contains text to display to client
before the logon prompt (page 260).
colormap.txt – Defines color to monochrome mappings
(page 171).
gs_auto.txt – Automatic logon Pre-configuration
file for GSW Client (page 111).
gs_ip_rt.txt – IP Based Login Scripting file (page 220).
gs_ipenc.txt – Encryption based of IP address scripting
file (page 96).
GS_SClnt.bat – Batch file that launches the GSW SSH2/Telnet Client (page 80).
gs_sssh.bat – Batch file that launches the GSW SSH
Client (page 80).
gs_color.txt – Specifies colors to re-map (page 181).
gs_lb.txt – Specifies the IP Addresses of your load
balancers. See text file for more detail.
gsw_ldef.txt - Specifies events that maintained in
the log file (page 212).
gs_logon.txt – Automatic logon Pre-configuration file
for 3rd party clients (page 183).
gs_tinit.txt – Initialization characters to send to
3rd party client. (page 184).
gs_xchar.txt – Character translations definitions
when sent to terminal/display (page 183).
thosts – Restrict Access based on IP address (page 98).
gs_l_usr.txt – Limit the number of connections by specific
User ID (page 102).
gs_l_ip.txt – Limit the number of Connections from
specific IP Addresses (page 104).
tsgroups.txt – Configure Strict Teams for Team Services
(page 134).
Georgia SoftWorks is pleased to introduce the GSW UTS
Configuration Tool. The GSW Configuration Tool provides the user with a Graphical
User Interface that is:
Intuitive
·
Windows Explorer style tree view allowing you to navigate to the
object of interest
·
Familiar to use operations such as
copy/paste/rename/delete/export/import are applied to configurations on user or
system basis
·
Easy to identify icons, color and shape coordinated to easy
identification
Time Saving
·
Create new user configurations by copy/paste
·
Create default configurations for objects
·
Quickly view the configuration summary data
·
Minimizes configuration errors
·
Flexible and enhances organization
·
Incredible granularity for configuration settings
·
Provides templates for storing configurations (Global System and
Per User)
·
Import/Export of configurations
·
Visualize Domain, Domain user, Local User
Powerful
·
Administrators have the ability to create multiple configuration
templates, providing quick configuration implementation as well as consistency.
Overview
Configuration of the
UTS is primarily composed of scripts, registry variables, environment variables,
text files and operating system configuration.
The GSW Configuration Tool
allows the use of a graphical user interface to set configuration parameters
that reside in the registry in addition to creation of folders, scripts and the
modification of UTS environment variables. Additionally, the GSW Configuration Tool
provides access to text file configurations via notepad.exe.
The UTS Configuration Tool
is organized based on either Global or Per Session configuration items.
Global
– per system configuration modifies the registry variables or allows editing of
text files used for provisioning the UTS. These text files and registry
variables are configuration items that are UTS wide in nature and apply to all
UTS Users.
User
– per session configuration sets environment variables or allows editing of text
files used for provision the UTS on a per session basis.
Both Global and User configurations
provide the capability to create templates. Templates allow the administrator
to create configurations and store with names of their choosing. The
administrator may want certain configurations for specific locations, departments,
users or circumstances. Templates allow the administrator to create and save the
various configurations. The saved configuration can simply be copied to the
Global Active Configuration (in the per system case) or to the specific User configuration
(in the Per User case) when needed. There is no need to reconfigure from scratch
or remember all the details each time.
Default configurations can
be applied to
·
All Users (All Domains, Domain Names, Local Users)
·
All Domains
·
All Users in a Domain Name
·
All Local Users
The administrator can
define a default configuration at none, some or all of the objects listed above.
If a configuration does not exist for a specific user then the “configuration tree”
is traversed to determine if a default configuration exists. The administrator
can set a few default configurations for most users and then have specific
configurations for specific cases. This minimizes the configuration required and
ensures that the proper configuration is used.
Launch the GSW Configuration Tool
From the Start Button,
select the Georgia SoftWorks UTS and then select the GSW Configuration Tool.
The initial display
will be similar to the figure below.

Figure 168: Initial Configuration
Screen
Navigating is intuitive
and similar to Windows Explorer. Use the mouse and click on the ‘+’ to expand
items and the ‘-’ to collapse them.
Global or User objects
are displayed on the left pane and context appropriate configuration, status or
description is displayed on the right pane.
As you expand items you
will notice a variety of icons that are associated with configurable objects from
either an organizational or directly configurable viewpoint.
The following table lists each icon and a brief description.
|
|
ICON
|
DCA
|
DESCRIPTION
|
|
1
|

|
|
Georgia
SoftWorks UTS Configuration Tool – tree root.
|
|
2
|

|
|
Global – per
system UTS Configuration Settings.
|
|
3
|

|
|
This icon represents the
Active System Configuration for the UTS. Expand to see configurations (property
pages) for the Active
Configuration.
|
|
4
|

|
|
This icon represents all the
UTS System Templates. Expand to see all the individual System Templates.
|
|
5
|

|
|
This icon represents a specific
UTS System Template. The template name is displayed to the right of the icon
and the template configuration items (property pages) are available by
expanding the object.
|
|
6
|

|
|
Configuration
Page – (property pages). A configuration object may have several property pages.
Property pages may have property pages too.
|
|
7
|
|
|
User – per session
configuration.
|
|
8
|

|

|
Represents
ALL users in all domains.
|
|
9
|

|

|
Represents
ALL users in the specific domain name. Domain name is displayed to right of
the icon.
|
|
10
|

|
|
A specific
User within a specific domain. Expand to see property pages.
|
|
11
|

|

|
This icon represents ALL Local
Users. Expand to see configurations for each specific local user.
|
|
12
|
|
|
This icon represents a specific
local user. The user name is displayed to the right of the icon and the specific
user configuration is available by expanding the object.
|
|
13
|

|
|
This icon represents the
default configuration associated with the parent object.
|
|
14
|
|
|
This
icon represents ALL IP Address/Range based User Configurations. Expand to
see configurations for each specific IP Address/Range.
|
|
15
|
|
|
The dark IP icon represents
a specific IP address/Range based User Configuration. The name of the IP Address/Range
configuration is displayed to the right of the icon and the specific IP
Address user configuration property pages are available by expanding the
object.
|
|
16
|

|
|
This icon represents ALL
Grandfathered Users. Expand to see configurations for each specific local user.
|
|
17
|

|
|
This icon represents a
specific Grandfathered User. The user name is displayed to the right of the
icon. Expand to see
property pages.
|
|
18
|

|
|
This icon represents User Templates.
Expand to see configurations for each specific user template.
|
|
19
|

|
|
This icon represents a specific
User Template. The template name is displayed to the right of the icon and
the template configuration is available by expanding the object.
|
Navigation within the UTS
Configuration Tool offers time saving right-click operations. Different objects
have different operations available. Some operations are only available at
appropriate times. For example, if an object has a paste operation, it will only
be available if a copy has first been performed.
The table below lists
the Right Click operations available for Global – per system configuration.
|
|
ICON
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|
1
|

GSW GUI
Root
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|

Global Configuration
Root
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
|

Active Global Configuration
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
4
|

All Global Templates
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5
|

Global Template
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
6
|

Property Page
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Table 56: UTS Configuration Tool – Global
Configuration Right Click Operations
User - per session - Right Click Operations
|
|
ICON
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|
7
|
User - per session
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
8
|

All Domains
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
9
|

Specific Domain
|
|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
10
|
 Domain Domain
User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
11
|

All Local Users
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
12
|

Local User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
13
|

Default
Configuration
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
14
|
All IP
Address /Ranges
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
15
|
IP Address
/Range
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
16
|

All Grandfathered Users
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17
|

Grandfathered
User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
18
|

All User Templates
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
19
|

User
Template
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Property Page
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Table 57 - UTS Configuration Tool – User Configuration
Right Click Operations
The root of the UTS Configuration tool is identified below
in Figure 169
|
Figure
169: UTS Configuration Tool - Root
|
Figure
170: Root Expanded
|
When expanded the configuration
objects for Global and User – per session are displayed as show in Figure 170
|

GSW GUI
Root
|
|
Georgia SoftWorks
UTS Configuration Tool –root.
|
This is the GSW UTS Configuration Tool root.
Click ‘+’ to expand to see the Global per system and User –
per session objects.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: None
Property Pages: None
Global – per system
|

Global Configuration
Root
|
|
Global – per
system UTS Configuration Settings.
|
This is the root of the
Global – per system UTS configuration object.
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the Active Configuration and the UTS System Templates objects as shown in Figure 171.
Figure 171: Global - per system expanded
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: None
Property Pages: None
|

Active Global Configuration
|
|
This
icon represents the Active System Configuration for the UTS. Expand to see
configurations (property pages) for the Active Configuration.
|
This is the Active
(live) configuration being used for the UTS.
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the configuration (property pages) for the Active Configuration as shown in
Figure 172.
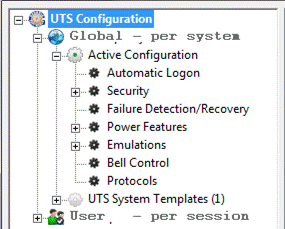
Figure 172: Active Configuration Expanded
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

Active
Global Configuration
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: The
Active configuration can be copied and pasted to a UTS System Template.
Paste: A copied UTS System Template can be pasted
over the Active Configuration. All contents of the Active Configuration are
replaced.
Export: The Active configuration can be exported
to XML format file. This is useful for backing up the Active configuration or
deployment to additional servers.
Import: The Active configuration can be imported
from a saved XML file. This is useful for restoring the Active configuration or
for deploying additional servers.
|

All Global Templates
|
|
This icon represents all the
UTS System Templates. Expand to see all the individual System Templates.
|
This is the root for
the UTS System Templates
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see each system template defined. In the example below (Figure
173) there are two templates defined. One named atlanta_master
and the other is london_master.
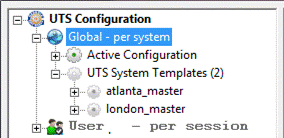
Figure 173: UTS System Templates - Expanded
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
|
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

All
Global Templates
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Paste: A copied UTS System Template or Active
Configuration can be pasted creating a new UTS System Template.
Import: A xml format file containing a Global – per
system configuration can be imported creating a new UTS System Template.
|

Global Template
|
|
This
icon represents a UTS System Template. The template name is displayed to the
right of the icon.
|
This is the root for a
specific UTS System Template.
Click ‘+’ to expand to see
the property pages for the UTS System Template as show in Figure
174.
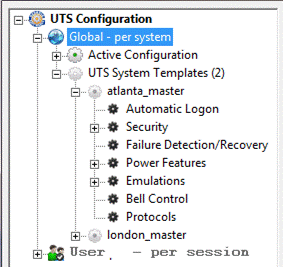
Figure 174: Specific System Template Expanded
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

Global Template
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: The UTS System Template can be copied and
pasted to a UTS System Template or Active Configuration.
Paste: A copied UTS System Template or Active
Configuration can be pasted over the UTS System Template. All contents of the
System Template are replaced.
Rename: Change the name of a UTS System Template.
Delete: Remove the UTS System Template.
Export: The UTS System Template can be exported
to XML format file. This is useful for backing up the UTS System Template configuration
or deployment to additional servers.
Import: The UTS System Template can be imported
from a saved XML file. This is useful for restoring the UTS System Template
configuration or for deploying additional servers.
User – Per Session
configurations are configurations that can apply to a session. The logon script
is the fundamental requirement for a User – per session configuration.
|
User Per Session
|
|
User – per session
configuration
|
|
|
|
User – per
session configuration with a default configuration defined.
|
This is the root of the
User – per session configuration object.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the Domains, Local Users, IP Address/Range, Grandfathered Users, User Template
objects and default User configuration (if it exists).
Figure 175: User - per session object expanded
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|
User - per session
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Create Default Configuration:
A default User – per session configuration
is created that will apply to any session if that session does not have a
specific configuration or one of its parent objects does not have a default
configuration.
|

All Domains
|
|
Represents
ALL users in all domains
|
|
|

|
Represents
ALL users in all domain with a default configuration defined.
|
This is the root of the
User – per session All Domains configuration object.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\DomainUsers
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the specific Domain Names and the default domains configuration (if it exists).
The example below (Figure 176) shows one domain name GSWATLANTA and a default
configuration defined.
Figure 176: Domains Expanded
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Add
Domain and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

All Domains
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
Add Domain Name:
Add a Domain Name to the UTS Per-session
configuration. This creates a folder with the name specified for the domain.
Create Default Configuration:
A default User – per session configuration
is created that will apply to any session if that session does not have a specific
Domain User configuration or specific Domain Name default configuration.
|

Specific Domain
|
|
Represents
ALL users in the specific domains
|
|
|

|
Represents
ALL users in the specific domain with a default configuration defined.
|
This is the root of the
User – per session All Domains configuration object.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\DomainUsers\[Domain
Name]
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the specific Domain Name Users and the specific Domain Name default configuration
(if it exists).
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Paste,
Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

Specific Domain
|
|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Add User: Add a User to the UTS Domain Name Per-session
configuration. This creates a folder with the name specified for the User.
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) to this specific Domain Name. This creates a folder with the name specified
for the User.
Rename: Rename a Domain Name.
Note: If you rename a Domain Name then all
associated Domain Users that are connected will get an error. This is because
the path to the folder is changed and the running logon script will try to path
to the original location. Please make sure that all users are logged off or can
safely be disconnected when renaming a domain name. If the Domain Name folder
contains User Folders then they are moved to the path associated with the new
name.
Delete: Delete a Domain Name.
Note: If you Delete a Domain Name then all
associated Domain Users that are connected will get an error. This is because
the folder that contains the Domain Name and Domain Users is deleted thus
altering the path. The running logon script will try to path to the original
location. Please make sure that all users are logged off or can safely be
disconnected deleting a domain name.
|

Domain
User
|
|
A specific User
within a specific domain. Expand to see property pages
|
This is the User Name for
the specific Domain.
Folder: [UTS Installation
Folder]\scripts\DomainUsers\[Domain Name]\[User Name]
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the property pages for the specific user.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Paste,
Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

Domain
User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: Copy the User configuration to an UTS copy
buffer. This configuration can then be pasted either creating a new User
Configuration object or overwriting and existing object.
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) to this specific Domain Name. This creates a folder with the name specified
for the User.
Rename: Rename a Domain User.
Delete: Delete a Domain User (see footnote 44)
Export: Export the Domain User configuration to
a XML formatted file.
Import: Import the Domain User configuration
from a XML formatted file.
Local Users
|

All Local Users
|
|
This
icon represents ALL Local Users. Expand to see configurations for each
specific local user
|
This is the root of all
Local Users.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\LocalUsers
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the list of Local User Names.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
Paste, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

All Local Users
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) configuration to the Local Users object. This creates a folder with
the name specified for the User.
Add User: Add a User to the UTS Local User – per session
configuration. This creates a folder with the name specified for the User.
Create Default Configuration:
A default Local User – per session
configuration is created that will apply to any session if that session does
not have a specific Local User configuration.
|

Local User
|
|
A specific Local
User
|
This is the User Name
for a specific Local User.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\LocalUsers]\[User
Name]
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the property pages for the specific user.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Paste,
Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

Local User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: Copy the User configuration to an UTS
copy buffer. This configuration can then be pasted either creating a new User
Configuration object or overwriting and existing object.
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) to this specific Name. This creates a folder with the name specified
for the User.
Rename: Rename a User.
Delete: Delete a Local User (see footnote 45)
Export: Export the Local User configuration to an
XML formatted file.
Import: Import the Local User configuration
from an XML formatted file.
|
All IP
Address /Ranges
|
|
This
icon represents ALL IP Address/Range based User Configurations
|
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the specific IP Address/Range logon scripts.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Paste,
Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|
All IP
Address /Ranges
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) to this specific IP Address/Range Logon Script. This creates a folder
with the name specified for the IP Address/Range logon script.
Export: Export the configuration to an XML
formatted file.
Import: Export the User configuration to an XML
formatted file
|
IP
Address /Range
|
|
This
icon represents a User Configurations that is associated with an IP Address/Range
|
Folder: [UTS Installation
Folder]\scripts\
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the property pages for the specific user configuration.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation: Paste,
Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|
Local User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: Copy the User configuration to an UTS
copy buffer. This configuration can then be pasted either creating a new User
Configuration object or overwriting and existing object.
Paste: Paste a copied Logon Script User (User
name or Template) to this specific Name. This creates a folder with the name
specified for the Logon Script.
Rename: Rename a IP Address/Range Logon Script.
Delete: Delete IP Address/Range Logon Script (see
footnote 46)
Export: Export the Logon Script User configuration
to an XML formatted file.
Import: Import the Logon Script User configuration
from an XML formatted file.
|

All Grandfathered Users
|
|
This
icon represents ALL Grandfathered Users.
|
This is the root for
all Grandfathered Users. Grandfathered users are users defined in a previously installed
version (8.02 or earlier) of the UTS. Folders with the name of a user in the scripts
folder that contain logon script are considered Grandfathered Users.
Their logon scripts
remain in the scripts folder until the administrator moves them to either a Domain
User or Local User. Additionally, if the administrator manually creates
folder is and logon script in the scripts folder then they will show up as
Grandfathered users.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the list of Grandfathered Users.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

All Grandfathered Users
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grandfathered User
|
|
A specific Local
User
|
This is the User Name
for a specific Grandfathered User.
Folder: [UTS Installation Folder]\scripts\LocalUsers]\[User
Name]
Click ‘+’ to expand to see
the property pages for the specific user.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
Paste, Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

Grandfathered User
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: Copy the user configuration to an UTS copy
buffer. This configuration can then be pasted either creating a new User Configuration
object or overwriting and existing object.
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) to this specific Name. This creates a folder with the name specified
for the User.
Rename: Rename a User.
Delete: Delete a User (see footnote 48
)
Export: Export the Local User configuration to an
XML formatted file.
Import: Import the Local User configuration
from an XML formatted file.
|

All User Templates
|
|
This is all
user templates. Expand to see list of User Templates
|
This is the root for all
User Templates.
Folder: [UTS Installation
Folder]\scripts\Templates\User\
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the user templates.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
Paste, Import and New
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

All User Templates
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or
Template) to this specific User Template. This creates a folder with the name specified
for the User Template.
Import: Import the User configuration from an
XML formatted file.
New: Create a new User Template. This creates
a folder with the name specified for the Template.
|

User Template
|
|
A specific Local
User
|
This is the User Template
Name for a specific User.
Folder: [UTS Installation
Folder]\scripts\Templates\User\[Template Name]
Click ‘+’ to expand to
see the property pages for the specific user template.
Click ‘-’ to collapse
Right Click Operation:
Paste, Rename, Delete, Add User and Create Default Configuration
|
|
Copy
|
Paste
|
Rename
|
Delete
|
Export
|
Import
|
New
|
Add Domain
|
Add User
|
Create Default Configuration
|
Contain Property Pages
|
|

User Template
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|
Copy: Copy the User configuration to an UTS
copy buffer. This configuration can then be pasted either creating a new User
Configuration object or overwriting and existing object.
Paste: Paste a copied User (User name or Template)
to this specific Name. This creates a folder with the name specified for the User.
Rename: Rename a User Template.
Delete: Delete a User Template.
Export: Export the User Template configuration
to an XML formatted file.
Import: Import the User configuration from an
XML formatted file.
For those customers
that are used to the pre-GUI method of configuration the UTS you have two options
·
Continue to use the legacy UTS configuration
The
advantage to using the legacy configuration is that you do not have to change
your methods or procedures for configuring the UTS.
Additionally,
most items the UTS can be configured via SSH and Telnet.
There
are new features that include Domain Names, Grandfathered Users, etc. that can
still be fully utilized with the legacy configuration techniques.
·
Migrate to the GUI
The
advantage to migrating to the GUI is that you gain all the benefits of the Graphical
User Interface including minimal training of new administrators on editing the
registry, adding environment variables to scripts etc.
1.
How much effort is it going to require migrating to the GUI?
Not
much at all. The GUI will come up and run out of the box with no changes. All
your existing users will show up as Grandfathered Users. It is recommended that
you move the users to either the Local Users or Domain Name Users categories.
2.
Can I still configure items the old way after I convert?
Yes.
You can switch back and forth as you desire.
3.
Do I have to restart the services after making a change?
Yes.
If it is a Global – per system configuration item
No. If
it is a User – per session configuration item
Logon scripts (user configurations)
created in pre-GUI versions of the UTS will
appear under Grandfathered Users in the GUI version. It is recommended to move
Grandfathered User configurations to either a Domain User or Local User
configuration location.
Example: Move the
Grandfathered configuration to a Local User
|
Right click Grandfathered
User configuration “tom” and select copy
|
Right Click on Local Users
and select paste
|
After pasting the result
will show Copy (1) of tom
|
|
Figure 177: Grandfathered User - Copy
|
Figure 178:
Grandfathered User - Paste
|
Figure 179:
Grandfathered User - after copy
|
|
Right click on “Copy (1)
of tom” and select Rename
|
Type in the new name
“tom”
|
Don’t forget to delete
the Grandfathered User Tom.
|
|
Figure 180: Local User - Rename
|
Figure 181: Local User - After Rename
|
Figure 182: Grandfathered User - Delete
|
The same process is used
to move a Grandfathered User to a Domain Name User.
Registry settings apply
to the Global – per system configuration and as such there is no required
migration.
Environment variable
settings apply to the User – per session configuration and show up in as part of
the Grandfathered Users configuration. They are migrated as described in the Logon
Script Migration (see page 363)
The UTS installation
folder contains a folder named scripts.
This folder and its subfolders contain batch files (scripts) for user sessions.
Pre-GUI versions of the UTS used subfolders with the User Name to associate the
script with the user. Post-GUI versions have three subfolders in the script
folder.
·
DomainUsers
·
LocalUsers
·
Templates
The DomainUsers folder may
contain a default configuration (if configured) for all domains. Additionally,
subfolders will exist with the name of any domain names configured.
Each Domain Name folder
may contain a default configuration (if configured) for all users within that
domain name. Additionally, subfolders will exist with the name of each user
configured for that domain.
Each user name folder
will contain scripts associated with that domain user name.
The LocalUsers folder
may contain a default configuration (if configured) for all Local Users. Additionally,
subfolders will exist with the name of any local User Names configured.
Each user name folder
will contain scripts associated with that local user name.
The Templates folder contains
two subfolders
·
System – contains templates for Global – per system configurations
Each
system template contains an XML file with the name of the template. This can be
copied to the active configuration or another system template.
·
User – contains templates for User – per session configurations
Each
template will be a logon script (batch file). This script can be copied to any
User – per session configuration.
Logon scripts are
automatically created with the configuration GUI. A logon script is created
each time a User – Per Session property page
is created. This includes:
Ø  Domain User
Domain User
Ø  Local User
Local User
Ø  IP Address/Range User
IP Address/Range User
Ø  Grandfathered User
Grandfathered User
Ø  User Template
User Template
Ø  Default Configuration
Default Configuration
For
legacy Logon Script description see page 218
Registry settings apply
to the Global – per system configuration.
The GSW Configuration Tool
eliminates the manual configuration of registry through the GUI. One or more
registry settings can be accomplished through a single GUI setting.
Environment variable
settings apply to the User – per session configuration.
The GSW Configuration Tool
eliminates the manual configuration of environment variables through the GUI.
One or more environment variables can be accomplished through a single GUI setting.
Text files associated
with the Global or User configurations can be accessed through the GUI. The GUI
will launch notepad.exe as the editor that allows you to edit and save the text
file configurations.
Global
– Active Configuration
The Global – per system
Active Configuration Summary provides the administrator with a quick view of most
of the Global – per system configuration settings on the right side of the
display. Some configuration values are stored in text files and they can be
viewed by clicking on a button to open the text file.
On the left side of the
display are categories that organize the Active configuration settings into
similar groups.
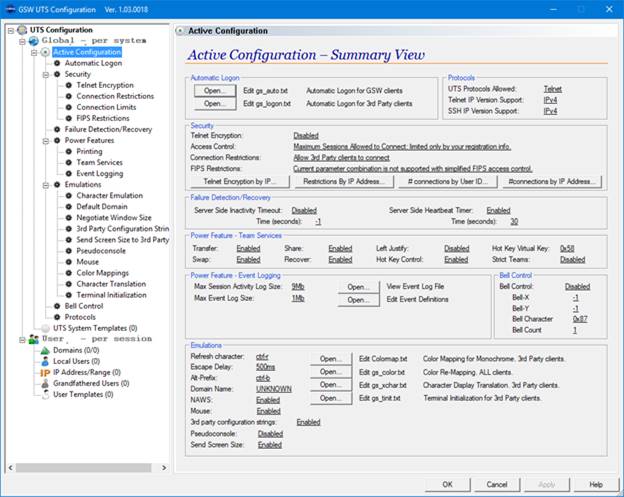
Figure 183: Global - per system Active Configuration Summary View
From the Active
Configuration Summary view it is easy to determine which property page to use to
edit the configuration setting. Each configuration setting resides within a frame
with a label. For example: Automatic Logon is a label on the frame around the
configuration settings associated with Automatic Logon. On the left side of the
display is the property page icon with Automatic Logon as the name. Clicking on
the property page Automatic Logon will display the properties associated with Automatic
Logon on the right side of the display.
Similarly, the Failure
Detection/Recovery frame on the display on the right contains the configuration
settings associated with Failure Detection/Recovery and on the left side of the
display is the property page icon with Failure Detection/Recovery as the name. Click
on the property page Failure Detection/Recovery will display the properties
associated with Failure Detection/Recovery on the right side of the display.
There are a few exceptions
to this direct association due to screen space but will still be easy to find.
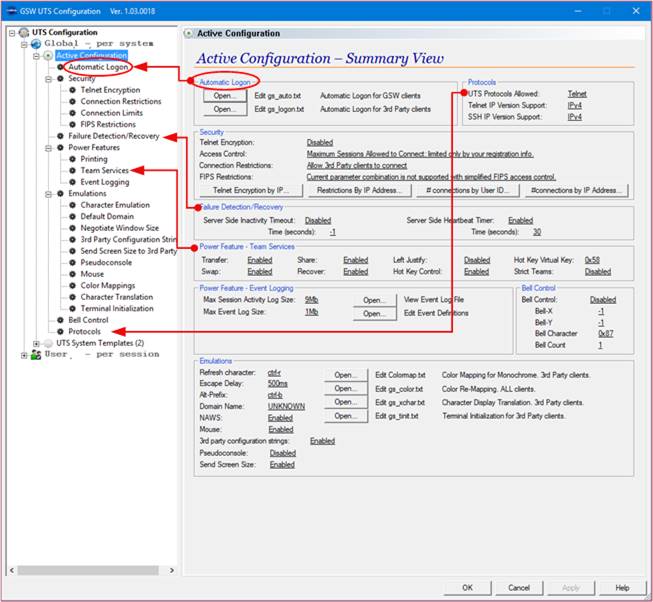
Figure 184: Active Configuration Summary View - Property Page and Frame Relationship
Automatic Logon
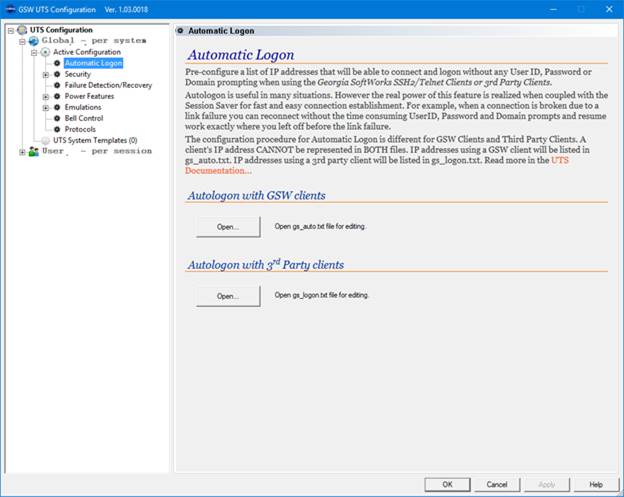
Figure 185: GSW UTS GUI - Automatic
Logon
Please see page 111 for details about Automatic Logon.
Security
Summary
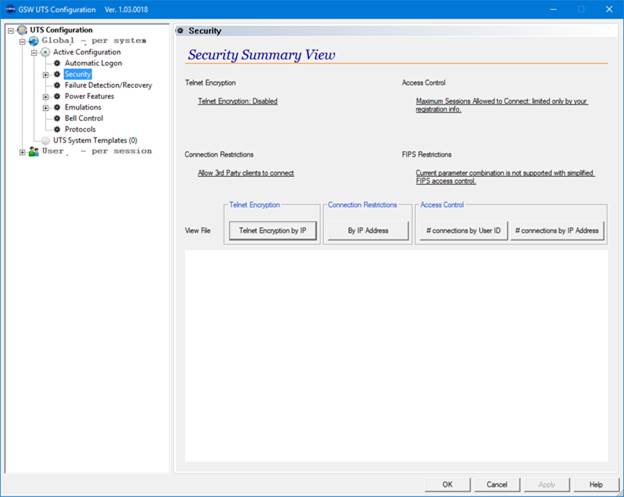
Figure 186: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Security Summary
The Security Summary
View provides a quick view of the:
·
Telnet Encryption (See page 93)
·
Access Control ( 98 )
·
Connection Restrictions (See page 98 )
·
FIPS Restrictions (See page 97)
and allows
viewing of the relevant text files
·
Telnet Encryption by IP Address (See page 96)
·
Connection Restrictions by IP Address (See page 104)
·
Access control for the number of connections by a User ID (See
page 102)
·
Access control for the number of connections by an IP Address (See
page 104)
Security - Telnet Encryption
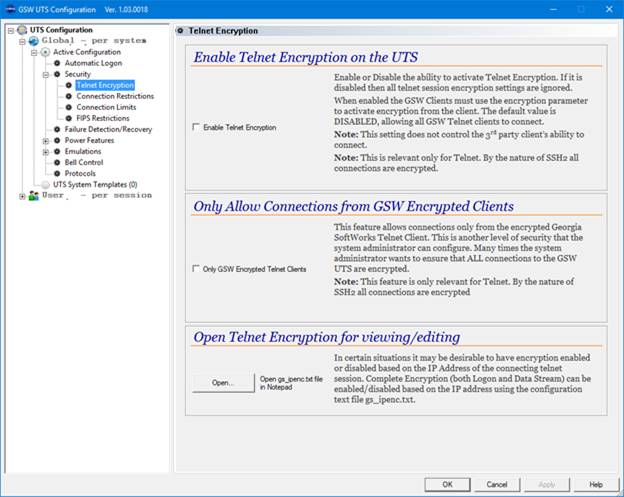
Figure 187: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Security - Telnet Encryption
The Telnet Encryption
configuration screen provides configuration of:
·
Enable Telnet Encryption – (See page 94)
·
Only GSW Encrypted Telnet Clients – (See page 107)
And
Opening and editing the
text file to enable or disable telnet encryption based on IP Address.
·
gs_ipenc.txt – (See page 96)
Security – Connection Restrictions
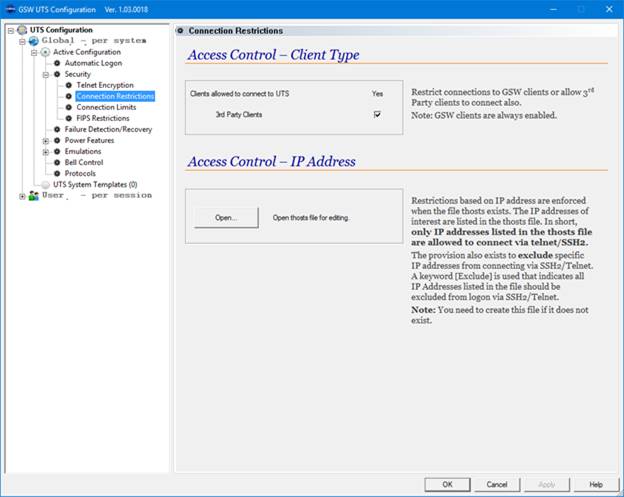
Figure 188: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Security - Connection Restrictions
The Connection Restrictions
configuration screen provides configuration of:
·
Allow 3rd Party clients to connect to the UTS – (See
page 100)
·
Opening and editing the text file to enable or disable telnet encryption
based on an IP Address. gs_ipenc.txt – (See page 96)
Security – Connection Limits
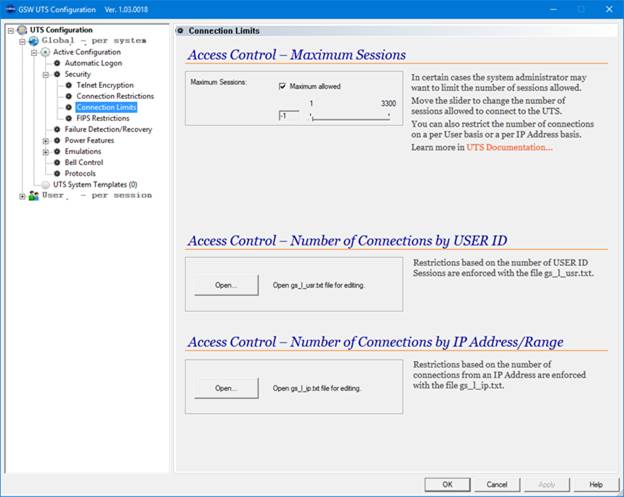
Figure 189: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Security - Connection Limits
The Connection Limits screen
provides configuration of the:
·
Maximum Sessions allowed (See page 101 )
and
allows viewing of the relevant text files
·
Access control for the number of connections by a User ID (See
page 102)
·
Access control for the number of connections by an IP Address
(See page 104)
Security
– FIPS Restrictions
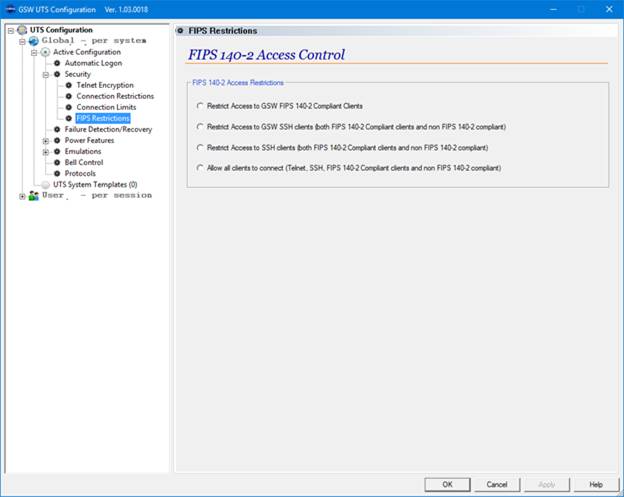
Figure 190: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Security - FIPS Restrictions
The FIPS 140-2 Restrictions
screen provides configuration for access control of FIPS clients.
This feature allows
connections only from the Georgia SoftWorks FIPS 140-2 SSH Clients. This is a
high level of security that the system administrator can configure. Many times,
the system administrator will insist that END to END FIPS 140-2 compliance is
the only allowable option.
The variables GSW_FIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients, AllowTelnetWithSSH and LcnOnLoopbackOnly are registry key
values. Used in conjunction, with specific values, these Registry keys enable
or disable the ability to restrict connection only by GSW FIPS 140-2 compliant clients.
The keys are:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\GSW_FIPSOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopBackOnly
Set
each registry key value to the following:
AllowTelnetWithSSH=0
EnableRFC854Clients=0
GSW_FIPSOnly=1
LsnOnLoopBack=1
This feature
allows connections only from the Georgia SoftWorks FIPS 140-2 SSH2 Clients. This
is a high level of security that the system administrator can configure. Many
times the system administrator will insist that END to END FIPS 140-2
compliance is the only allowable option.
The variables
Gsw_FIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients, AllowTelnetWithSSH and LcnOnLoopbackOnly are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific
values, these Registry keys enable or disable the ability to restrict
connection only by GSW FIPS 140-2 compliant clients. The keys are:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\GSW_FIPSOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopBackOnly
Set each
registry key value to the following
AllowTelnetWithSSH=0
EnableRFC854Clients=0
GSW_FIPSOnly=1
LsnOnLoopBack=1
This feature
allows connections only from the Georgia SoftWorks FIPS 140-2 SSH2 Clients.
This is a high level of security that the system administrator can configure.
Many times the system administrator will insist that END to END FIPS 140-2 compliance
is the only allowable option.
The variables
Gsw_FIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients, AllowTelnetWithSSH and LcnOnLoopbackOnly are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific
values, these Registry keys enable or disable the ability to restrict
connection only by GSW FIPS 140-2 compliant clients. The keys are:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\GSW_FIPSOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopBackOnly
Set each registry
key value to the following
AllowTelnetWithSSH=0
EnableRFC854Clients=0
GSW_FIPSOnly=1
LsnOnLoopBack=1
(both FIPS
140-2 compliant clients and non FIPS 140-2 compliant)
The variables GSWFIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH are registry key values. Used in
conjunction, with specific values, these Registry keys enable or disable the
ability to restrict connection only by GSW SSH clients. The keys are:
The variables GswFIPSOnly, EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH
are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific values, these Registry
keys enable or disable the ability to restrict connection only by GSW SSH clients.
The keys are The variables GswFIPSOnly, EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH
are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific values, these Registry
keys enable or disable the ability to restrict connection only by GSW SSH
clients. The keys areHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\GSW_FIPSOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopBackOnly
Set
each registry key value to the following:
AllowTelnetWithSSH=0
EnableRFC854Clients=0
GSW_FIPSOnly=0
LsnOnLoopBack=1
(both FIPS
140-2 compliant clients and non FIPS 140-2 compliant)
The variables GSWFIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH are registry key values. Used in
conjunction, with specific values, these Registry keys enable or disable the
ability to restrict connection only by GSW SSH clients. The keys are:
The variables GswFIPSOnly, EnableRFC854Clients and
AllowTelnetWithSSH are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific
values, these Registry keys enable or disable the ability to restrict
connection only by GSW SSH clients. The keys are The variables GswFIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH are registry key values. Used in conjunction,
with specific values, these Registry keys enable or disable the ability to
restrict connection only by GSW SSH clients. The keys areHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\GSW_FIPSOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopBackOnly
Set each
registry key value to the following:
AllowTelnetWithSSH=0
EnableRFC854Clients=1
GSW_FIPSOnly=0
LsnOnLoopBack=1
(Telnet,
SSH, both FIPS 140-2 compliant clients and non FIPS 140-2 compliant)
The variables GSWFIPSOnly,
EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH are registry key values. Used in
conjunction, with specific values, these Registry keys enable or disable the
ability to restrict connection only by GSW SSH clients. The keys are:
The variables GswFIPSOnly, EnableRFC854Clients and AllowTelnetWithSSH
are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific values, these
Registry keys enable or disable the ability to restrict connection only by GSW
SSH clients. The keys are The variables GswFIPSOnly, EnableRFC854Clients and
AllowTelnetWithSSH are registry key values. Used in conjunction, with specific
values, these Registry keys enable or disable the ability to restrict connection
only by GSW SSH clients. The keys areHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\AllowTelnetWithSSH
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\EnableRFC854Clients
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\GSW_FIPSOnly
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\GS_Tnet\Parameters\LsnOnLoopBackOnly
Set
each registry key value to the following:
AllowTelnetWithSSH=0
EnableRFC854Clients=1
GSW_FIPSOnly=0
LsnOnLoopBack=1
Failure Detection / Recovery
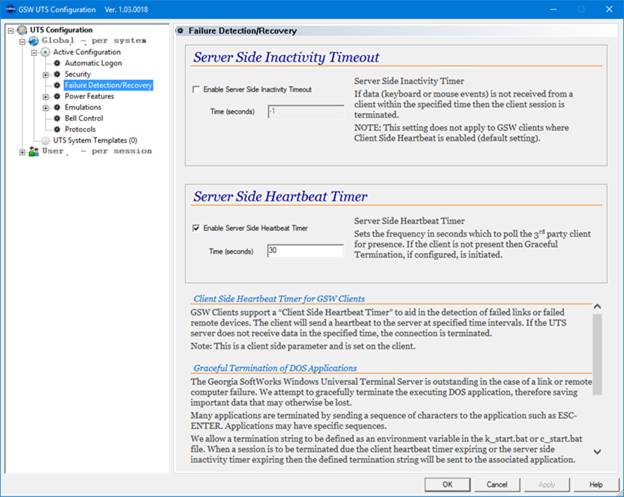
Figure 191: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Failure Detection and Recovery
The Failure Detection/Recovery
screen provides configuration of the:
·
Server-Side Inactivity Timeout (See page 153)
·
Server-Side Heartbeat Timer (See page 155)
Power
Features Summary
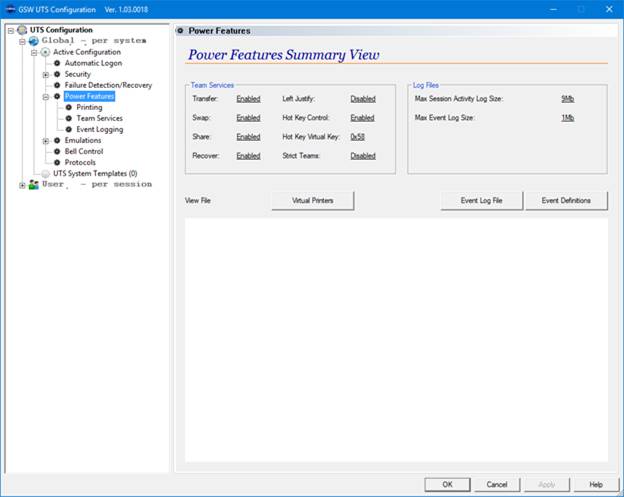
Figure 192: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Power Features Summary
The Power Features Summary
View provides a quick view of the
·
Team Services configuration (See page 117)
·
Log Files configuration
·
Max Session Activity Log File Size (See page 215)
·
Event Log File Size (214)
and
allows viewing of the relevant system printer configuration
·
Virtual Printers (See page 227)
and
allows viewing of the relevant text files
·
Event Log File (See page 213)
·
Event Definitions File (See page 212)
Power Features – Printing
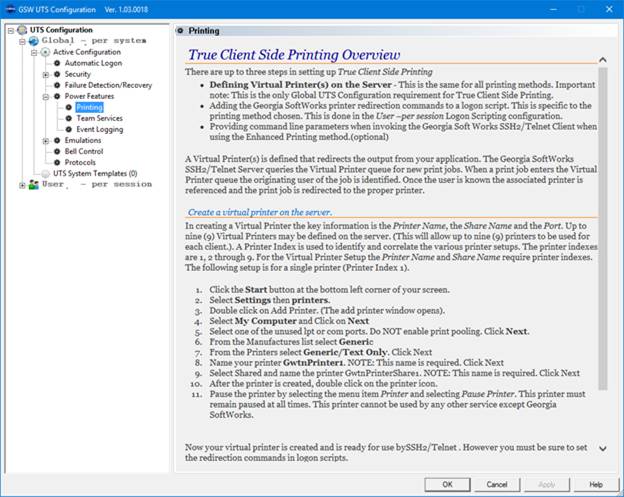
Figure 193: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Power Features - Printing
The True Client-Side Printing
Overview briefly describes the steps to set up client-side printing. For a full
description please see page 226.
Power Features – Team Services
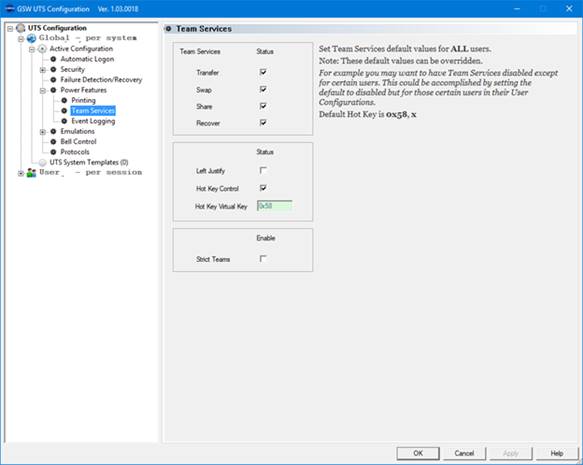
Figure 194: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Power Features - Team Services
The Team Services
configuration screen provides configuration for the Team Services default values.
Note that default values can be overridden on a per user basis.
·
Team Services General Operation (See page 117)
·
Team Services Transfer (See page 139)
·
Team Services Swap (See page 140)
·
Team Services Share (See page 141)
·
Team Services Recover (See page 138)
·
Team Services Left Justify (See page 142)
·
Team Services Hot Key Control (See page 143)
·
Team Services Hot Key Virtual Key (See page 143)
·
Strict Teams (See page 134)
Power Features – Event Logging
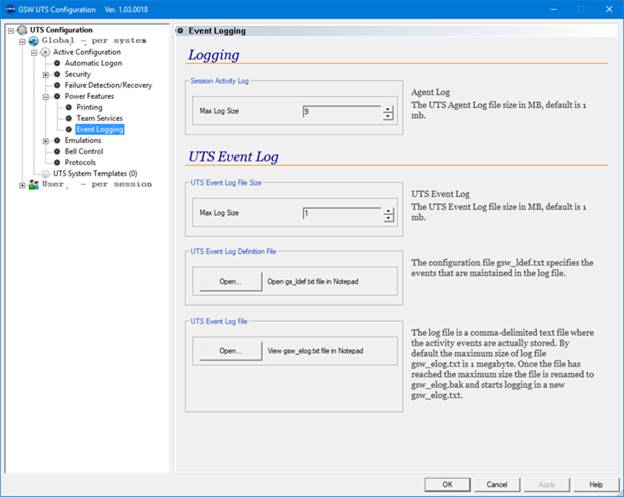
Figure 195: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Power Features - Event Logging
The Event Logging configuration
screen provides configuration for:
·
Session Activity Log - Max Log Size (215)
·
UTS Event Log File Size – Max Log Size (See page 214)
and
allows viewing of the relevant text files
·
UTS Event Log Definition File (See page 213)
·
UTS Event Log File (See page 212)
Emulations
Summary
Figure 196: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations Summary
The Emulations Summary
View provides a quick view of the configuration for:
·
Refresh Character (See page 250)
·
Escape Delay (See page 174)
·
Alt-Prefix (See page 172)
·
Domain Name (See page 282)
·
NAWS (Negotiate Windows Size Telnet Option) (See page 175
)
·
3rd Party
Configuration Strings (See page 175)
·
Send Screen Size
to 3rd Party clients. (See page 177 , for Logon Script override)
·
Enable Pseudoconsole (See page 178,
for Logon Script override)
·
3rd Party Mouse Support – (See page 163
)
·
Device and client configuration strings (See page 175)
and allows
viewing of the relevant text files
·
Color Mapping (See page 170)
·
Color Re-Mapping (See page 181)
·
Character Translation (See page 183)
·
Terminal Initialization (See page 184)
Emulations - Character Emulation

Figure 197: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations - Character Emulation
The Character Emulation
screen provides the configuration for:
·
Refresh Character (See page 250)
·
Escape Delay (See page 174)
·
Alt-Prefix (See page 172)
Emulations – Default Domain
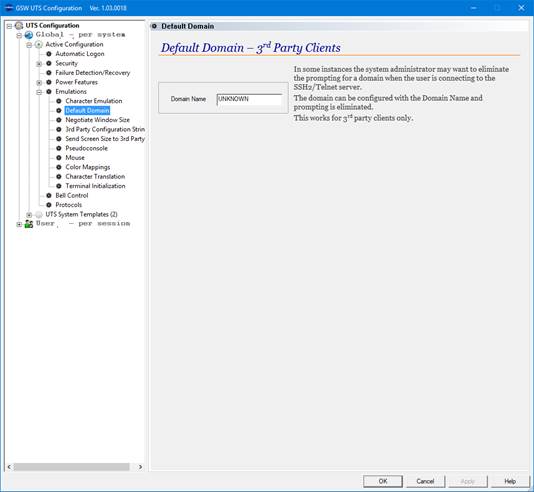
Figure 198: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations - Default Domain
The Emulations Default
Domain screen provides configuration for:
·
Domain Name (See page 282)
Emulations
– Negotiate Windows Size
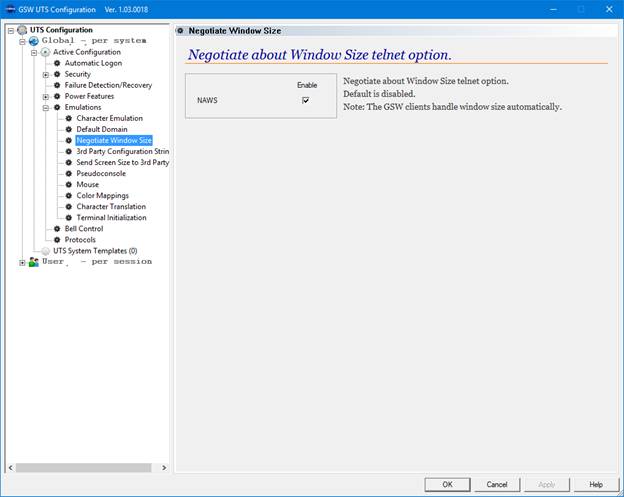
Figure 199: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations - NAWS (Negotiate About Windows Size)
The Emulations
Negotiate Windows Size screen provides configuration for:
·
NAWS (Negotiate Windows Size Telnet Option) (See page 175
)
Emulations – GSW ConnectBot Device
and Client Info (Strings)
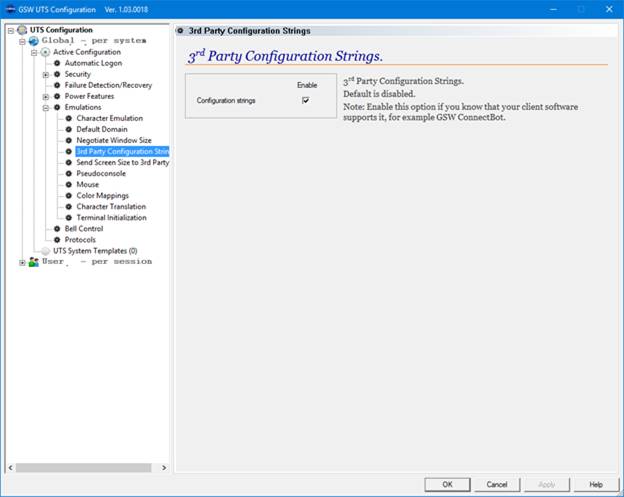
Figure 200: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations – Device and Client Information (Strings)
Currently this feature
is available to work with GSW ConnectBot – SSH/Telnet client for Android.
When enabled, a number
of environment variables can be accessed by the application to obtain device
and client information. This setting is configurable on a Global or User
basis. The device and client information can be used by the application in any
manner deemed useful. The uses range from reports to application logic
decisions based on device specific specifications such as display density etc.
When enabled a variable
will be added to the users Logon Script as follows:
set gwtn_enable_3rd_party_config_strings=y
The number and list of
variables available is device dependent.
To view the list of available
variables you can use the command line “set gswncl_“command from within a SSH
or Telnet session. See the example below.
Figure 201: Device and Client
Information Set gwtncl_ cmd
To manually configure Device
and Client information strings see page
(See page 175 )
Emulations – Send Screen Size to 3rd Party
Clients
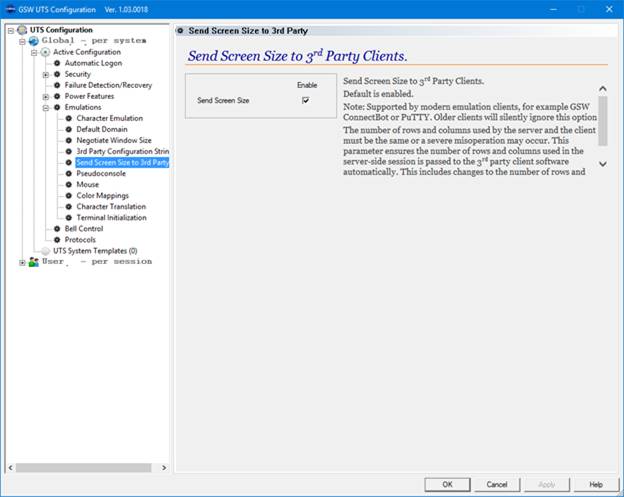
Figure 202: Send screen size to 3rd
party client
Default is Enabled.
The GSW UTS will send screen size information to 3rd
party clients. The number of rows and columns used by the server and the client
must be the same or a severe misoperation may occur. This GLOBAL parameter
ensures that the number of rows and columns used in the server-side session is
passed to the 3rd party client software automatically.
Sometimes, certain client features may require this
parameter is disabled. The logon scripts can override the global setting. For example,
if you are using any of the GSW ConnectBot features that require the client
screen size parameters to be 0,0, then you will want to disable this parameter using
the Logon script.
See page 177, to see how to use a Logon Script override.
If the GSW ConnectBot (or any other) client is setting
the screen size to non-zero values, then the Send Screen Size to 3rd
Party client value should stay Enabled.
Emulations – Pseudoconsole
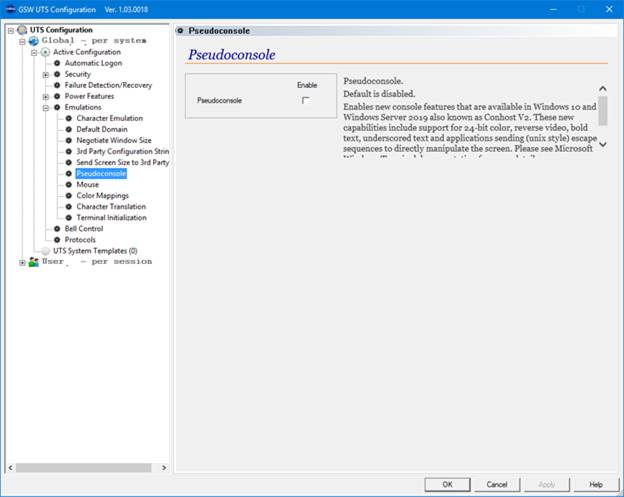
Figure 203: Enable Pseudoconsole
Default is disabled
Enables new console features
that are available in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019 also known as Conhost
V2 (ConPty). These new capabilities include support for 24-bit color, reverse
video, bold text, underscored text and applications sending (Unix style) escape
sequences to directly manipulate the screen. Please see Microsoft Windows
Terminal documentation for more details. Please make sure that this option is
disabled on Windows machines that do not support Pseudoconsole.
This GLOBAL parameter can
be overridden using a logon script.
Please see page 178
to see how to use a logon script for this purpose.
Emulations – 3rd Party
Mouse Support
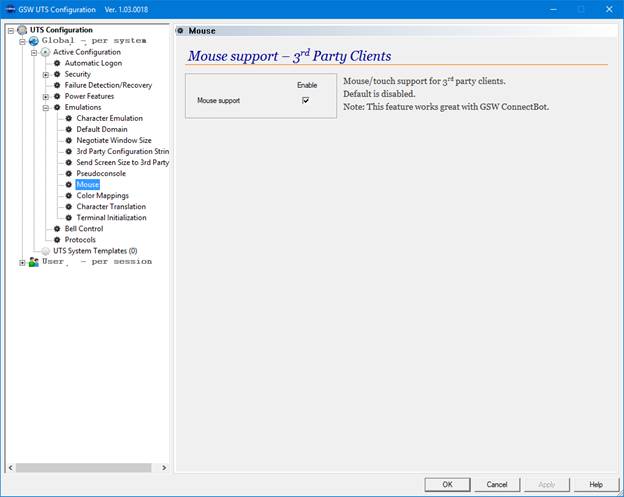
Figure 204: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations – Enable 3rd Party Mouse
This feature works with
GSW ConnectBot SSH/Telnet client for Android and other 3rd party
clients supporting mouse, e.g. PuTTY.
When enabled, users
using a touchscreen/mouse capable device will be able to select and use the features
of the mouse enabled application as expected. In the case of touch screens, touch
events will be translated to mouse events. This setting can be configured on a
Global or per User basis.
The per User basis can
be used to easily handle a mix of clients where some of them support mouse and
others do not.
To manually configure Mouse
Support for 3rd party clients, see page (See page 163 )
Emulations – Color Mappings
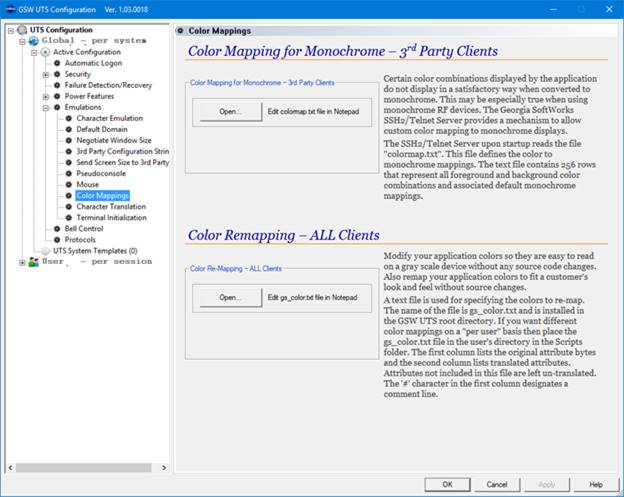
Figure 205: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations - Color Remapping
The Emulations Color
Mappings screen allows viewing/editing of the relevant text files:
·
Color Mapping (See page 170)
·
Color Re-Mapping (See page 181)
Emulations – Character Translation
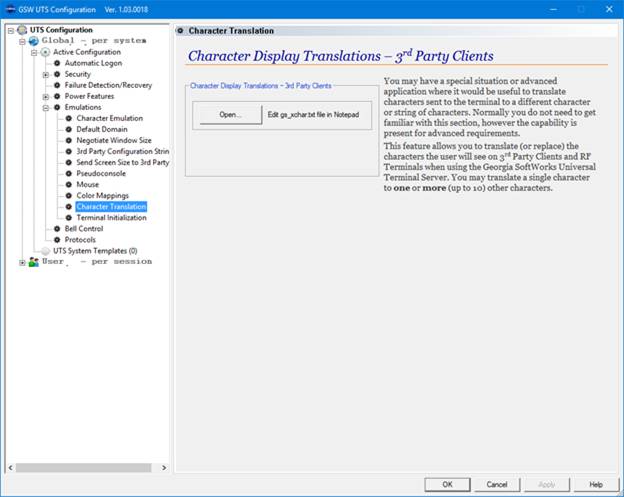
Figure 206: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations - Character Translation
The Emulations Character
Translation screen allows viewing/editing of the relevant text files:
·
Character Translation (See page 183)
Emulations – Terminal Initialization
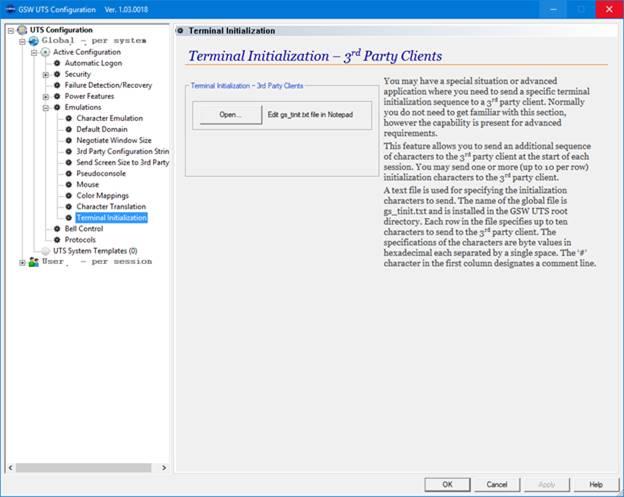
Figure 207: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Emulations - Terminal Initialization
The Emulations Terminal
Initialization screen allows viewing/editing of the relevant text files:
·
Terminal Initialization (See page 184)
Bell
Control
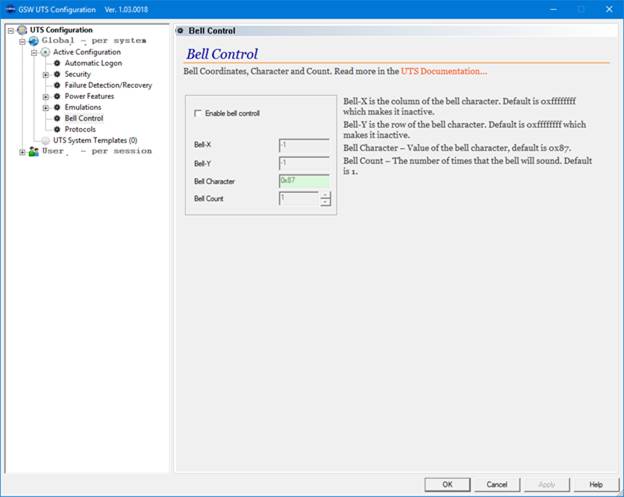
Figure 208: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Bell Control
The Bell Control screen
provides configuration of the:
·
Enable Bell Control (See page 279)
·
Bell-X (See page 279)
·
Bell-Y (See page 279)
·
Bell Character (See page 279)
·
Bell Count (See page 279)
Protocols
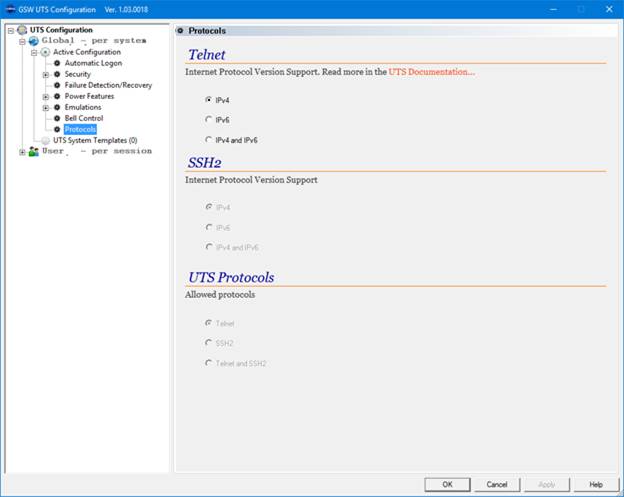
Figure 209: GSW UTS GUI - Active
Configuration - Protocols
The Protocols screen
provides configuration of:
·
Telnet Internet Protocol Version Support (See page 256)
·
SSH Internet Protocol Version Support (See page 257)
·
UTS Protocols – Allowed Protocols (See page 258)
Note: The UTS Service
needs to be restarted before any of the protocol changes will occur.
UTS
System Templates
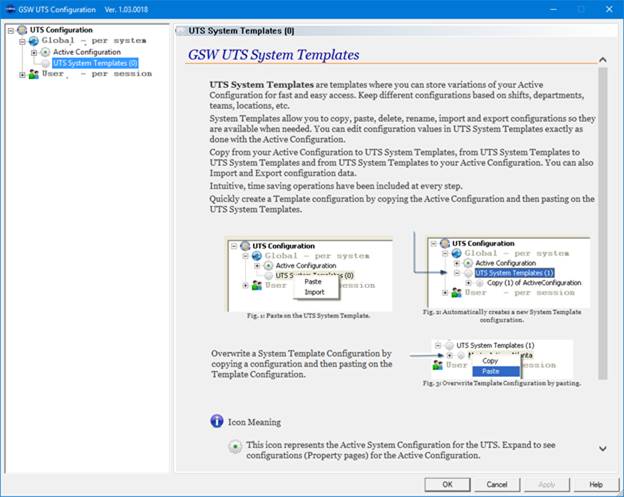
Figure 210: Global - System Templates
UTS System allows you
to create and store variations of your active configuration for fast and easy access.
NOTE: Text files
used for configuration are not available in Templates.
If you
want to ensure configuration text files are associated with a specific
template, then you should manually backup the text file(s) with a corresponding
name.
UTS System Template - Individual
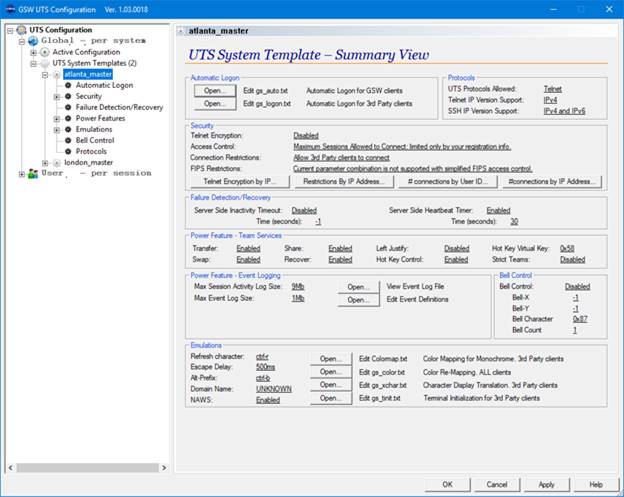
Figure 211: Global - System Template - Individual
Each Template is of the
same format as the Active Configuration. Please see the Active Configuration
for details.
NOTE: Text files
used for configuration are not available in Templates.
If you
want to ensure configuration text files are associated with a specific template,
then you should manually backup the text file(s) with a corresponding name.
User – per session Configuration
– Features
Each session has an associated configuration. This is true
of sessions initiated by Domain Users, Local Users, Grandfathered Users, and IP
Address/Range connections.
Each of the session configurations is termed “User – per
session” or “User” configuration.
The GSW Configuration GUI Tool allows the administrator to
organize the configurations based on Domains, Domain Names, Domain Name Users, Local
Users, IP Address Ranges, Grandfathered Users and User Templates. Additionally,
a default configuration may be specified for different objects.
This provides a powerful user configuration hierarchy that
can be traversed and the UTS will apply the appropriate configuration. It is
important to understand the configuration hierarchy.
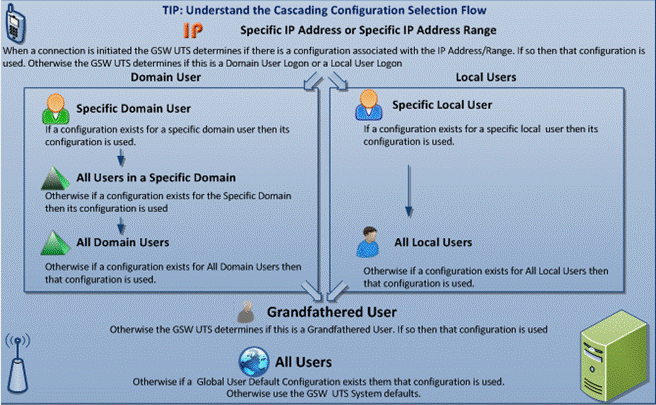
Figure 212: Cascading Configuration
Selection
As pointed out above,
when a connection is initiated the UTS checks for an existing configuration is
in the IP Address/Range objects. If a matching configuration
is not found then the UTS determines if the connection is either a Domain User
or Local User.
If it is a domain user,
then the UTS determines if there is a matching Domain User within the matching
Domain Name. If not, then the UTS determines if a Default configuration exists
for the specific Domain Name. If not, then the UTS determines if there is a Default
configuration for All Domain Users. If not then the UTS checks to see if there is
a configuration match with Grandfathered User. If there is no
match then the UTS checks if there is a Default configuration for All Users, and
if there is still no match then the UTS system defaults are used.
Continuing from above if
the connection being initiated is not a domain user then the UTS but a local
user then the UTS determines if there is a matching Local User configuration.
If no match exists, then the UTS determines if a Default configuration exists
for all Local Users. If not then the UTS checks for a configuration match
with Grandfathered User. If there is no match then the UTS checks if there is a
Default configuration for All Users, and if there is still no match then the
UTS system defaults are used.
Default Configurations
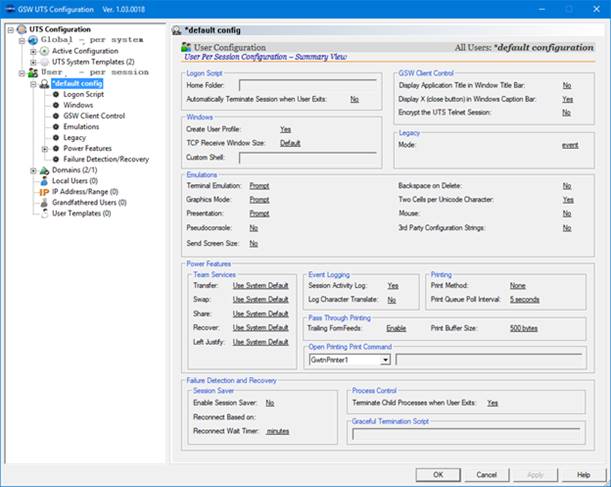
Figure 213: GUI Tool - User Default Configuration
Default
configurations may be created for the objects listed in Table
58. You can quickly
determine if a default configuration exists for an object by viewing if it has
the black circle with a white check in the bottom right of the icon as shown
below.
|
|
ICON
|
Create Default Configuration
|
|
|
7
|
User - per session
|

|
If a session for a user (domain or local) is initiated
and there no specific configuration for that user and there is not a default
configuration for in the Specific Domain or All Domains (for domain user) or
All Local Users (for a local user) then use the User - per session default
configuration.
|
|
8
|

All Domains
|

|
If a session for a domain user is initiated and there
is not a specific configuration for that domain user and there is not a default
configuration for that domain name, then use the ALL Domains Default configuration.
|
|
9
|

Specific Domain
|

|
If session for a specific
domain name is initiated and there is not a specific configuration for that
domain user, then use the Specific Domain Name Default Configuration
|
|
11
|

All Local Users
|

|
If a local user session
is initiated and there is not a specific configuration for the user, then use
the All Local Users Default Configuration
|
Table 58- Objects that may have a Default Configuration
A default configuration
is a user configuration. It is configured in the same way as a user
configuration. A default configuration is created by right clicking and selecting
“Create Default Configuration”.
Domains
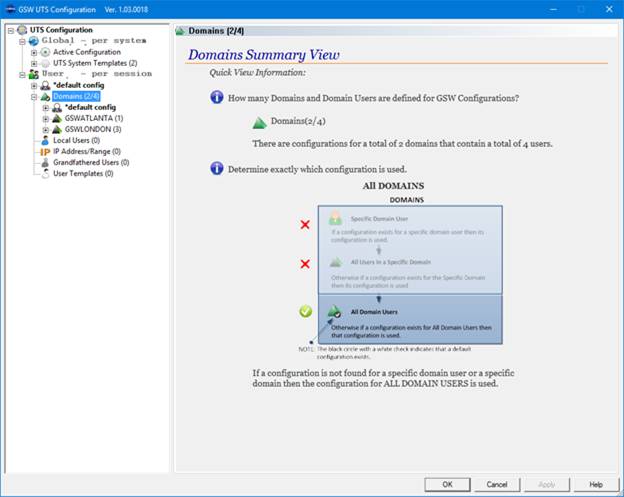
Figure 214: GUI Tool - Domains
The
Domains screen allows you to view quick status information such as how many
domains configurations are defined, how many users are defined for each domain.
Additionally, the administrator may perform right click operations at the Domain
level such as adding, deleting domains, creating default configurations etc.
Domain
Name
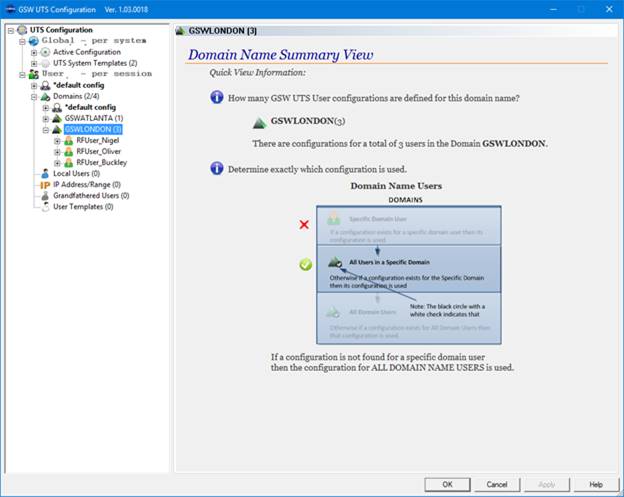
Figure 215: GUI Tool - Domain Names
The Domain Name screen
allows you to view quick status information such as how many user configurations
are defined for this domain name. The administrator may also perform right
click operations at the Domain Name level such as adding, deleting users for
this Domain Name, creating default configurations, etc.
Domain
Name – User and Summary
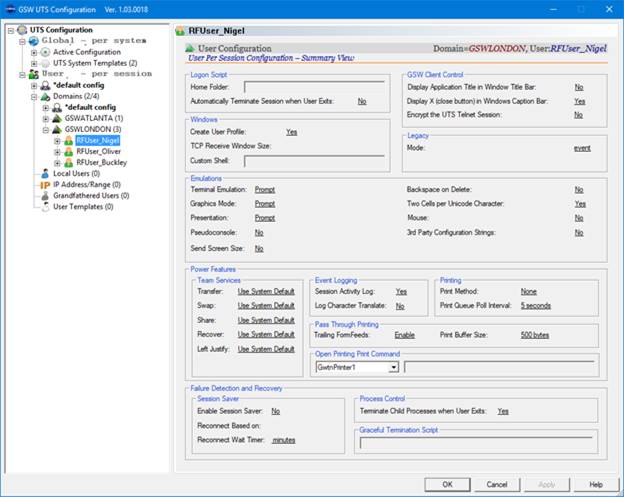
Figure 216: Domain Name User
The configuration
summary description for a Domain Name User, Local User, Grandfathered User and
User Template are the same. Differences are noted in the overview section of
each object.
Please see the Local
User Configuration for details on the property pages for Users on page 405.
Local
Users
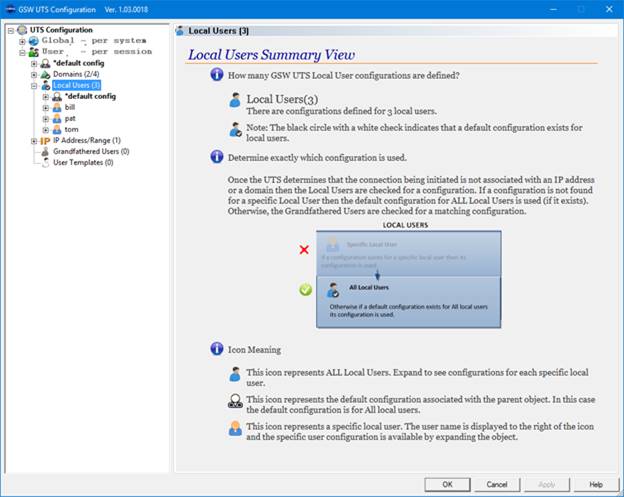
Figure 217: GUI Tool - Local Users
When expanded the Local
Users Summary View provides the administrator with the number of Local Users
that have a configuration defined, the Local User names and if a default
configuration exists for the Local Users object.
Expand each Local User
to access their configuration property pages.
Local User - Summary
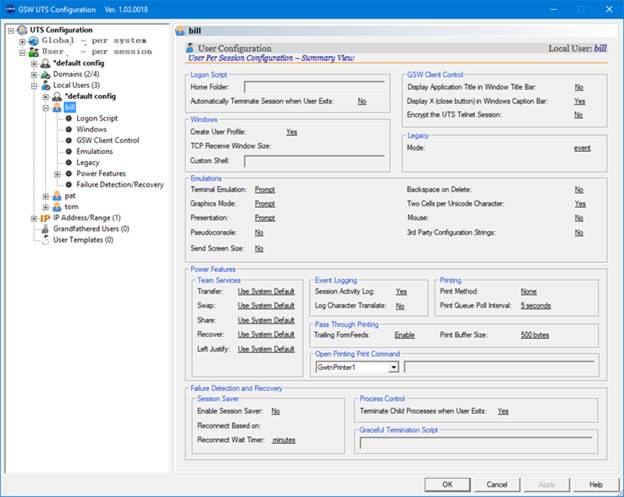
Figure 218: GUI Tool - Local User Summary
The Local User Summary
provides the administrator with a quick view (on the right side of the display)
of most of the Local Users configuration settings. From the User Summary view it
is easy to determine which property page to use to edit the configuration
setting. Each configuration setting resides within a frame with a label. For
example: Logon Script is a label on the frame around the “Home Folder”
configuration setting. On the left side of the display is the property page
icon with Logon Script as the name. The Home Folder property is available in
the Logon Script property page. Simply click on the Logon Script property page
to display its properties for editing. There are a few exceptions to this direct
association due to screen space but will still be easy to find.
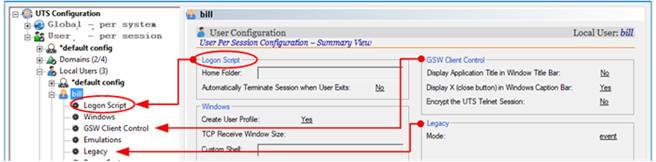
Figure 219: User Configuration Summary Labels and Property Page association.
Local
User – Logon Script
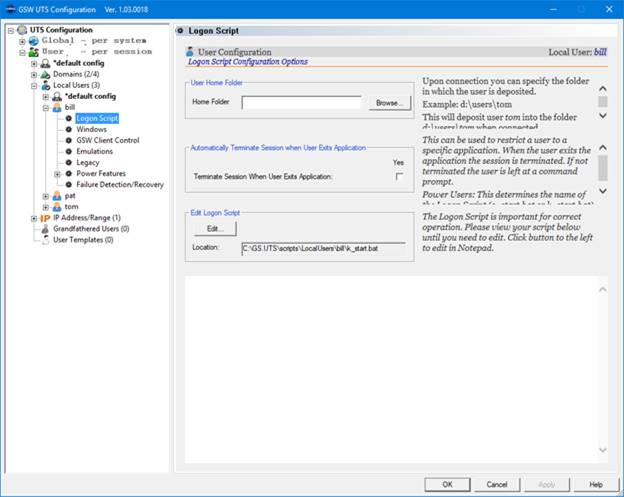
Figure 220: GUI Tool - Local User Logon Script
The Logon Script provides
configuration for:
·
Home Folder (See page 299 )
·
Automatically Terminate Session when User Exits Application (See
page 218 and page 100)
and allows editing of the
batch text file
·
Logon Script Batch File (See page 218)
Local
User - Windows
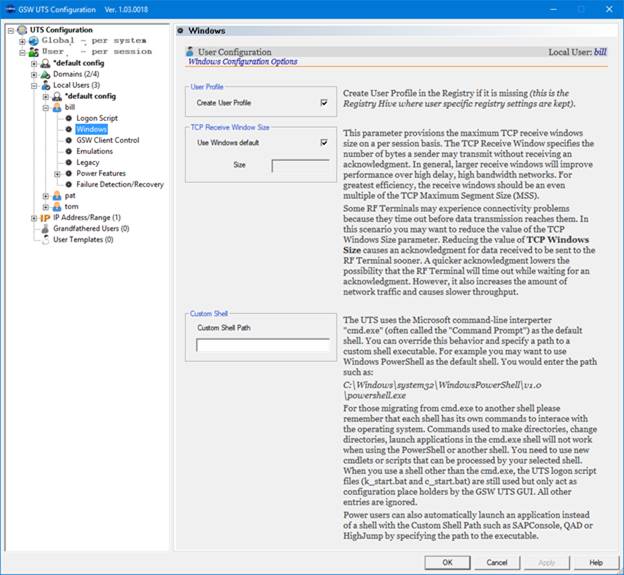
Figure 221: GUI Tool - Local User Windows
The Windows Configuration
options provides configuration for:
·
Create User Profile (See page 247)
·
TCP Receive Window Size (See page 246)
·
Custom Shell Path (See page 249)
Local
User – GSW Client Control
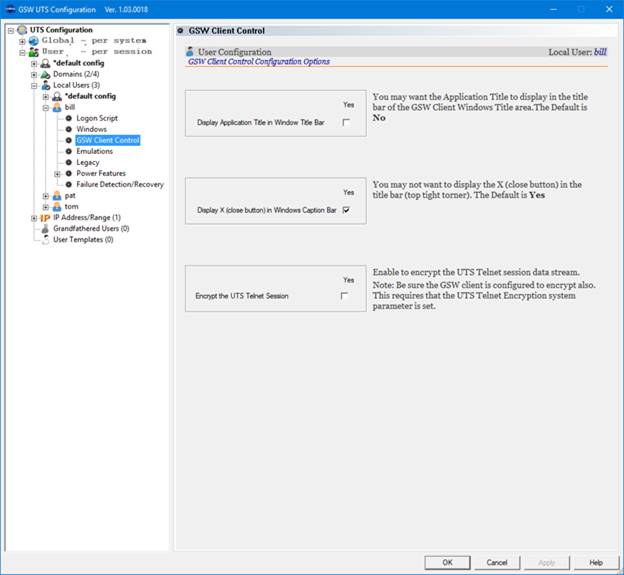
Figure 222: GUI Tool - Local User GSW Client Control
The GSW Client Control
provides configuration for:
·
Display Application Title in Window Title Bar (See page 85)
·
Display X (close button) in Windows Caption Bar (See page 86)
·
Encrypt the UTS Telnet Session (See page 93
)
Local
User – Emulations
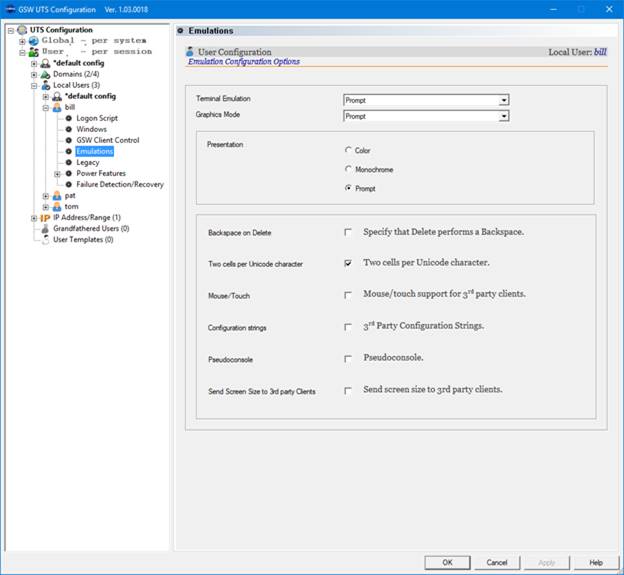
Figure 223: GUI Tool - Local Users - Emulations
The Emulation page
provides configuration for:
·
Terminal Emulation (See page 166)
·
Graphics Mode (See page 168 )
·
Presentation (Color, Monochrome or Prompt) (See page 170
)
·
Backspace on Delete (See page 185)
·
Two cells per Unicode character (See page 186)
Local User
– Legacy
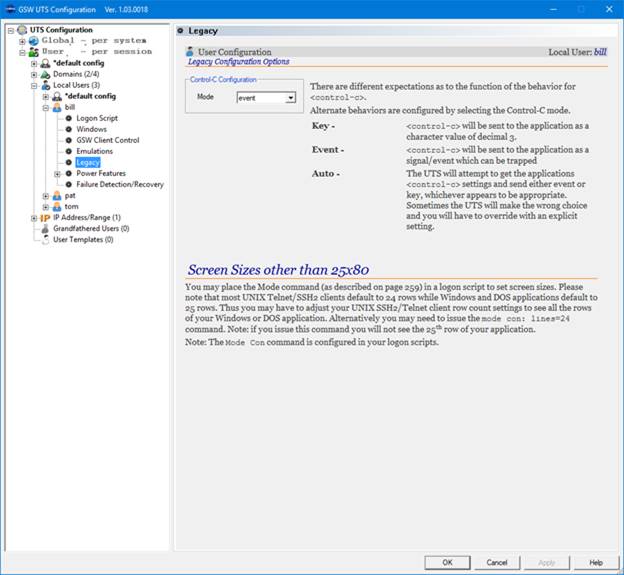
Figure 224: GUI Tool - Local Users - Emulations
The Legacy page
provides configuration for:
·
Control-C (See page 164)
Local User – Power Features – Summary
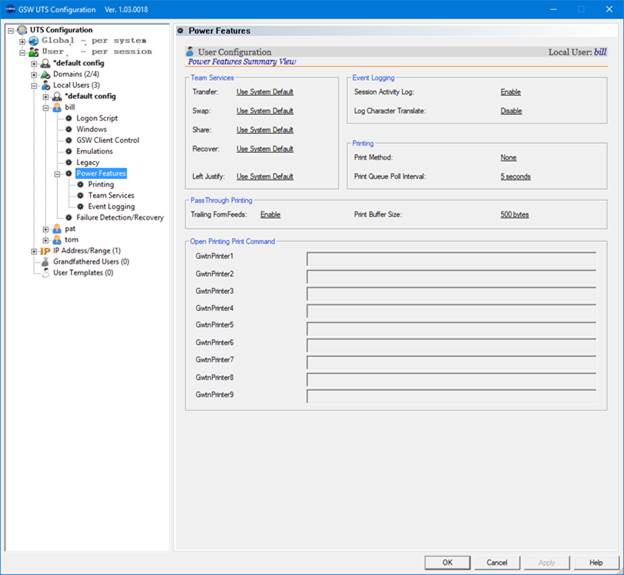
Figure 225:
GUI Tool - Local Users – Power Features Summary
The Power Features
Summary View provides a quick view of the
·
Team Services configuration (See page 117)
·
Log Files configuration
·
Session Activity Log (See page 215)
·
Log Characters Translate (See page 217)
·
Printing Configuration
·
Print Method (See page 226 )
·
Print Queue Poll Interval (see page 331)
·
Pass Through Printing – Trailing Form Feeds and Print Buffer Size
(See page 241)
·
Open Printing Print Command (See page 236 )
Local User – Power Features - Printing

Figure 226: GUI Tool - Local Users – Power Features - Printing
The Power Features
Printing provides configuration of:
·
Print Method (See page 226 )
·
Print Queue Poll Interval (See page 331)
·
Pass Through Printing – Trailing Form Feeds and Print Buffer Size
(See page 241)
·
Open Printing Print Command (See page 236 )
Local User – Power Features – Team
Services
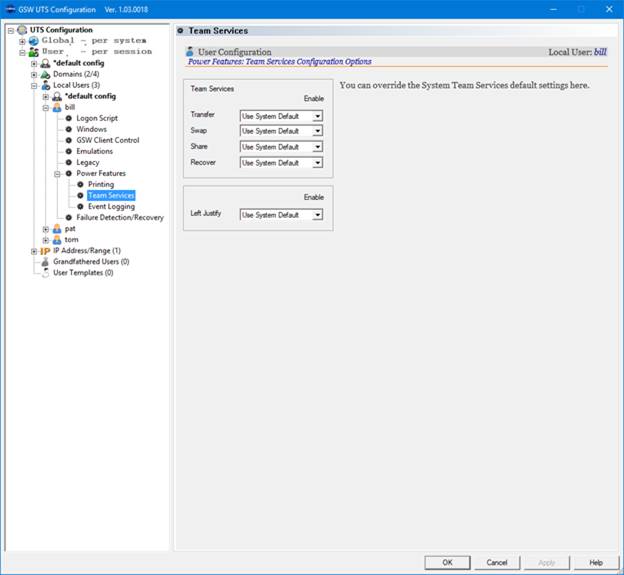
Figure 227: GUI Tool - Local Users – Power Features – Team Services
The Power Features –
Team Services provides configuration of:
·
Team Services Override Overview (See page 137
)
·
Override Transfer (See page 139)
·
Override Swap (See page 140)
·
Override Share (See page 141 )
·
Override Recover (See page 138 )
·
Override Left Justify (See page 142)
Local User – Power Features – Event Logging

Figure 228:
GUI Tool - Local Users – Power Features – Event Logging
The Power Features –
Event Logging provides configuration of:
·
Session Log Enable (See page 215)
·
Log Character Translate (See page 217 )
Local User – Failure Detection/Recovery
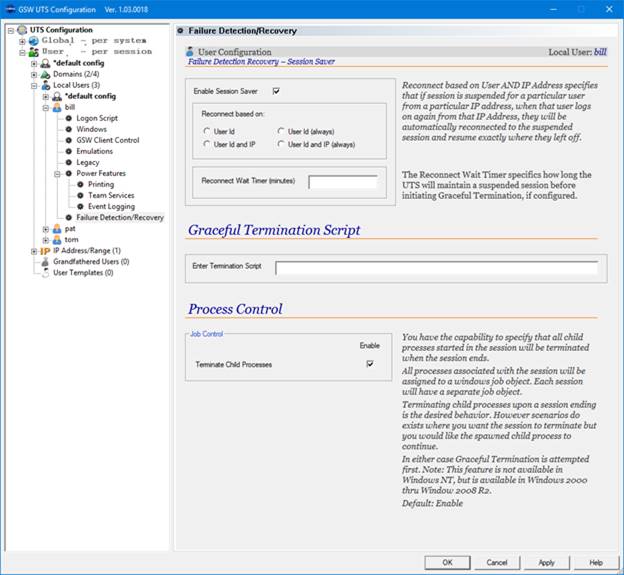
Figure 229: GUI Tool - Local Users – Failure Detection/Recovery
The Failure Detection
and Recovery configuration of:
·
Enable Session Saver (See page 149 )
·
Reconnect Based on…. (See page 151)
·
Graceful Termination Script (See page 158)
·
Process Control (See page 162)
IP
Address Range
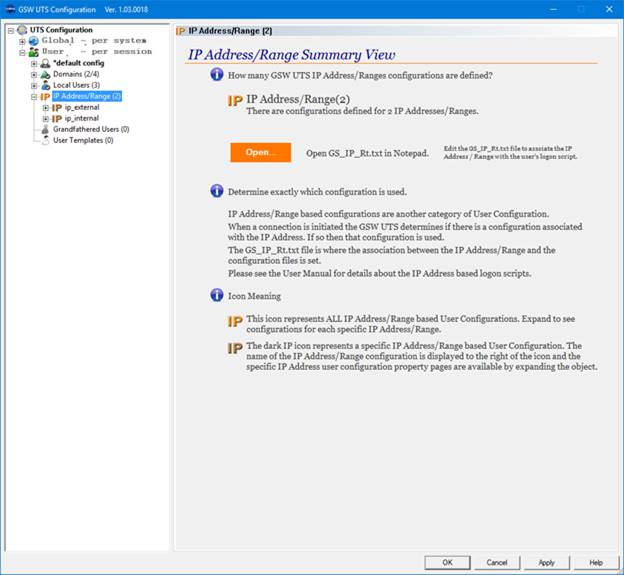
Figure 230: GUI Tool - IP Address / Range
The IP Address/Range
Summary View and Specific IP Address/Range provides configuration of:
·
IP Address Range Logon Scripts (See page 220)
·
User Configuration for IP Address
The
association between the logon script and the IP address is specified in the
GS_IP_Rt.txt file.
Note:
IP Address/Ranges user configurations contain the same property pages as all
session users. Each page is described in the Local Users section (For details
on each property page please see page 405)
Grandfathered
Users
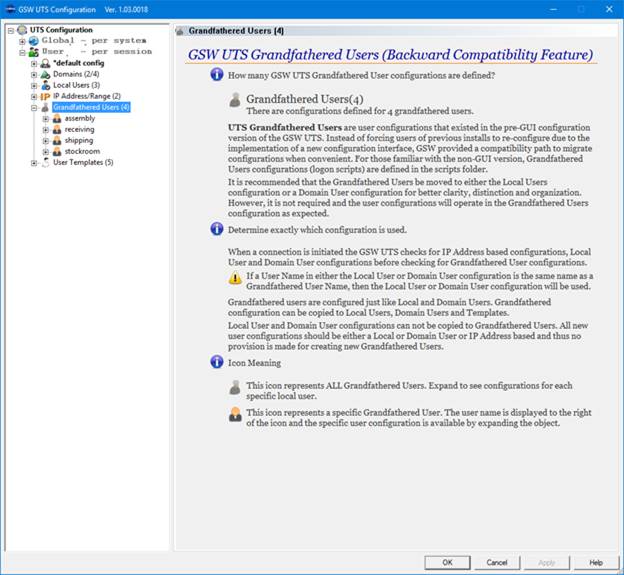
Figure 231: GUI Tool - Grandfathered Users
The Grandfathered Summary
View and Specific Grandfathered User configuration provides:
·
User Configuration for the Grandfathered User
Note:
Grandfathered Users contain the same property pages as all session users. Each
page is described in the Local Users section (For details on each property page
please see page 405)
User Templates
Figure 232: GUI Tool - User Templates
The User Templates View
and Specific User Templates configuration provides:
·
User Configuration for the User Templates
·
Note: User Templates contain the same property pages as all session
users. Each page is described in the Local Users section (For details on each property
page please see page 405)
.
The registration software
obtains a system signature that is unique to your system. This signature is an
added security measure to inhibit unauthorized personal to obtain working
copies of the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server for Windows.
The signature is
comprised of hardware and software identifiers that exist on your system that
make the target system unique. These identifies are hashed into a Product ID
and a Serial Number can be generated from this Product id.
If major hardware components
of your system are removed, replaced or modified your Serial Number may
discontinue to work and you may need a new Serial Number to obtain access
to the Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet Server for Windows.
If this occurs, please re-register the product (See page 16).
Please contact Georgia SoftWorks Technical Support if needed.
GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server Operating System Platforms
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH2/Telnet
Server operates on:
Windows Versions: Windows 7/8/10/VISTA/Server 2008/Server
2008 R2/Server 2012, Server 2016, Server 2019, NT/XP/2000/Server 2003
The Georgia SoftWorks Telnet Server operates with 3rd
Party RFC 854 Telnet clients and GSW Telnet Clients.
The Georgia SoftWorks SSH Server operates with 3rd
Party SSH compliant clients and GSW SSH Clients.
The Georgia SoftWorks Desktop SSH2/Telnet
Client operates on Windows 95/98/ME,
Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7/8/10, 2008,
2008 R2, 2012, 2016, 2019 and Windows operating System Versions.
Desktop Client Device
Including but not limited to
·
MobileDemand xTablet T7000 (Windows 7)
Georgia
SoftWorks Telnet Clients for Windows CE are available for
- Pocket
PC 2003 class devices
- Windows
CE .NET 4.2/5/6
- Windows
Mobile 5+
Georgia
SoftWorks SSH Clients for Windows CE are available for
- Many
Windows CE Version 4.2/5/6 class devices
Including
but not limited to:
·
Datalogic Elf, Falcon X3
·
Honeywell LXE MX3X, LXE Thor,
Dolphin 6500
·
Intermec CK30
·
Janam XG100
·
Psion-Teklogix 7535, Psion-Teklogix
8525, Omni XT10
·
Motorola MC9190, Symbol MC 9060G,
·
PSC Falcon 4410
- Many
Windows Mobile versions class devices
Including
but not limited to:
·
Bluebird Pideon BIP-6000
·
Intermec CK71
·
Honeywell Dolphin 9950
- Pocket
PC 2003 class devices
Georgia SoftWorks also offers the GSW ConnectBot for
Android. In addition to being full featured industrial grade Telnet/SSH client,
it has the strongest SSH security of any SSH client commercially available.
Also available is a license server that makes licensing and upgrades smooth and
easy. Learn more about the GSW ConnectBot.
Please see the GSW SSH User’s Guide for FIPS 140-2 client requirements
Georgia SoftWorks Java Client and the Georgia SoftWorks
Java applet – Telnet Only
Please read the section on the GSW Telnet Java Client
(page 294 ) and the section on the GSW Telnet Java Client applet (page 286
) to see the requirements for correct operation.
GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server System Requirements
GSW recommends 16 MB of
RAM per session in order to utilize all the features offered in the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server. If you are using SAPConsole the recommendation is an additional 16 MB
of RAM per session for a total 32+ MB RAM per session. It is recommended to use
the Windows Task Manager to determine the SAPConsole memory requirements for
your system.
Processor requirements
vary based on the primary or main application running on the host system. In general,
the processor requirements for running the number of instances of the primary
application will be sufficient for most customers. However, the type of application
will ultimately determine the SSH2/Telnet
processor requirements. The usage patterns including the number of users who
actively input text and the frequency of screen updates should be taken into
consideration. If minimal and exact sizing is required the best course of
action is to download the Free trial copy of the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server and empirically determine the requirements using the actual application.
At least 60 MB of Disk
space are recommended for the program, User’s Guide and log files.
In order to keep basic Technical
Support Free please help us to keep our cost down.
1.
Gather all relevant system information.
2.
Write your question down. This not only helps us but also helps you in
articulating the question.
Please open a support
ticket at GSW Support
and include all relevant information described below in the Technical Support
Tips below.
Or Call 706.265.1018
EST, M-F 9:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. and have your Product ID ready. Tech Support tickets
and phones are monitored after hours at various times.
If it is an emergency please
call after submitting a ticket. If no one immediately answers please leave a message
and you will be contacted.
Technical Support
Tips:
To expedite support for
suspected problems please perform the following test steps below to help us diagnose
the issue.
1.
Disconnect all users. Make sure that no other user connects at the time
of the test.
2.
Wait 5 minutes
3.
Delete all log files from the GSW SSH2/Telnet
Server installation ‘Log’ subdirectory on the computer running the GSW SSH2/Telnet Server. (Usually c:\GS_UTS\Log)
4.
To expedite resolution, reboot the server if possible.
5.
Duplicate the problem.
6.
Open a ticket at GSW Support
and include:
a.
A description of the problem, including User ID’s, Domain and IP
Addresses.
b.
Attach all files in the Georgia SoftWorks log folder. It is usually located at c:\gs_uts\log but
may be different depending on the installation folder selected.
c.
The logon script associated with the user experiencing the problem.
(That is the c_start.bat or the k_start.bat file that resides in the
scripts folder in the GSW SSH2/Telnet Installation directory.
d.
And of course, your contact information.
Open or check status of a support ticket:
at GSW
Support
Call 706.265.1018 EST, M-F 9:00
a.m. to 5:00 p.m. and have your Product ID ready